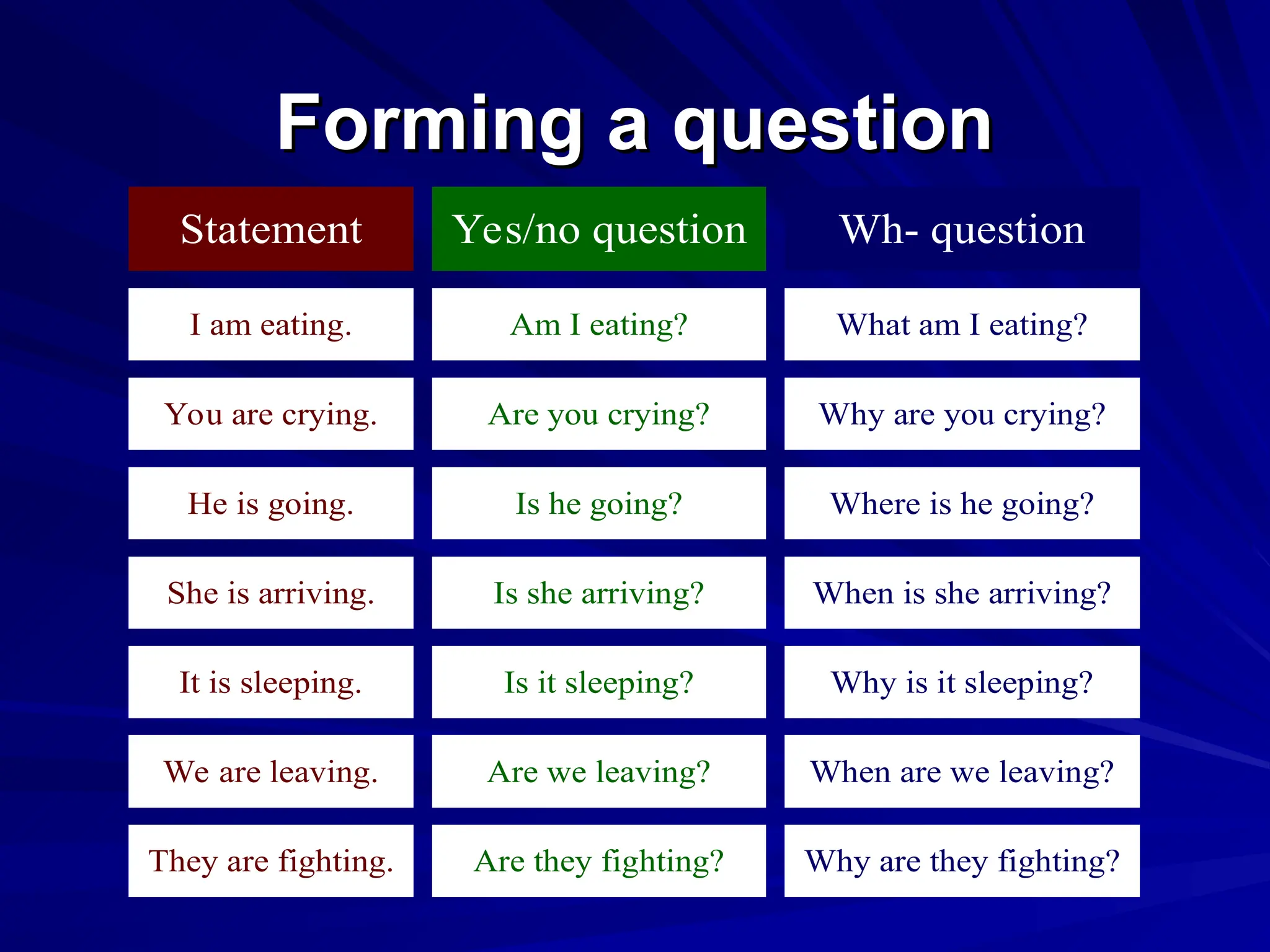
