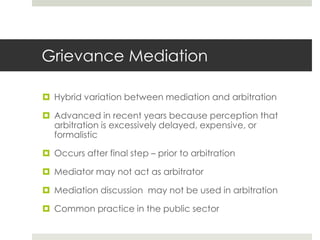
Arbitration is an alternative dispute resolution process where parties present evidence to an impartial arbitrator, who makes a final and binding decision. It is commonly used to settle labor, commercial, and international disputes. The arbitration process is typically outlined in an agreement and involves selecting an arbitrator, scheduling a hearing, presenting evidence and arguments, and receiving a final ruling. While arbitration is a more informal and private process than litigation, its use has increased as courts now generally support and enforce arbitration awards.


















![Labor Arbitration ObservationArbitration….is a school, an arena, a theatre. Everyone both participates and observes. The whole company of actors-arbitrator, union and employer officials, the…[grievant], and the witnesses (mostly employees)—sits at one table. Argument, assertion, testimony, charge and countercharge, even angry abuse-sometimes spontaneous, sometimes “for the record” –flow freely in quick continuous intercourse. The arbitrator may let the discussion takes its head for a moment, then rein it in; an occasional question, a request for clarification…… Labor Arbitration and the Individual WorkerJaffe, Annals of The American Academy of Political and Social Science 34, 40-41 (May 1953)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionga-100828200527-phpapp02/85/Arbitration-Overview-20-320.jpg)