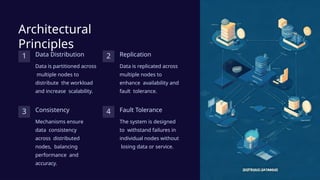
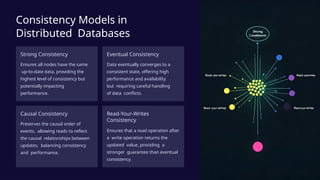
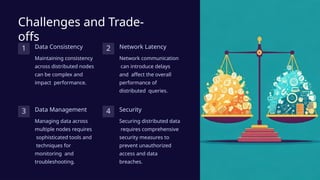
Distributed databases provide a scalable, fault-tolerant architecture by partitioning and replicating data across multiple servers, enhancing performance for modern applications. Key principles include data distribution, replication strategies, and consistency models, each with trade-offs impacting performance and availability. Emerging trends like cloud-native databases and edge computing are shaping the future of distributed database management.