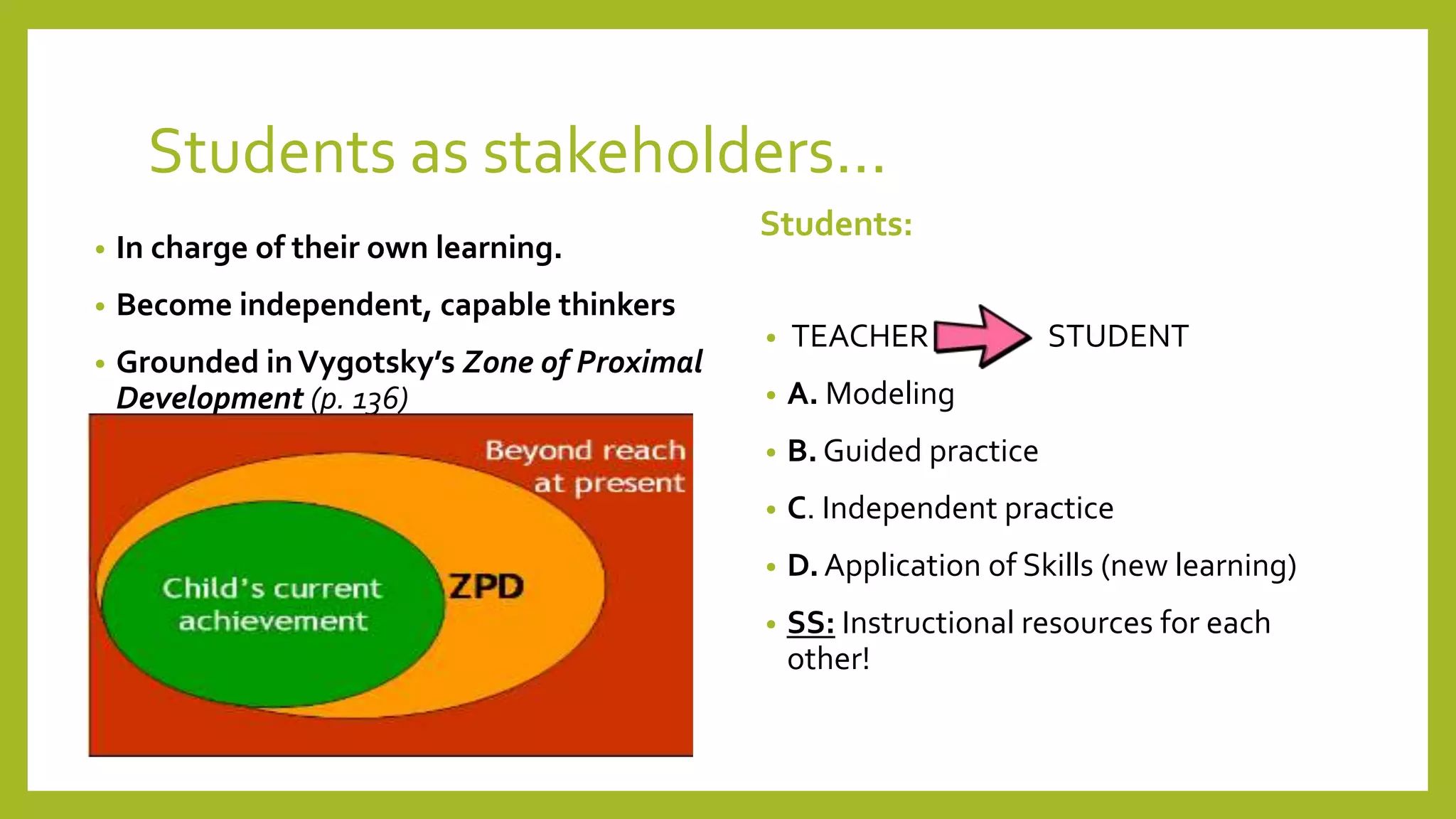
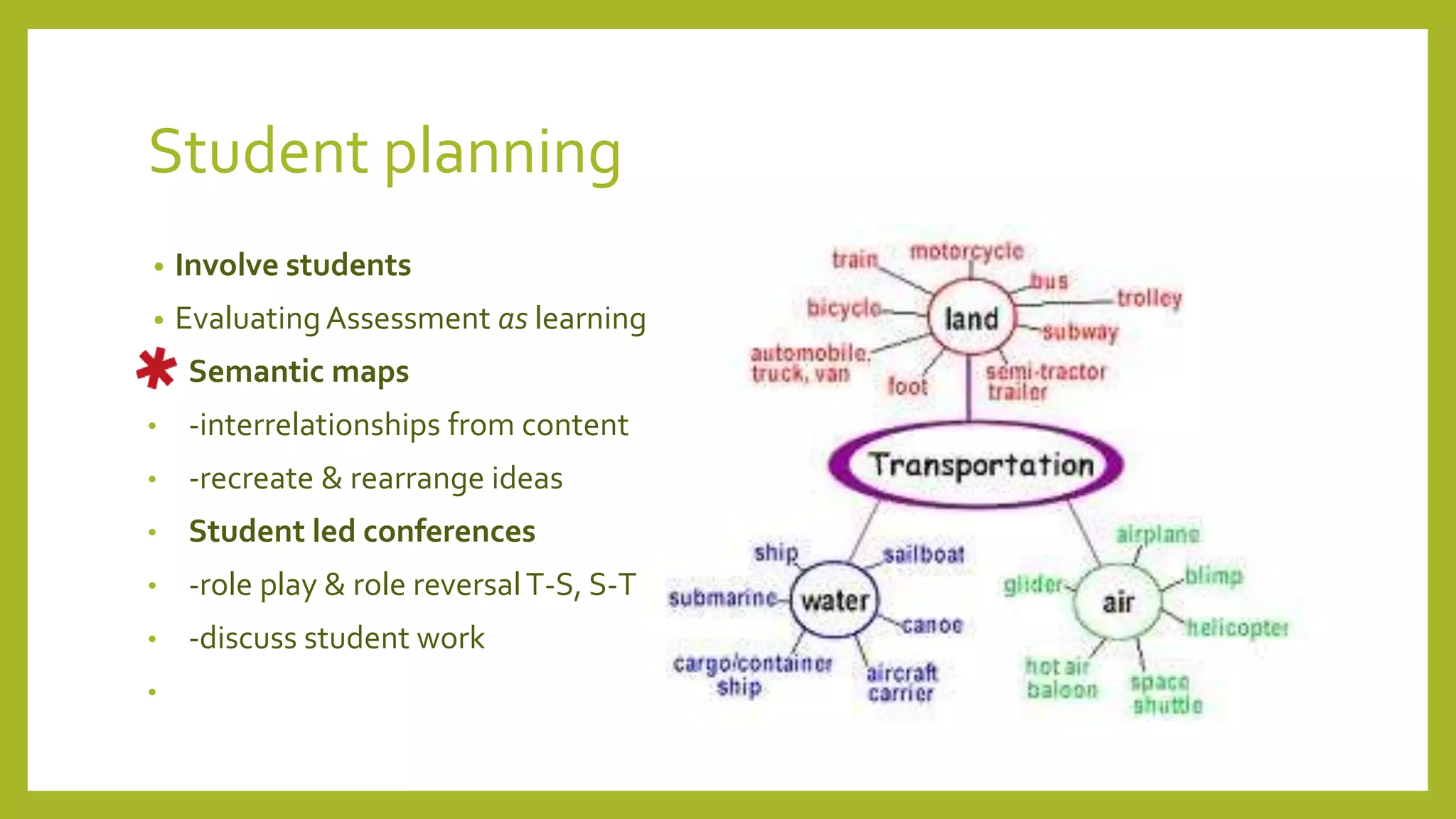
