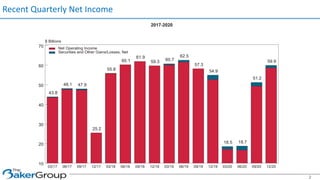
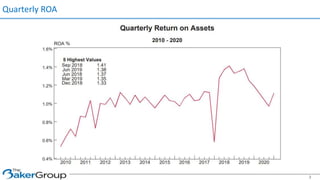
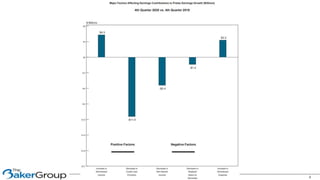
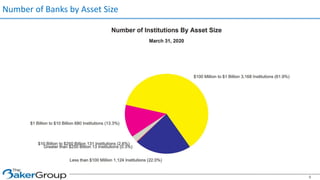
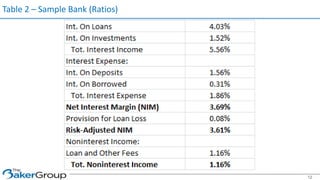
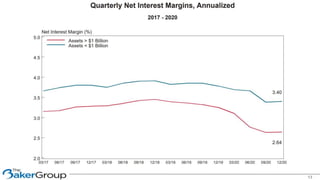
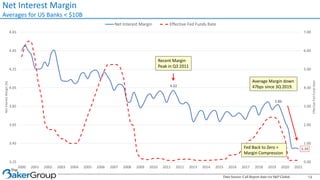
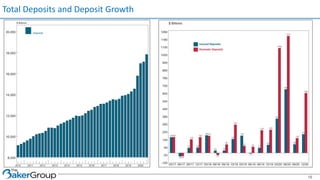
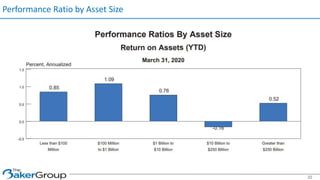
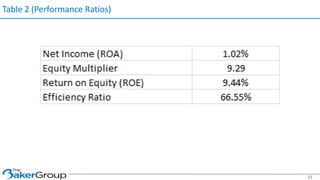
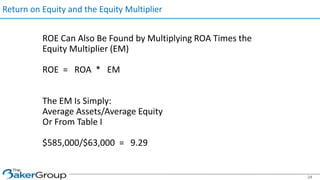
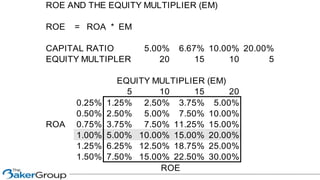
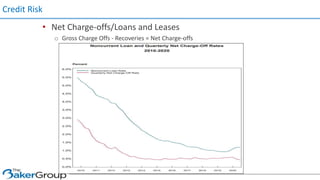
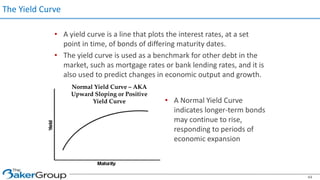
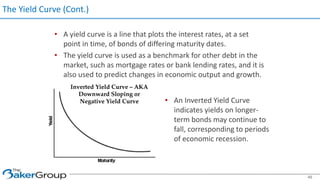
This document provides an overview of asset/liability management for banks. It discusses key concepts like net interest margin, yield curves, types of interest rate risk including repricing risk and option risk. It describes how the asset/liability committee (ALCO) oversees pricing, profitability, cash flows, interest rate risk management and other risks. An effective ALM program identifies goals, assesses risks, uses tools to evaluate strategies before implementation, and works to maximize bank performance while managing different types of risks.