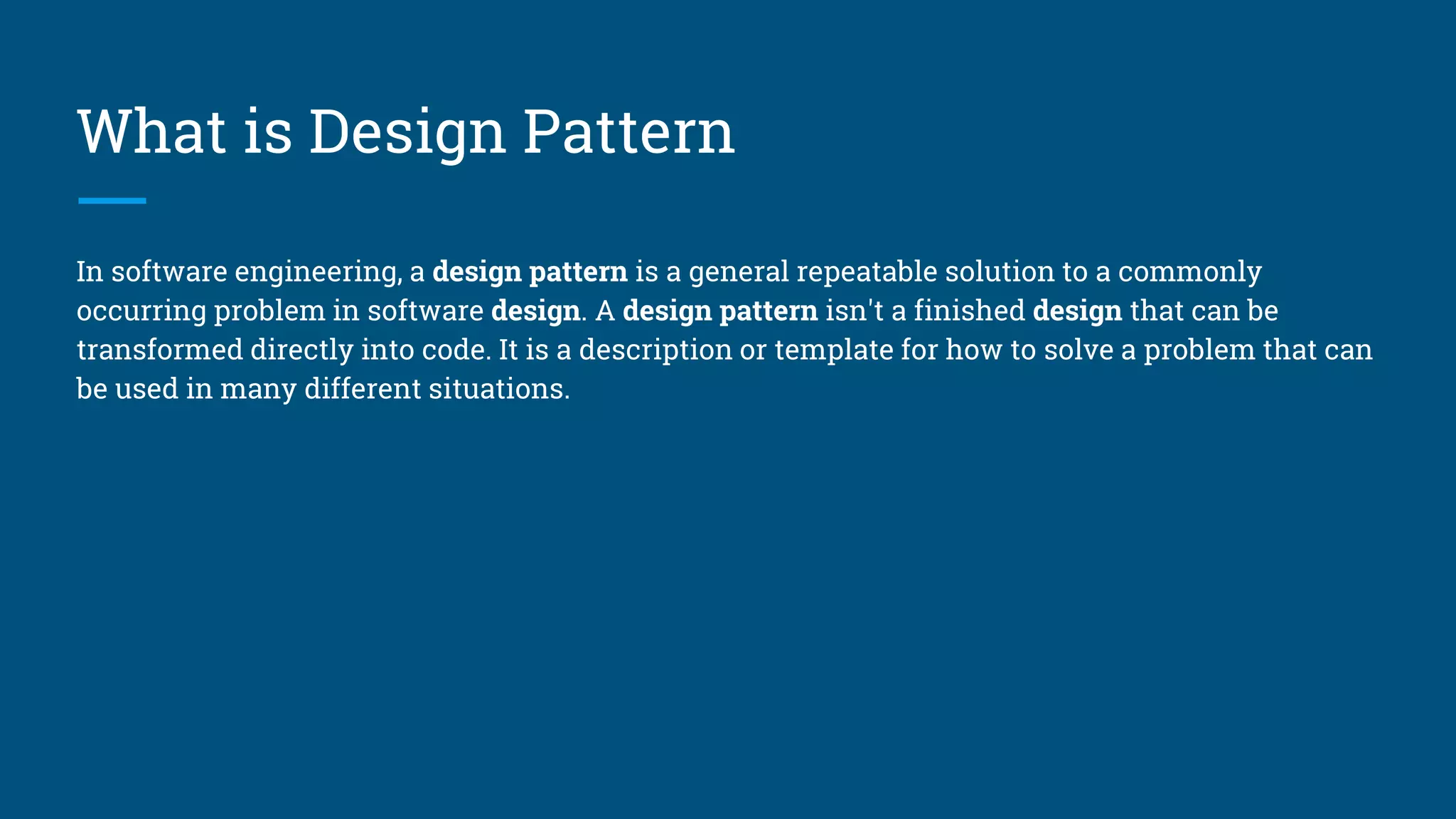
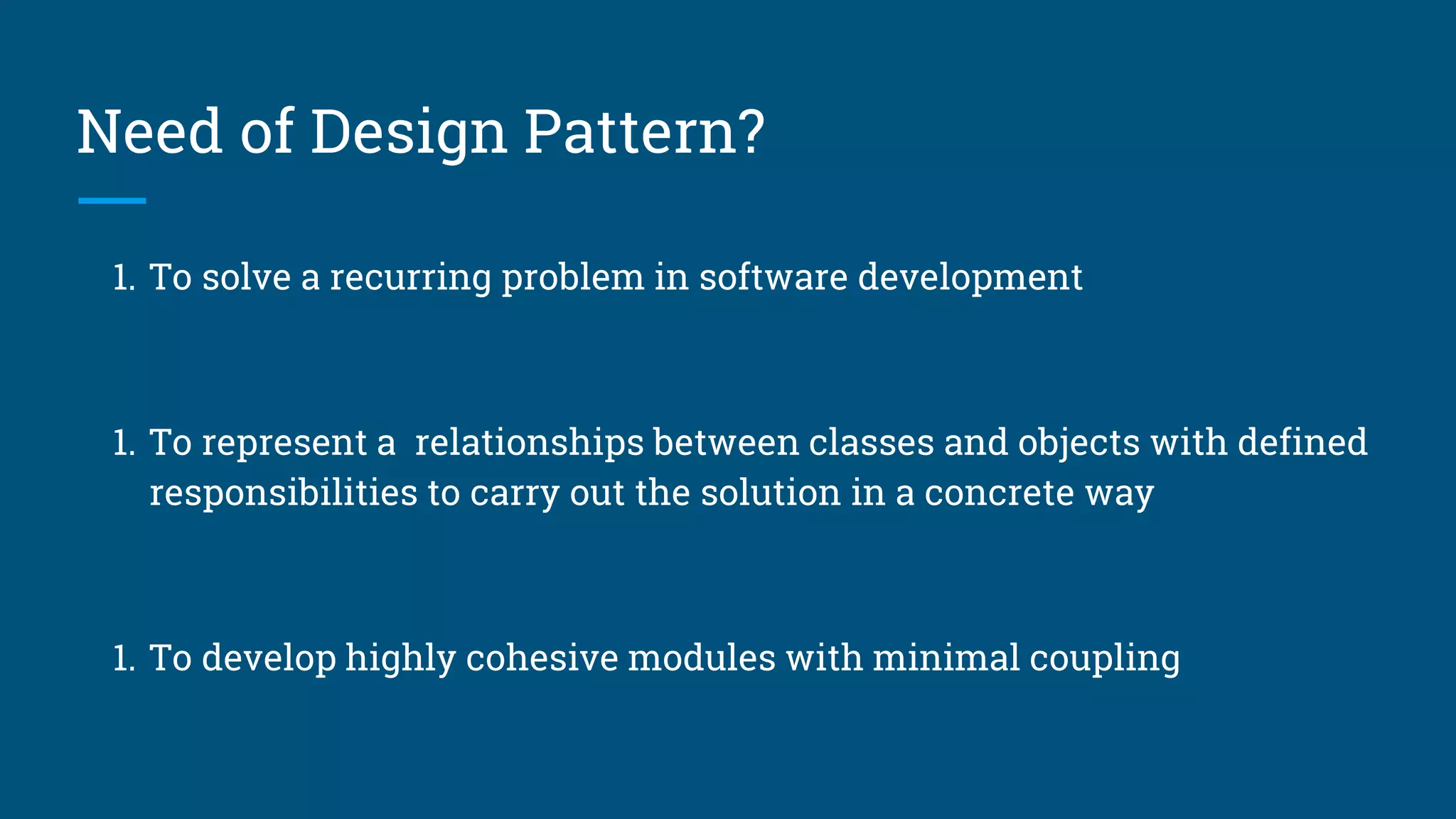
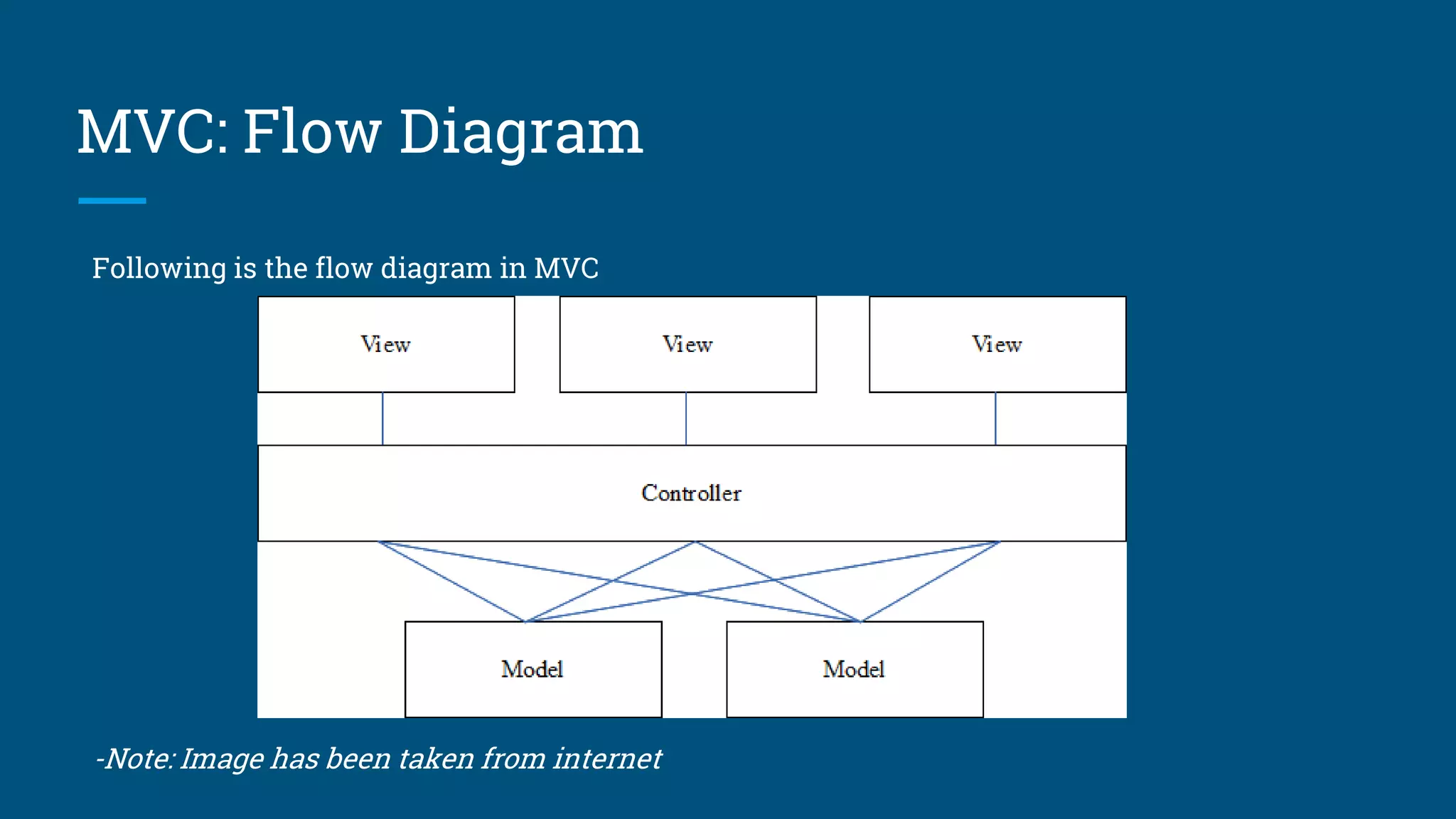