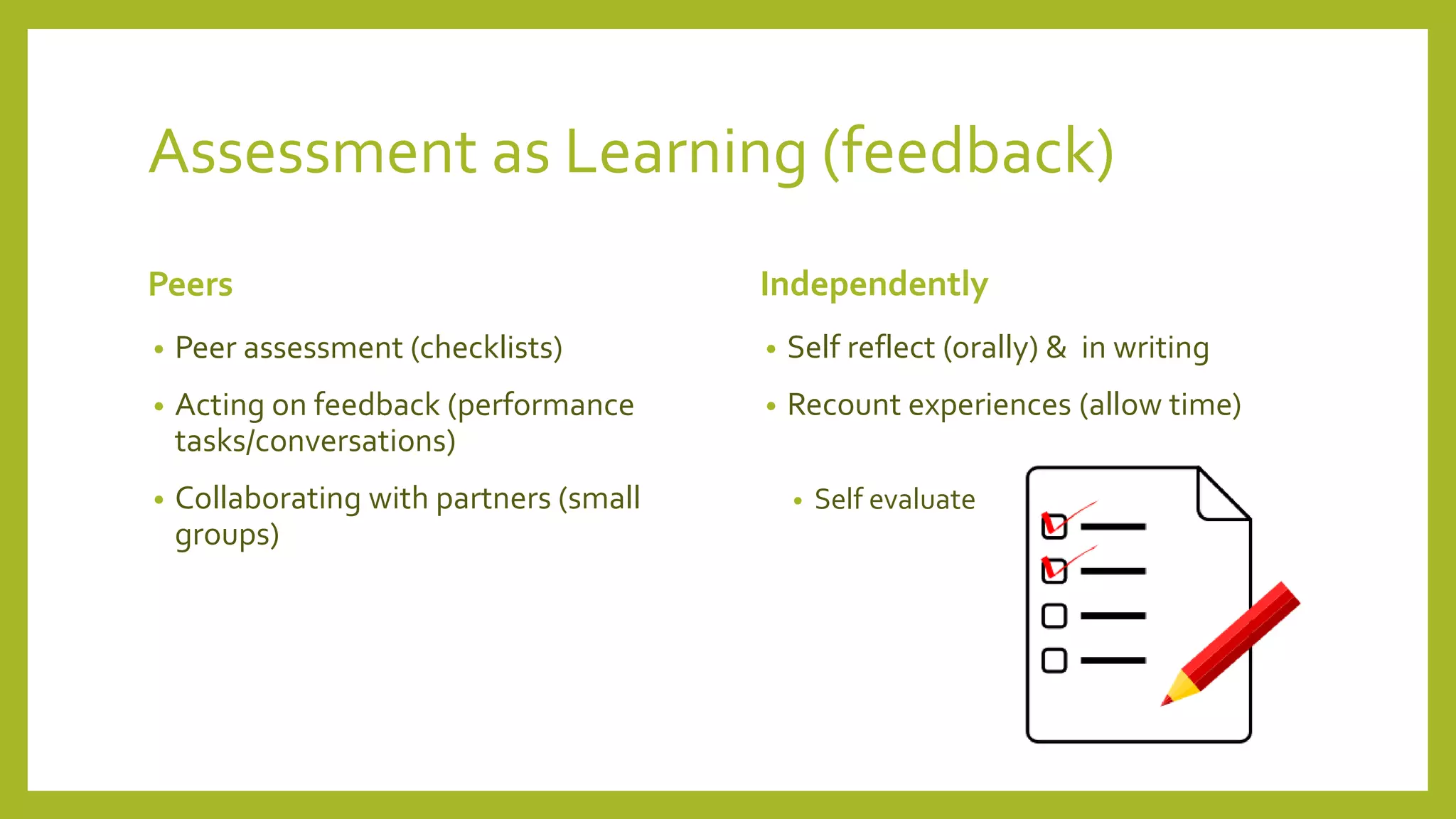
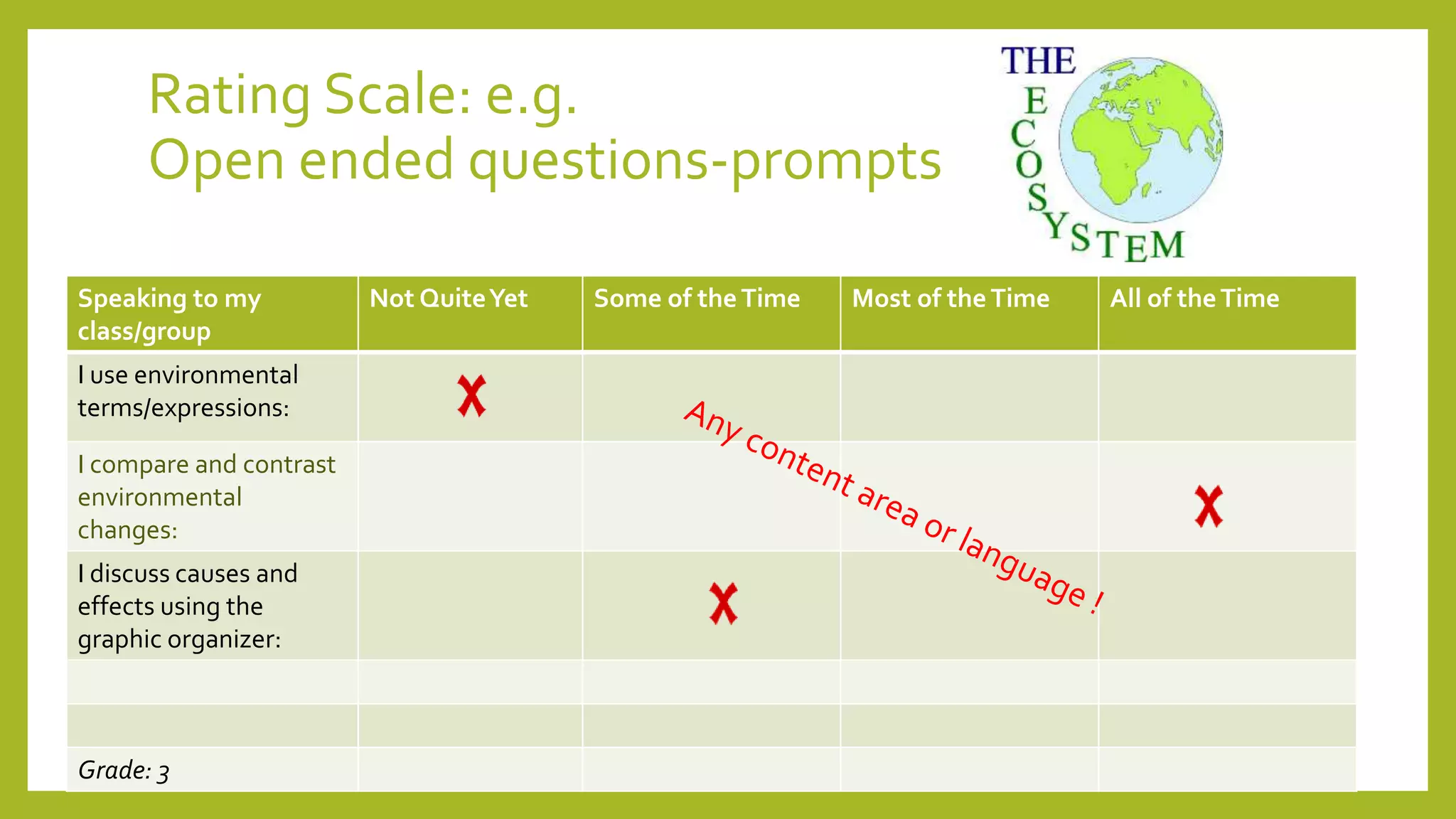
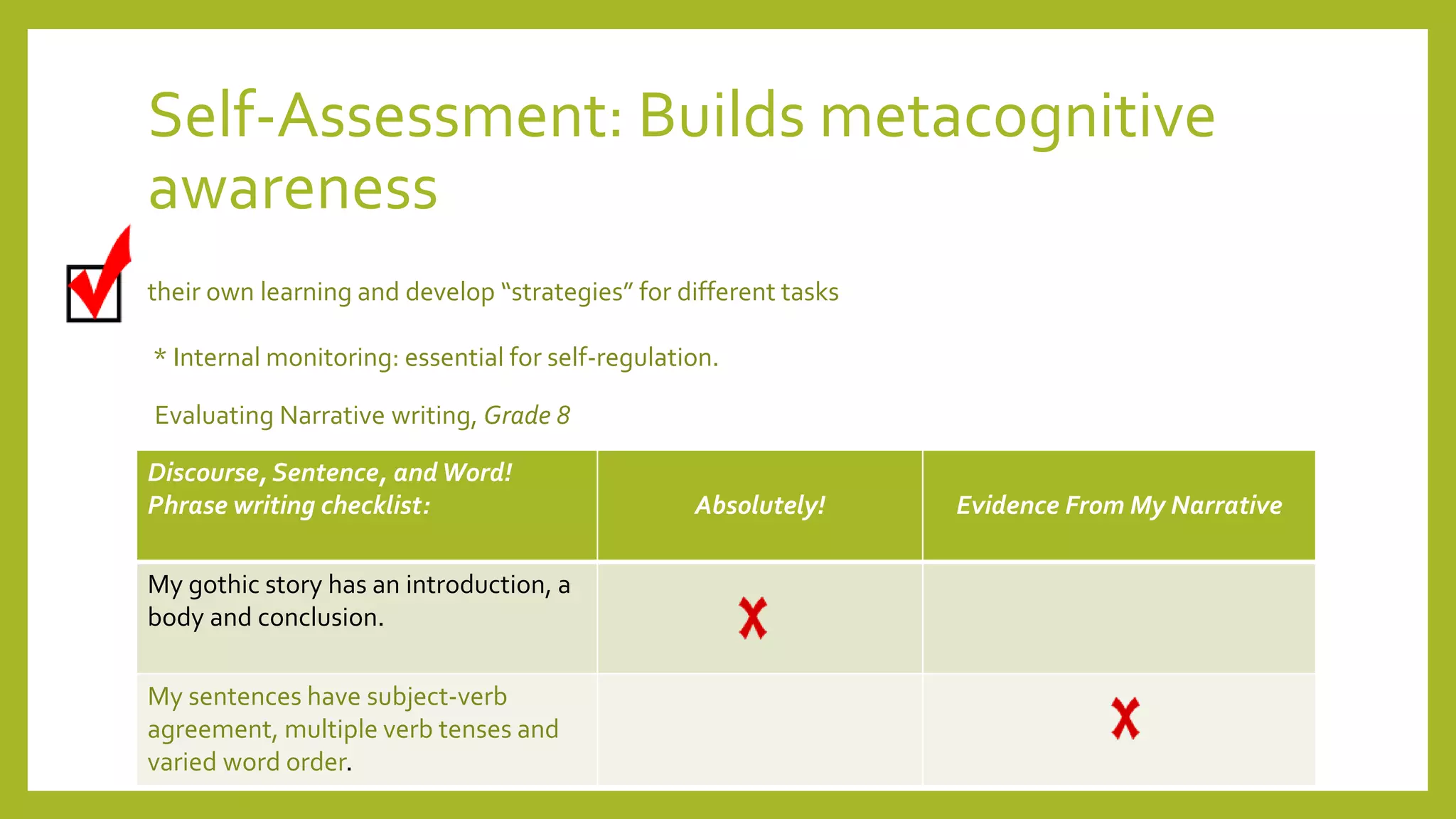
