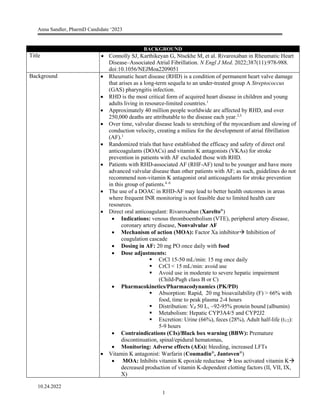
The study evaluated the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared to vitamin K antagonists for stroke prevention in patients with rheumatic heart disease-associated atrial fibrillation (RHD-AF). Over 4565 patients from 24 countries were randomized to receive either rivaroxaban 20 mg daily or a vitamin K antagonist such as warfarin, with a mean follow up of 3.1 years. The primary outcome occurred in 560 patients (8.21% per year) in the rivaroxaban group and 446 patients (6.49% per year) in the vitamin K antagonist group, showing rivaroxaban to be less effective with a hazard ratio of 1.25. There were no significant