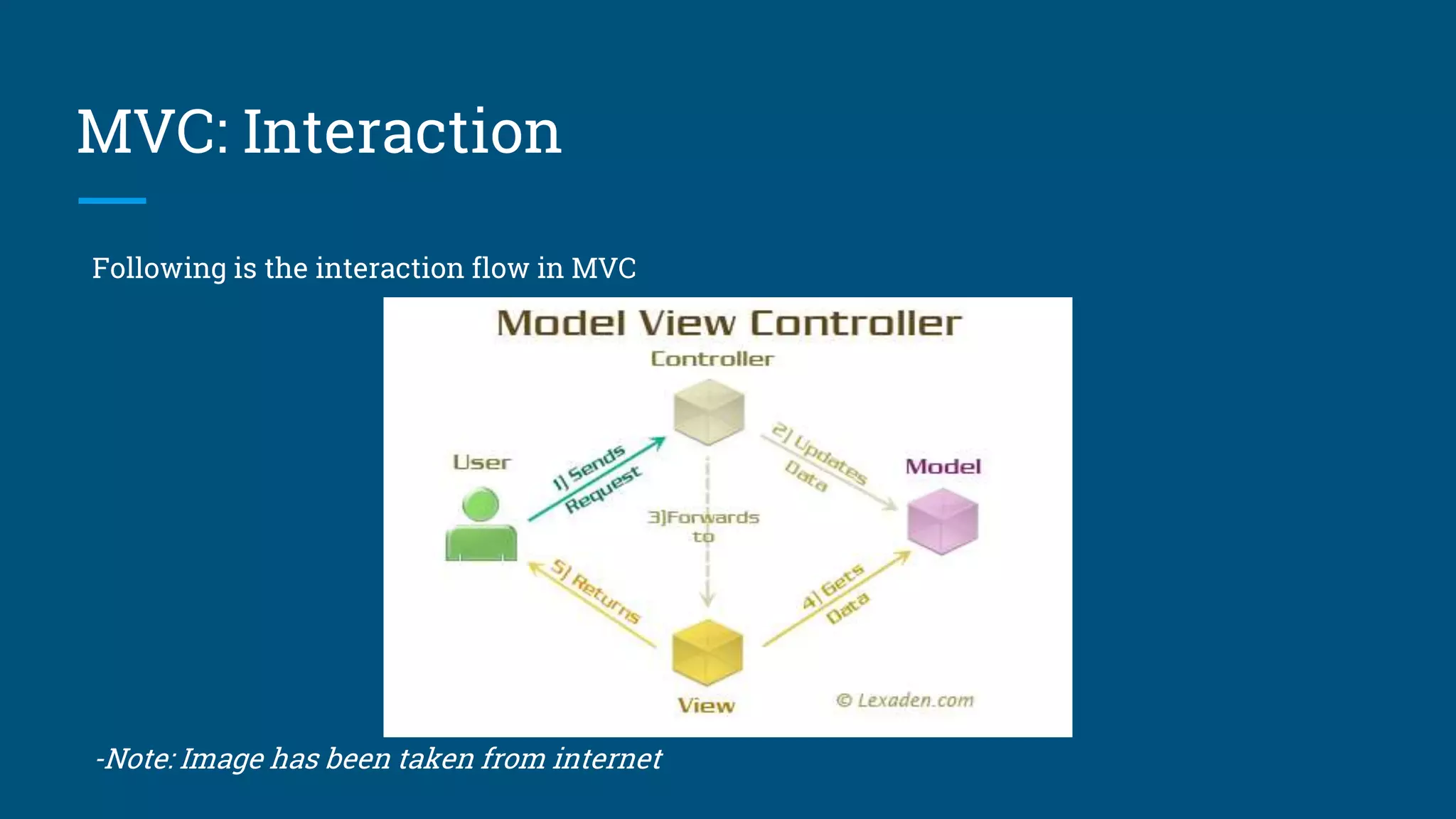
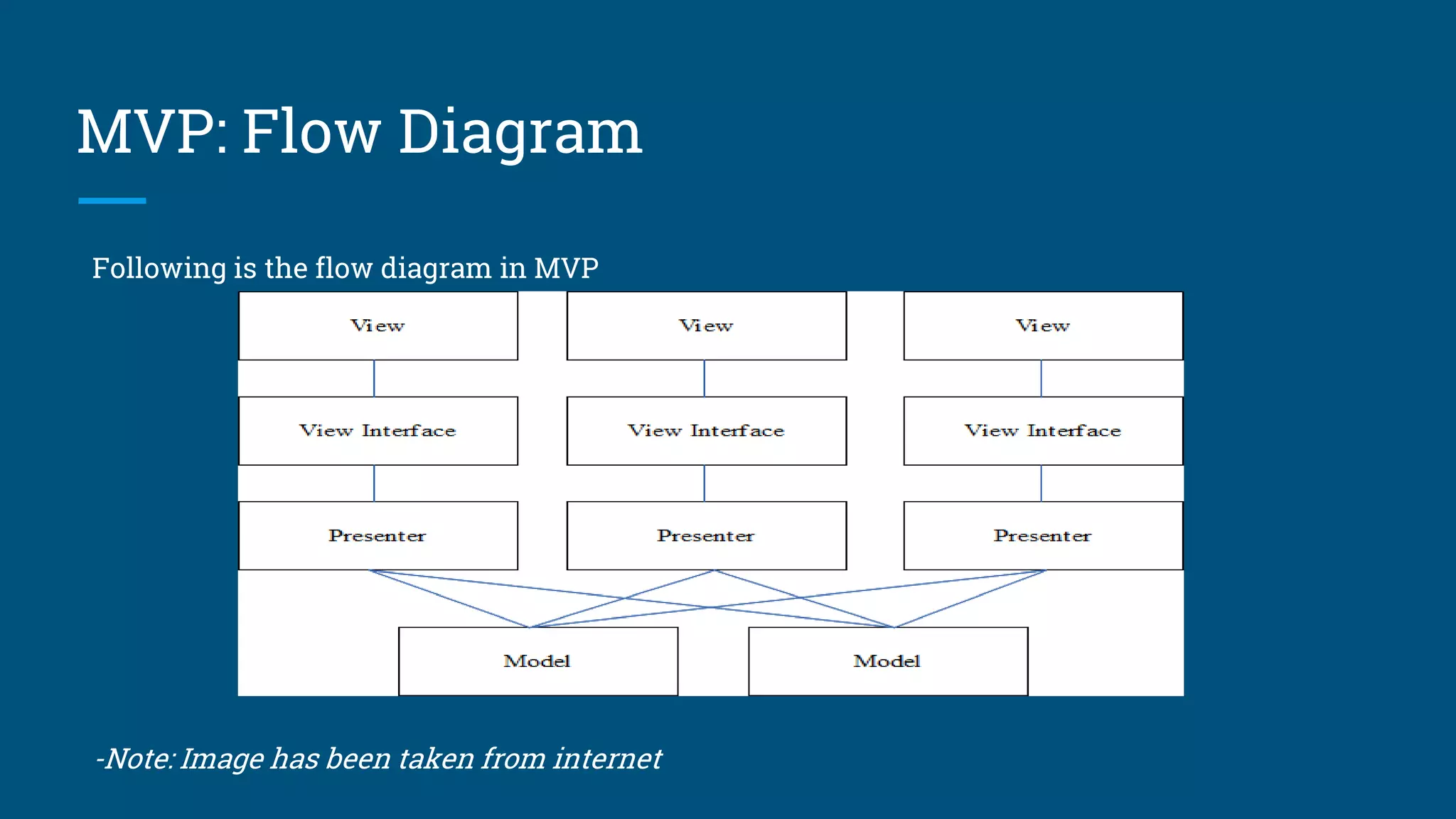
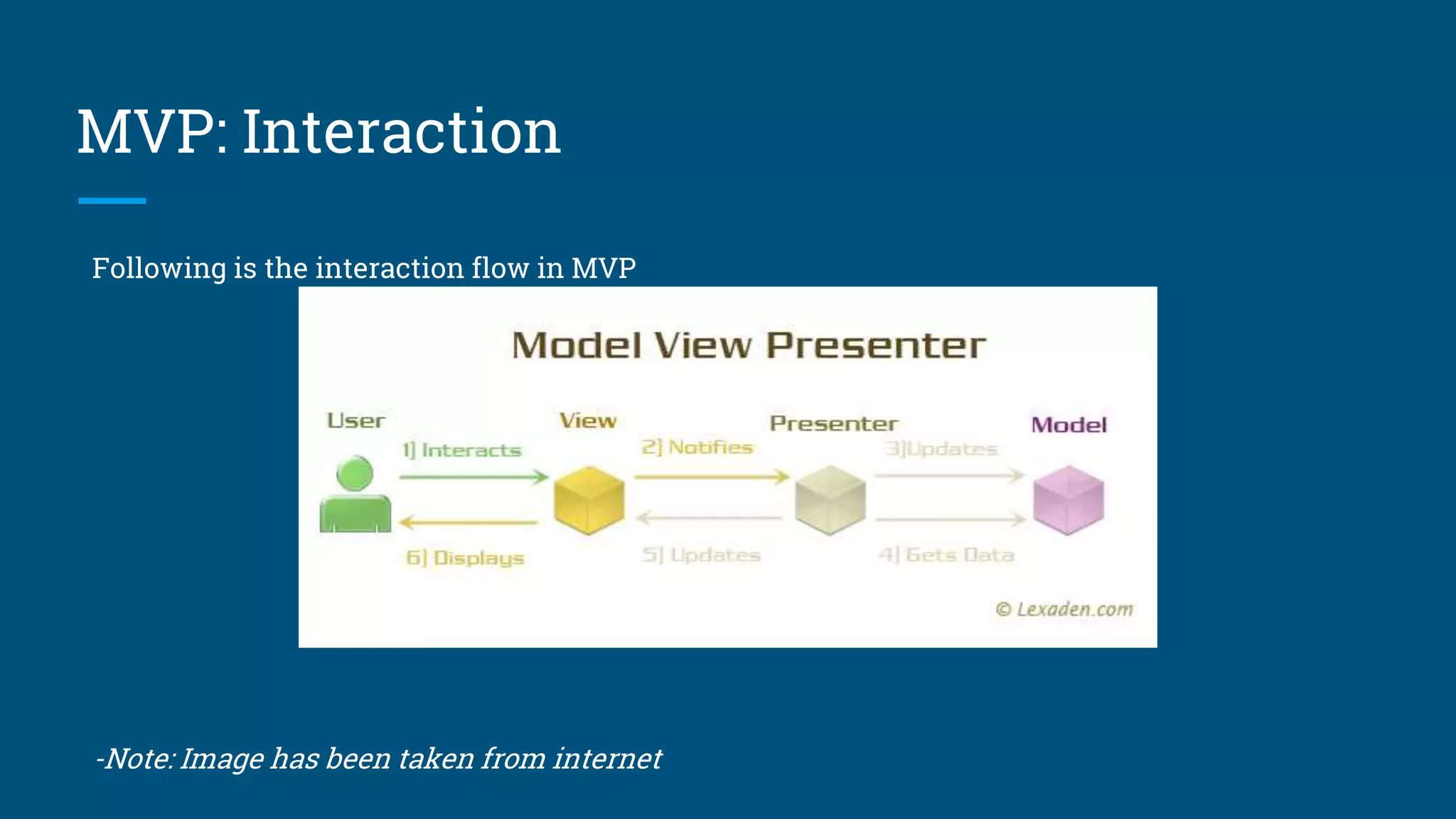