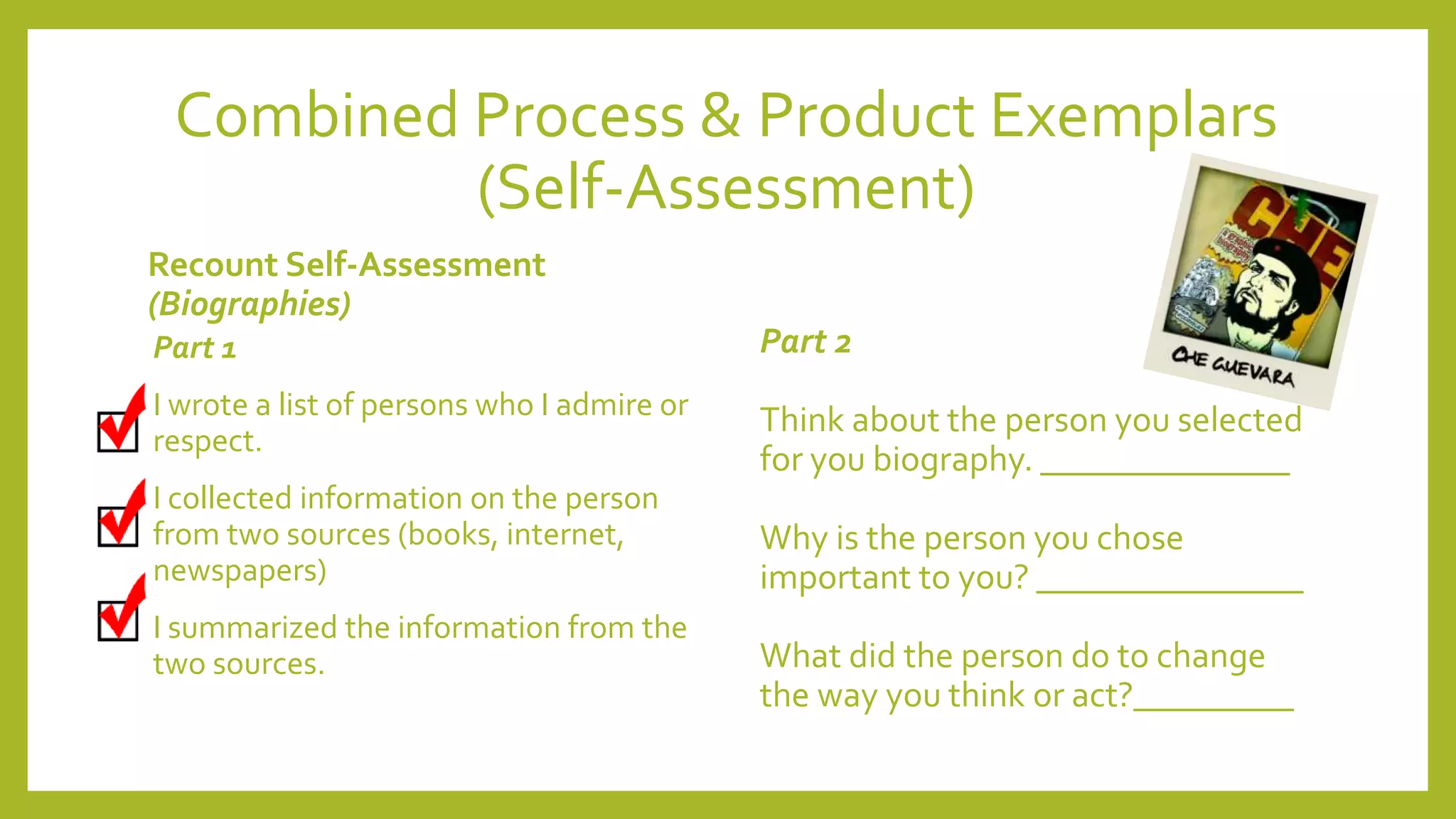
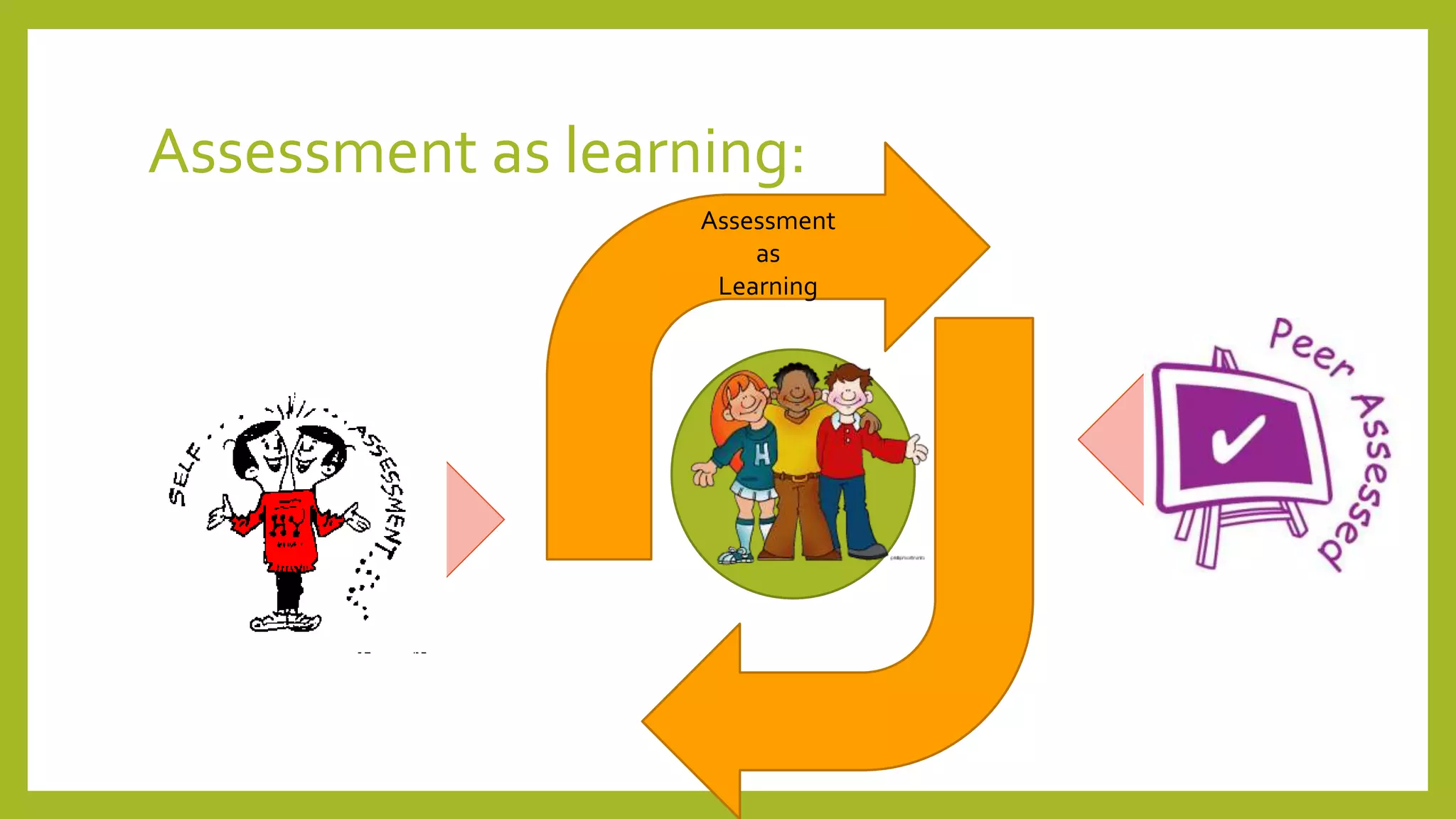
