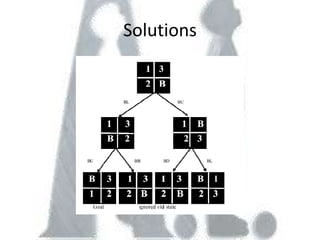
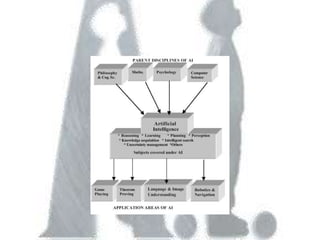
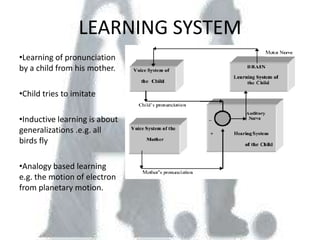
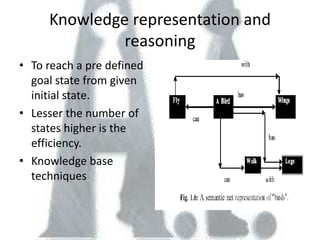
Artificial intelligence has its origins in humans' desire to create intelligent models and statues of themselves, and early work using technologies like Babbage's Analytical Engine and thermoionic valves. The document discusses several approaches to problem solving in AI like state space searches, as well as major topics in the field including learning systems, knowledge representation, planning, knowledge acquisition, and fuzzy logic and artificial neural networks. It provides an overview of the history and concepts within the study of artificial intelligence.