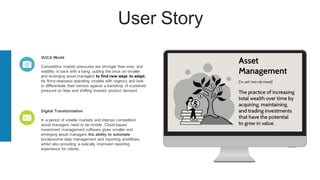
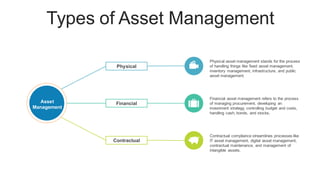
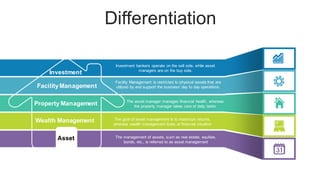
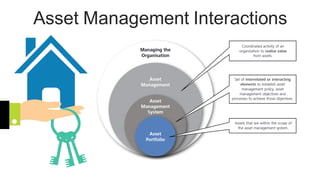
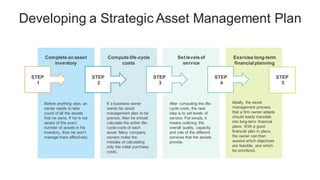
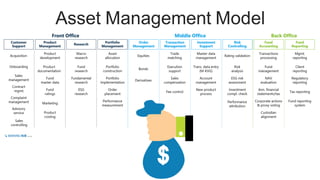
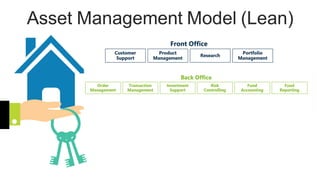
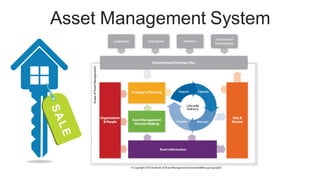
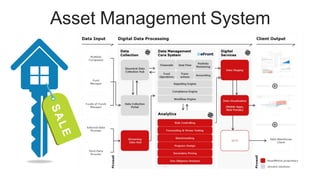
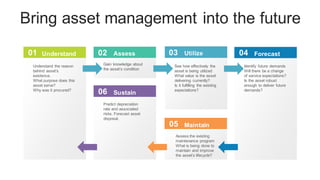
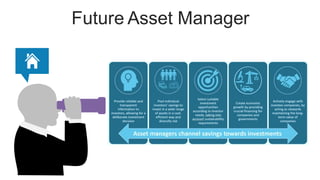
The document discusses the current trends and challenges in asset management, highlighting the need for smaller firms to adapt quickly to competitive pressures and technological advancements. It defines key concepts in asset management, such as its types and frameworks, and explains the role of trust companies in providing comprehensive financial services. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of digital transformation and risk management in enhancing operational efficiency and client servicing within the industry.