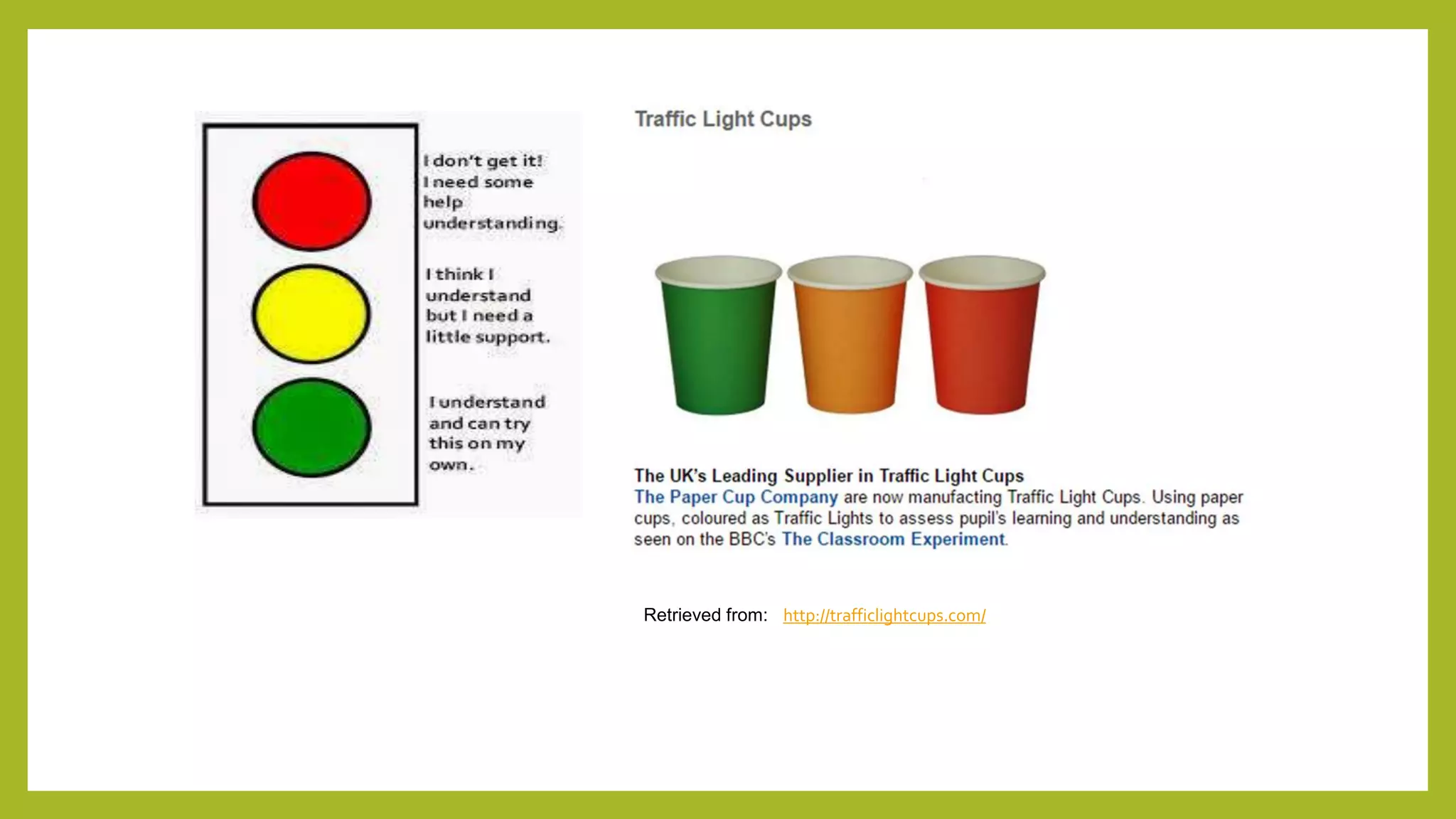
The document discusses the concept of 'assessment as learning' which emphasizes student independence and engagement in their own educational processes. It focuses on strategies for involving students in assessment through self-assessment, peer assessment, and community connections, highlighting the importance of learner autonomy and reflective practices. Additionally, it outlines the role of teachers in facilitating this approach and promoting equity among diverse learners.