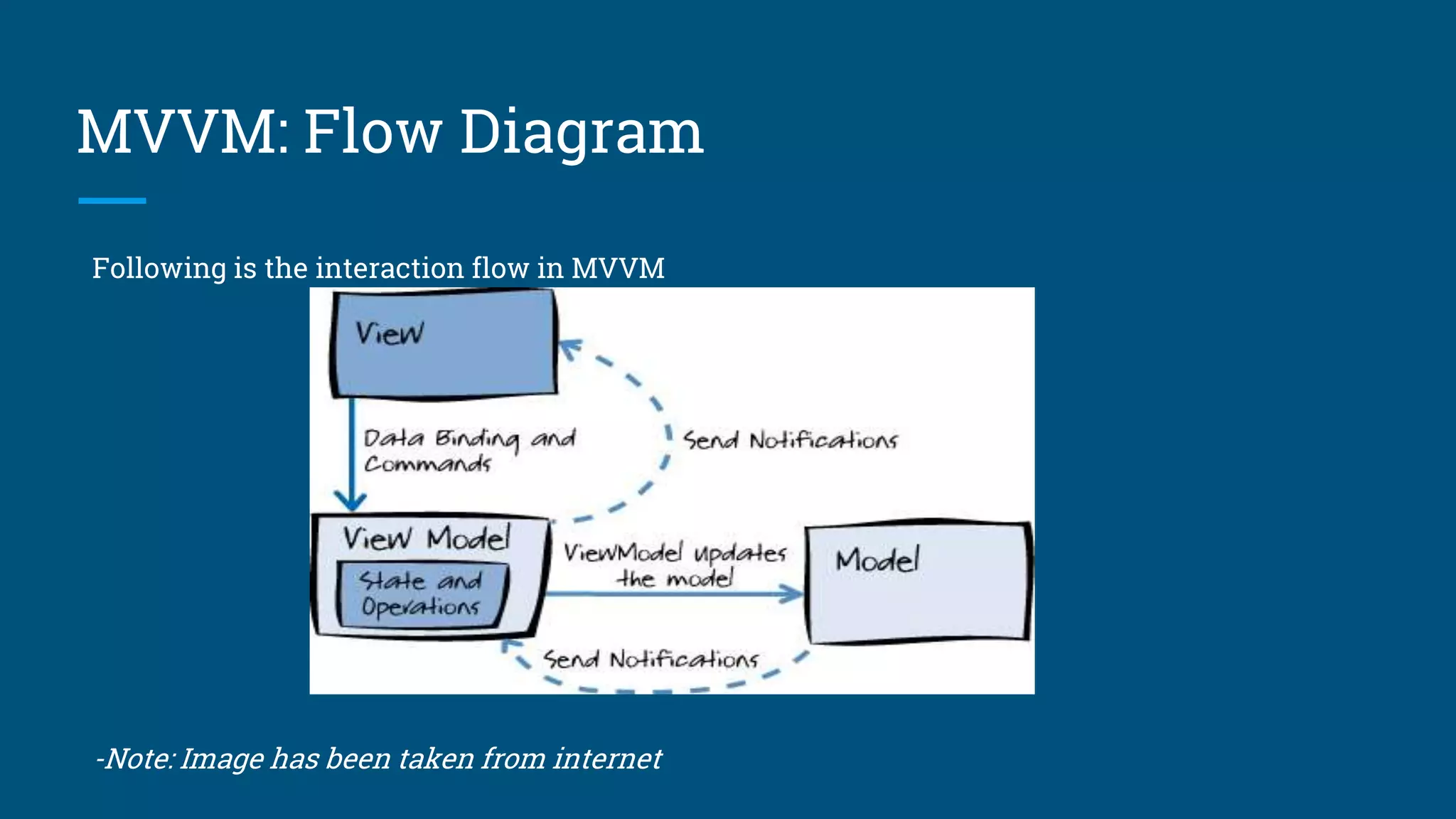
The document discusses architectural design patterns MVC, MVP, and MVVM. It explains that MVC separates an application into three components - the model, the view, and the controller. MVP adds a presenter layer between the model and view to avoid direct communication. MVVM uses data binding between the view and view model layers, allowing two-way communication to automatically update the view when data changes. While any pattern can be used, the author recommends MVP with data binding to reduce code and prevent mistakes.