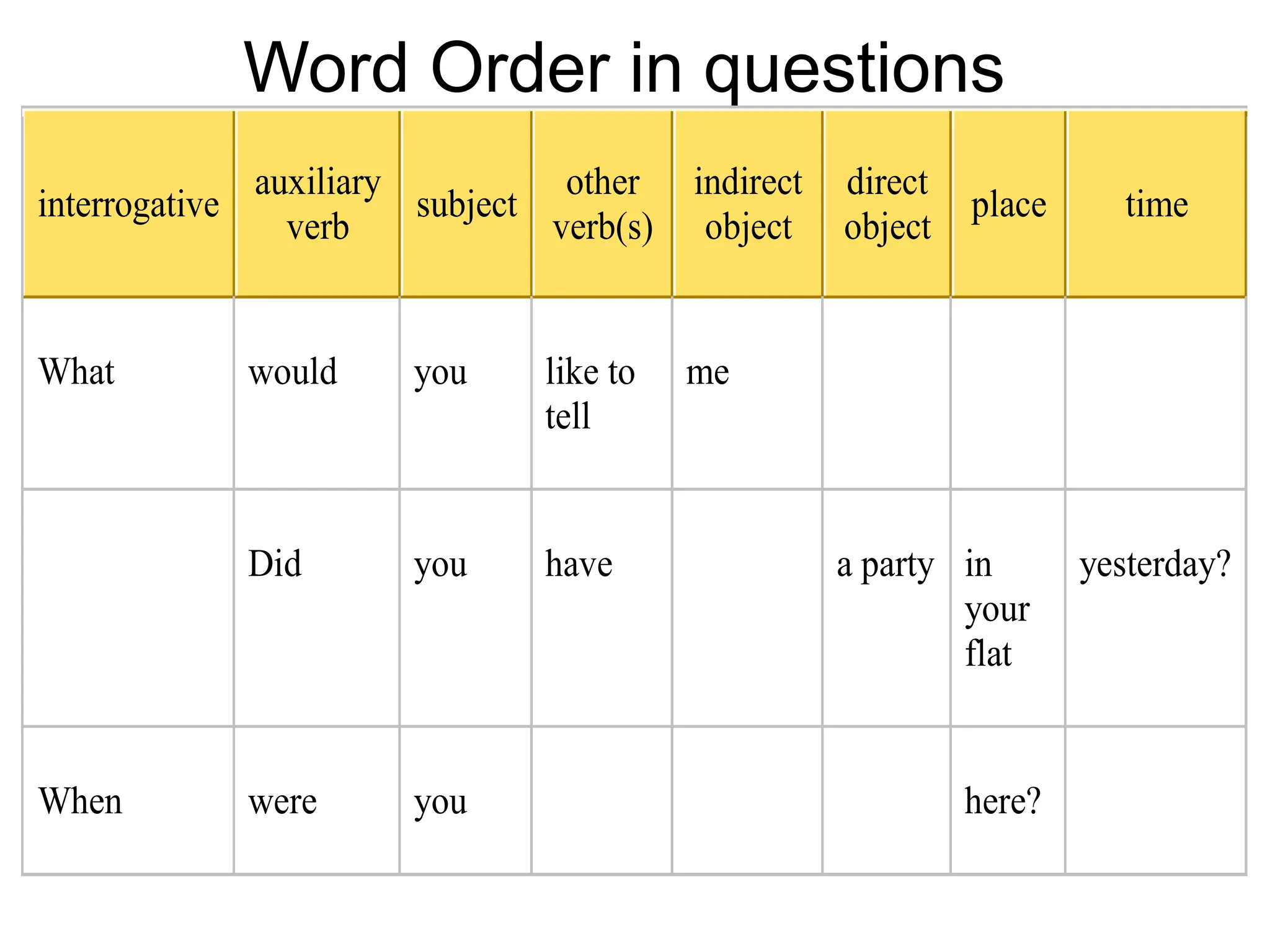
