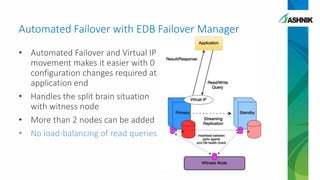
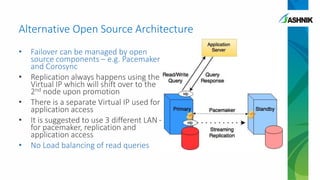
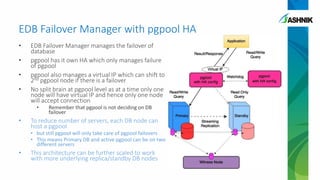
The document details the architecture and management of scalable and highly available PostgreSQL clusters, emphasizing options for load balancing and fault tolerance. It discusses various replication strategies, the roles of tools like pgpool and EDB failover manager, and architectural considerations for high availability. Key benefits include the ability to add standby servers for redundancy and the possibility of migrating databases to PostgreSQL while maintaining availability and recoverability.