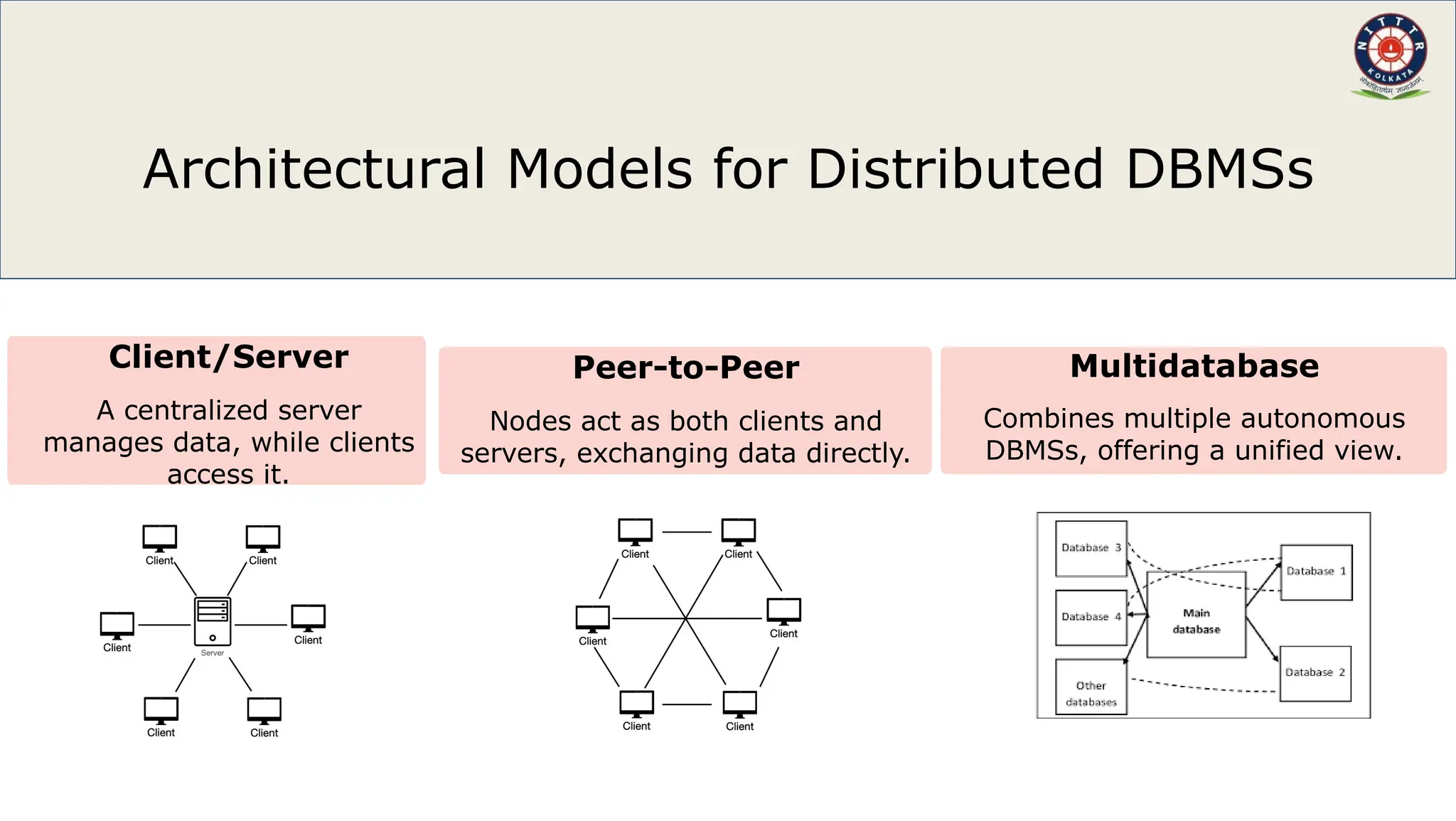
This document introduces distributed database management systems (DDBMS), highlighting their importance for scalability, reliability, and availability. It discusses various architectural models such as peer-to-peer and client/server systems, emphasizing the roles of nodes and data management processes. Additionally, it notes future trends in DDBMS, including cloud integration and the use of NoSQL databases.