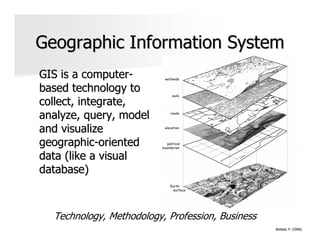
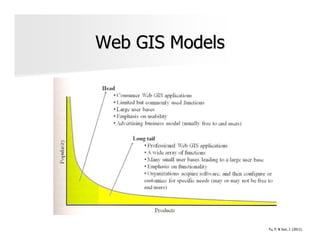
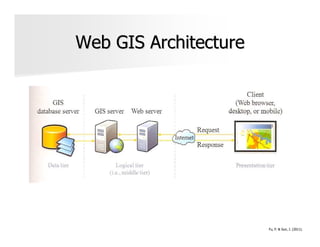
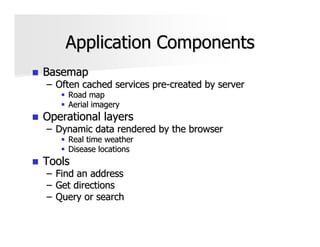
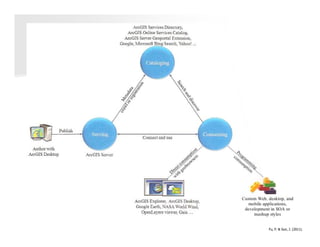
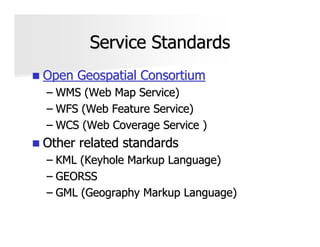
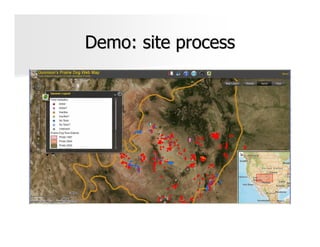
The document discusses the significance and applications of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), emphasizing its role in mapping and spatial analysis. It outlines various GIS software and technologies, including their capabilities for data integration, visualization, and real-time services. Additionally, it highlights web GIS architectures, service functions, and offers resources for further learning about GIS principles and applications.