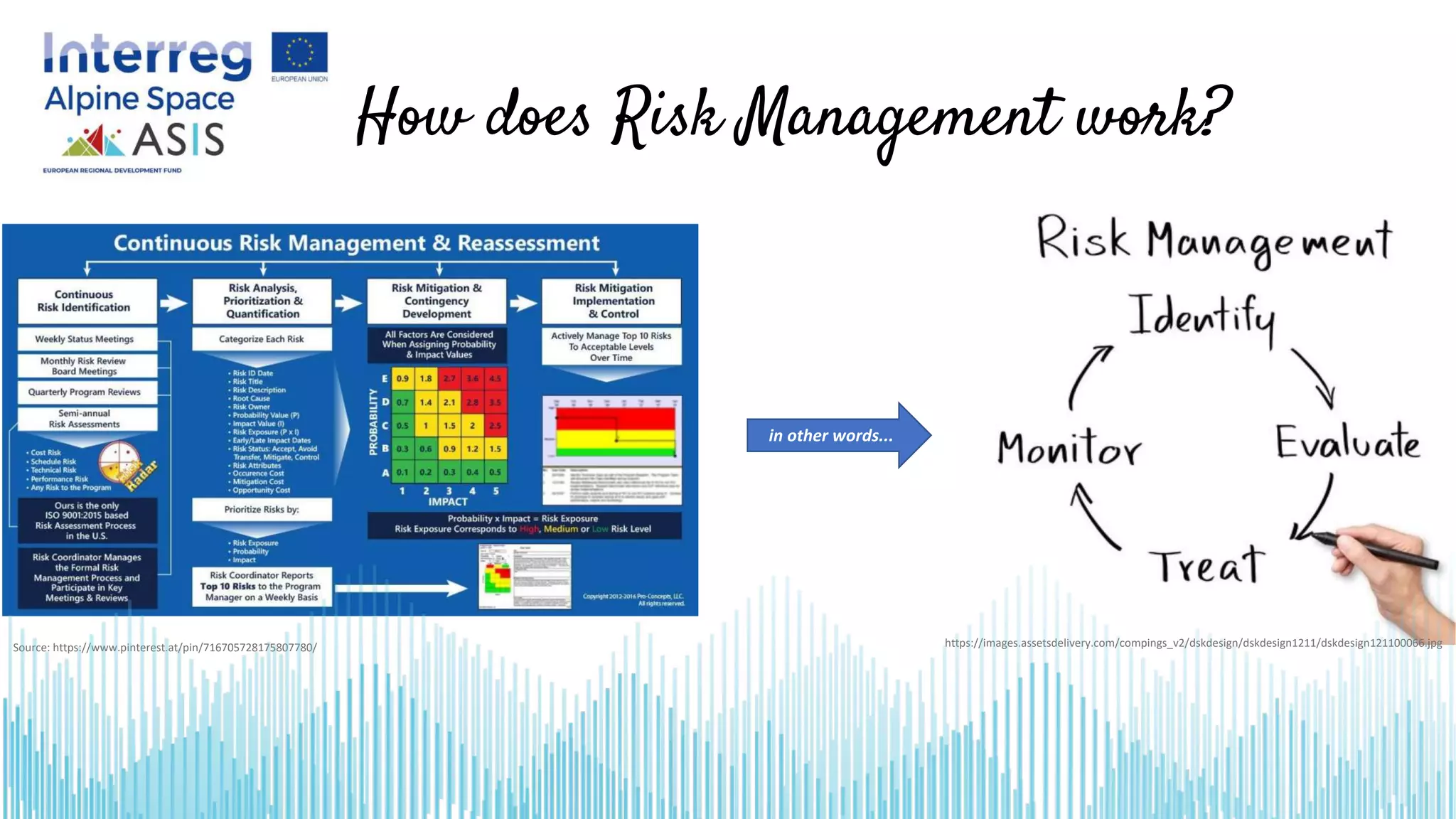
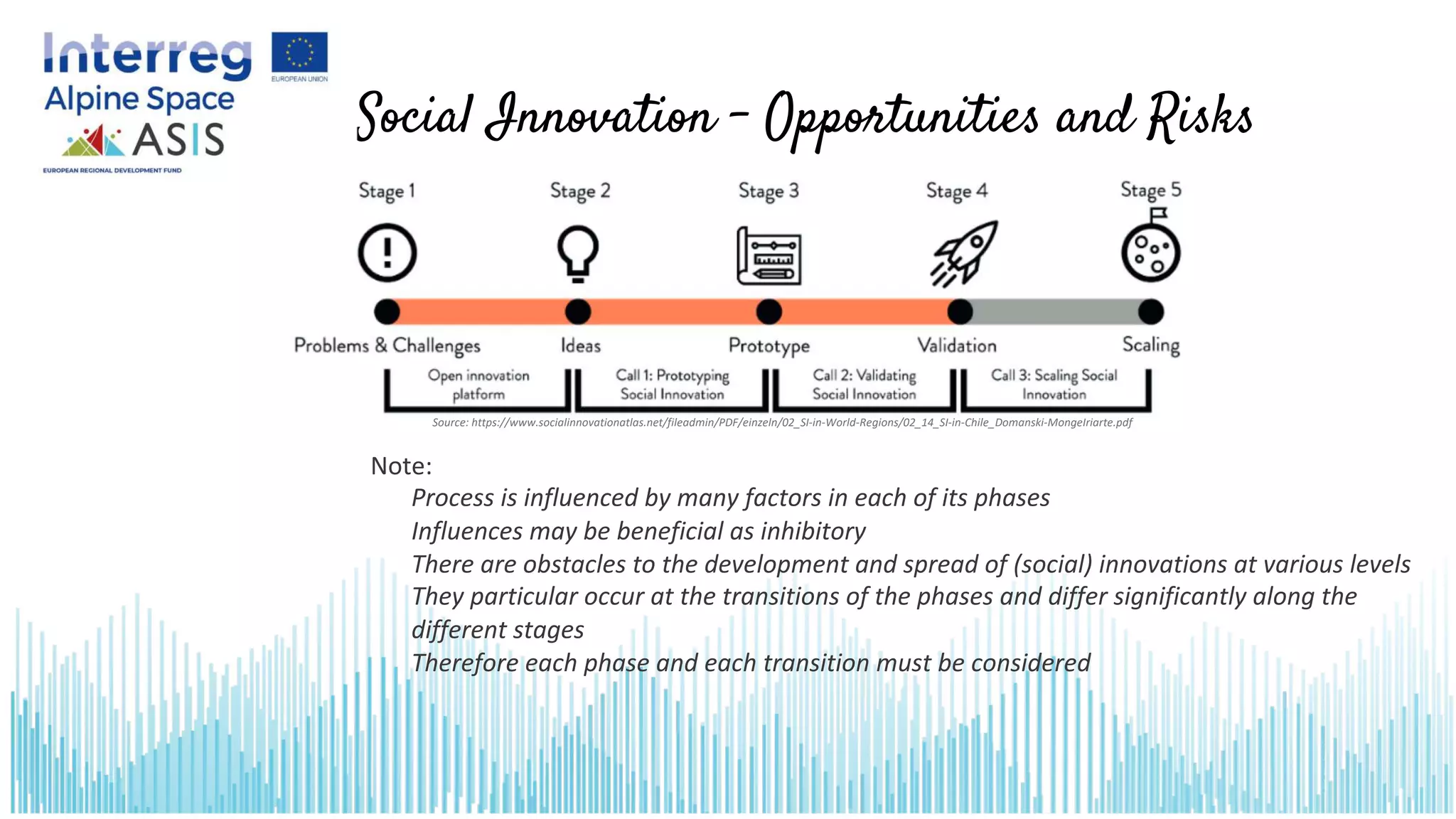
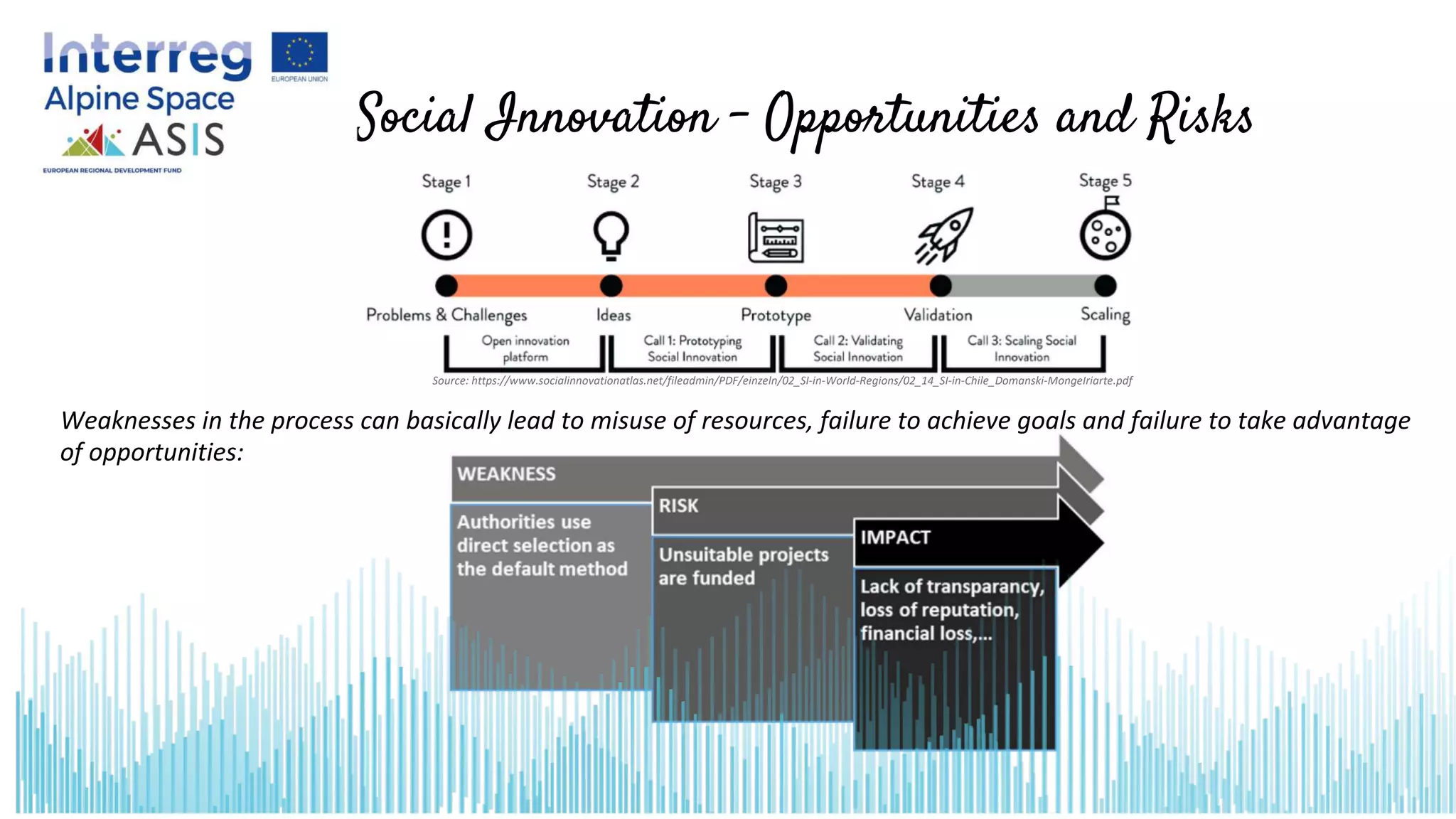
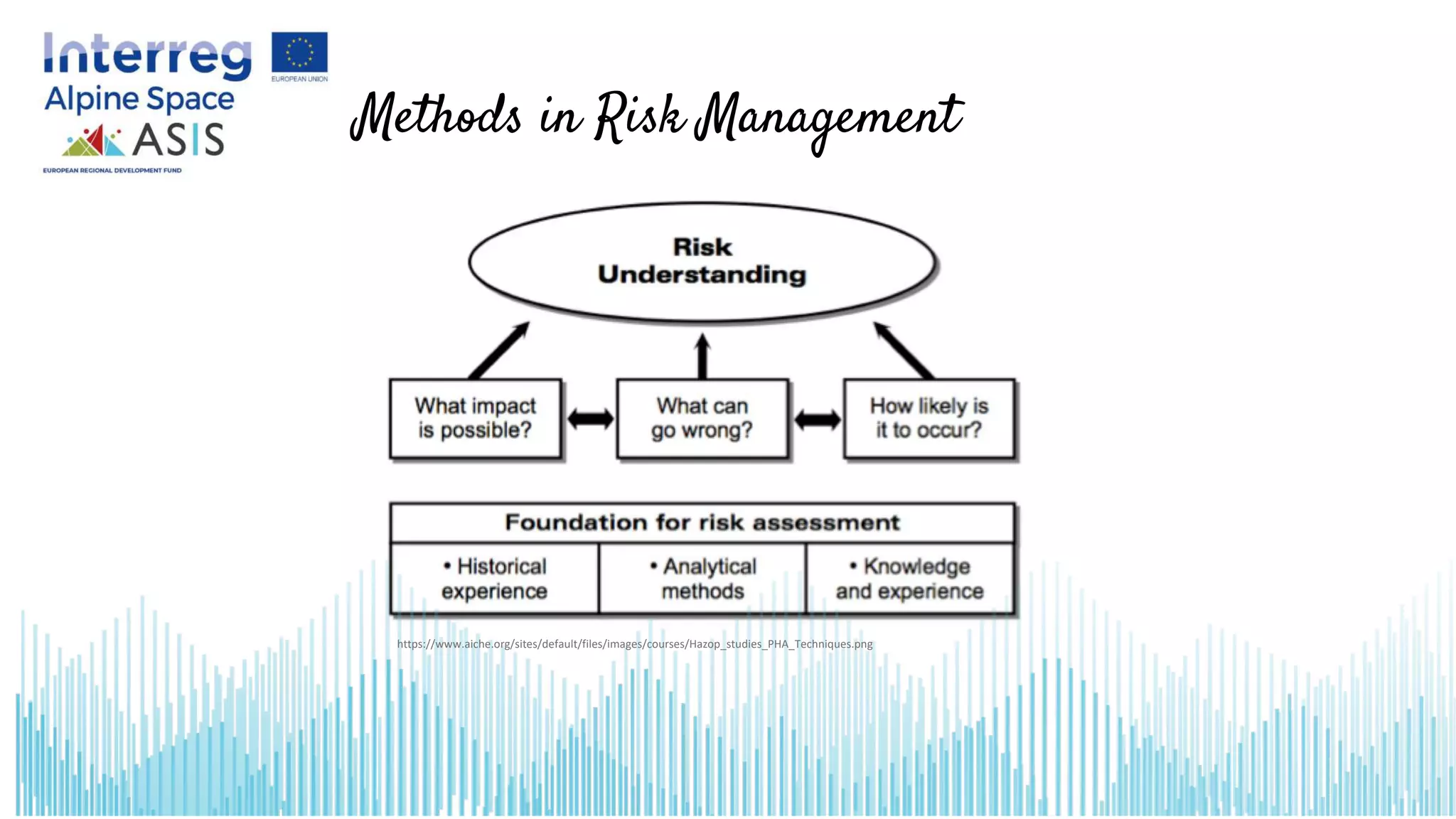
