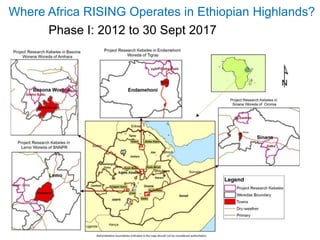
Africa RISING operates in two phases in the Ethiopian Highlands. Phase I from 2012 to 2017 focused on technology identification, testing, and validation through action research. Phase II from 2016 to 2021 aims to scale these innovations through partnerships with development organizations. Africa RISING works on projects like irrigated forages, post-harvest management, fodder trees, and nutrient amendments. In 2017, it reached over 60,000 households across four regions, covering 20,397 hectares of land. While scaling of validated technologies presents opportunities, funding uncertainties pose challenges to partnerships and further work.