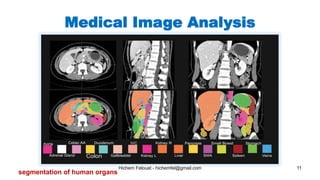
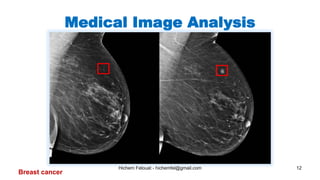
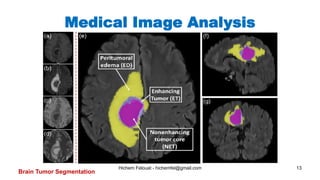
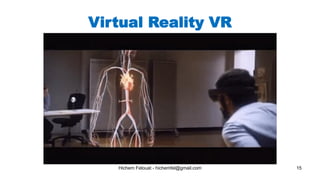
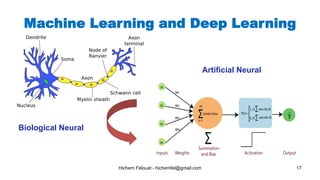
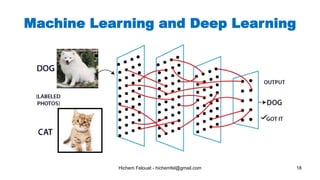
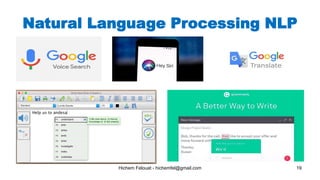
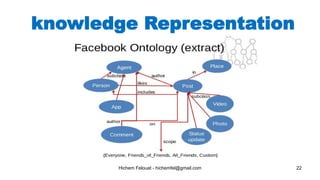
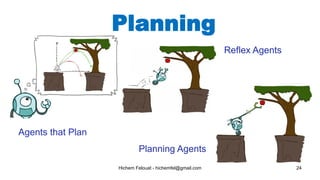
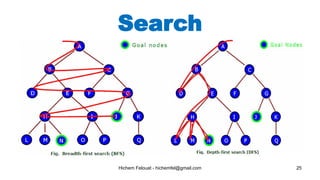
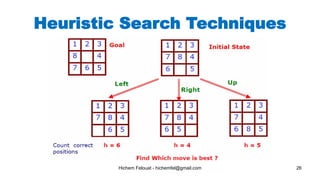
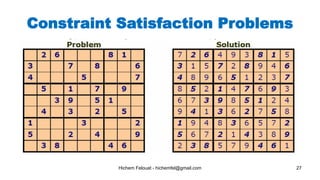
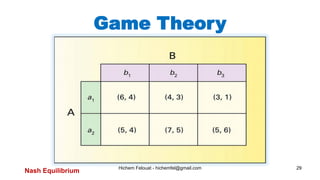
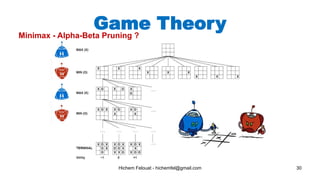
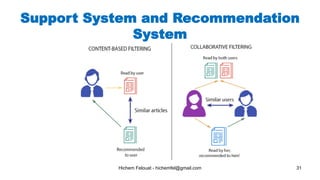
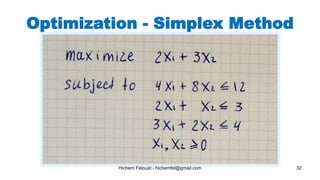
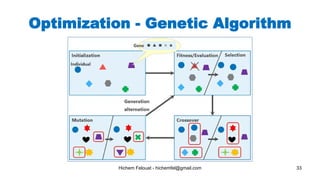
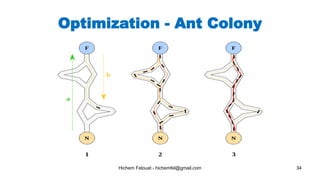
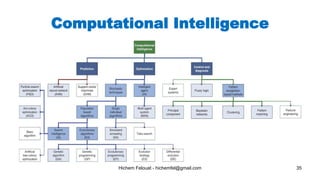
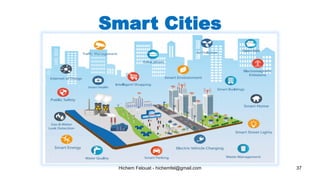
The document discusses various topics in artificial intelligence including its history and definition. It provides overviews of several subdomains of AI like computer vision, machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics. It also examines applications such as medical image analysis, chatbots, game theory, and smart cities. The document aims to introduce readers to the broad field of artificial intelligence and some of its technical components and real-world uses.