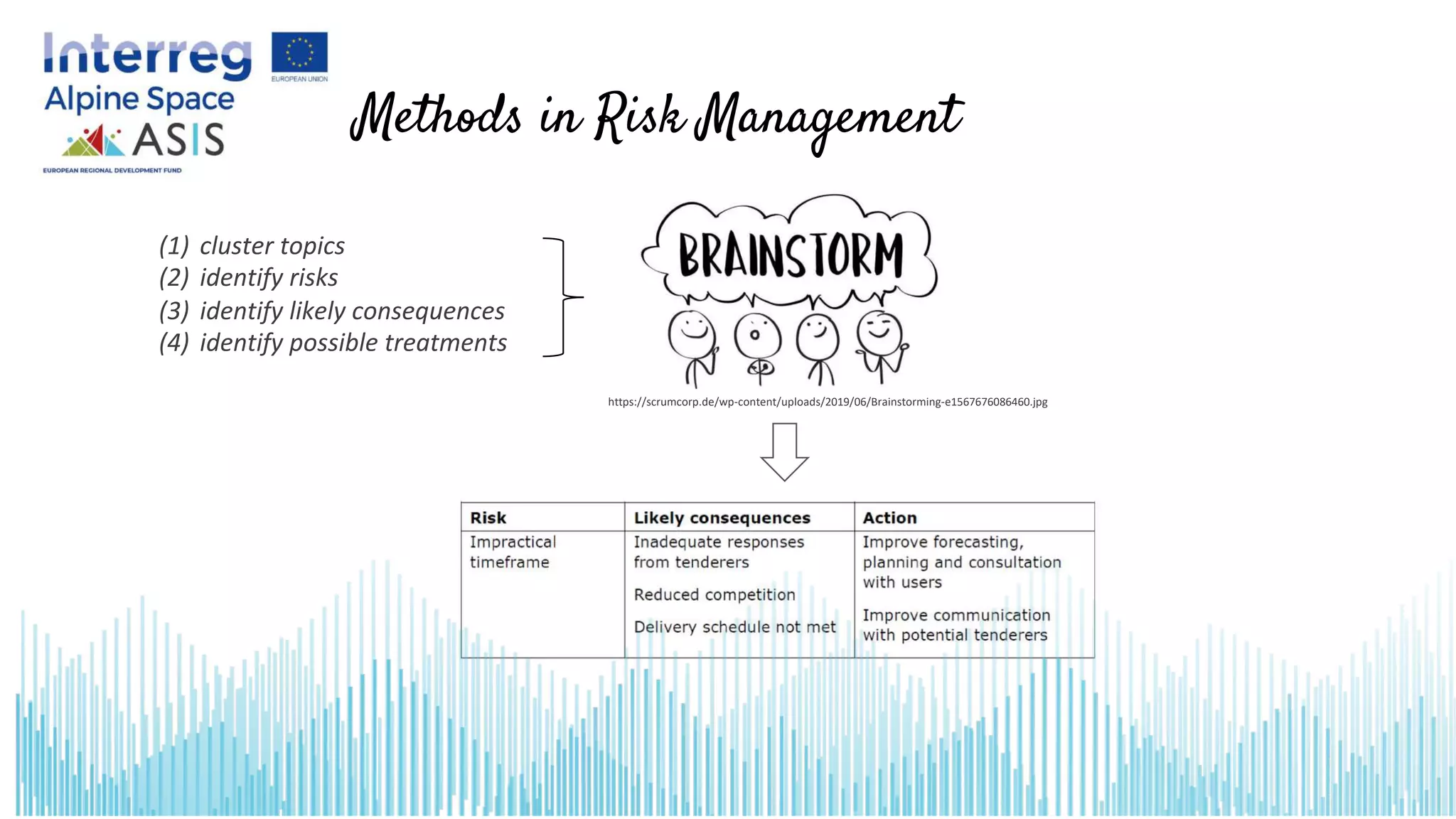
This document introduces opportunities and risks in social innovation and how to deal with them through risk management. It defines risk and risk management, outlines the risk management process, and discusses specific opportunities and risks related to social innovation. Methods in risk management discussed include checklists, which provide a quick overview of identified risks and potential measures. The conclusion notes that many social innovations fail due to resistance, so risk management can help procurement processes realize potential opportunities while managing adverse risks.