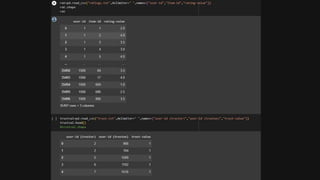
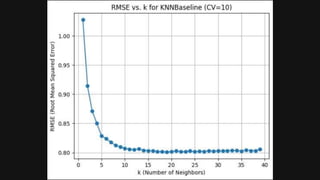
The project aims to enhance recommender systems by addressing the cold start problem and data sparsity using collaborative filtering and k-nearest neighbors (KNN) techniques. It creates a user-item similarity matrix and a prediction matrix to deliver personalized recommendations, demonstrating success particularly with the k-nnbaseline approach. The implementation effectively improves accuracy and relevance in recommendations for new users or items with limited historical data.