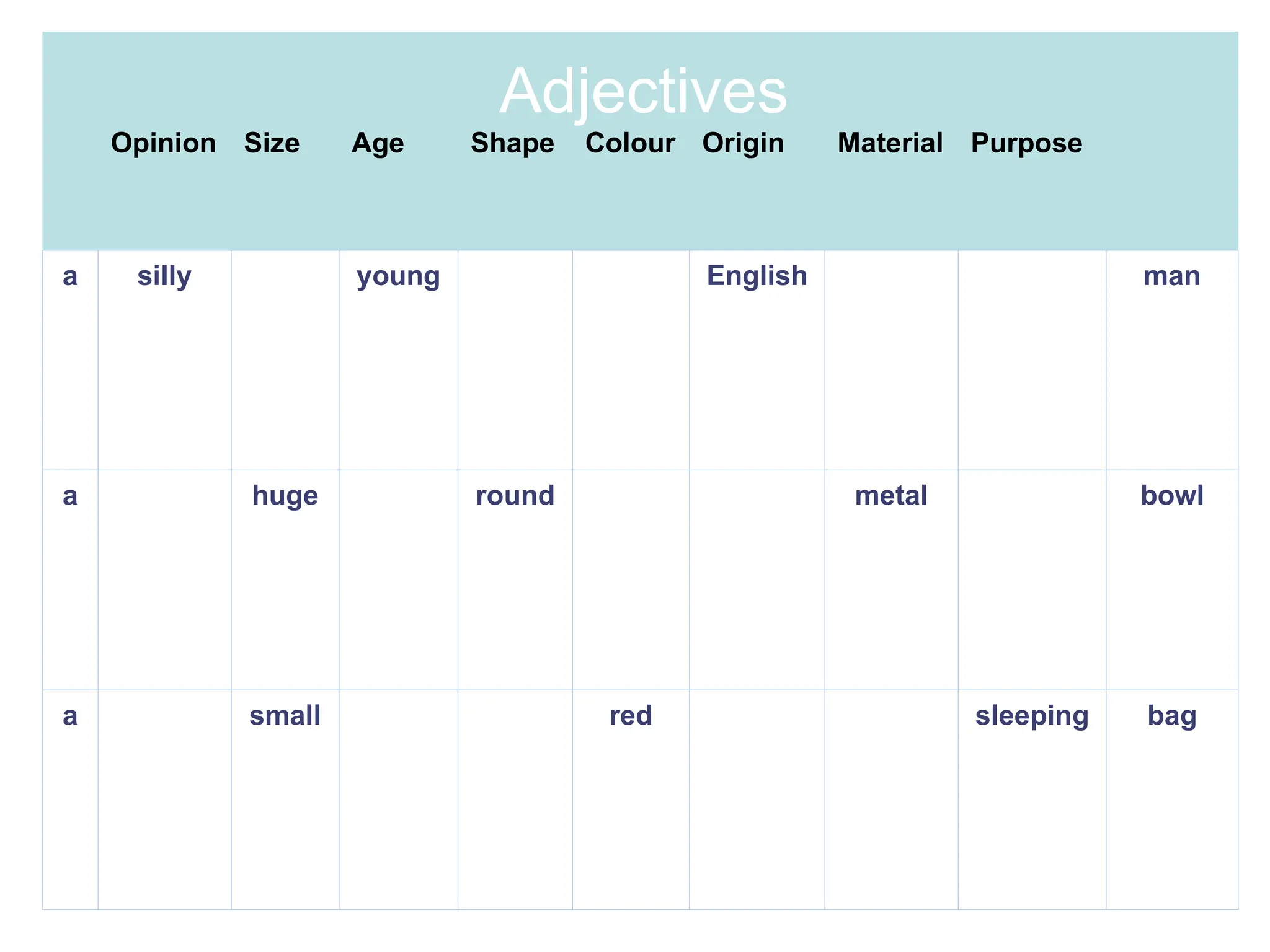
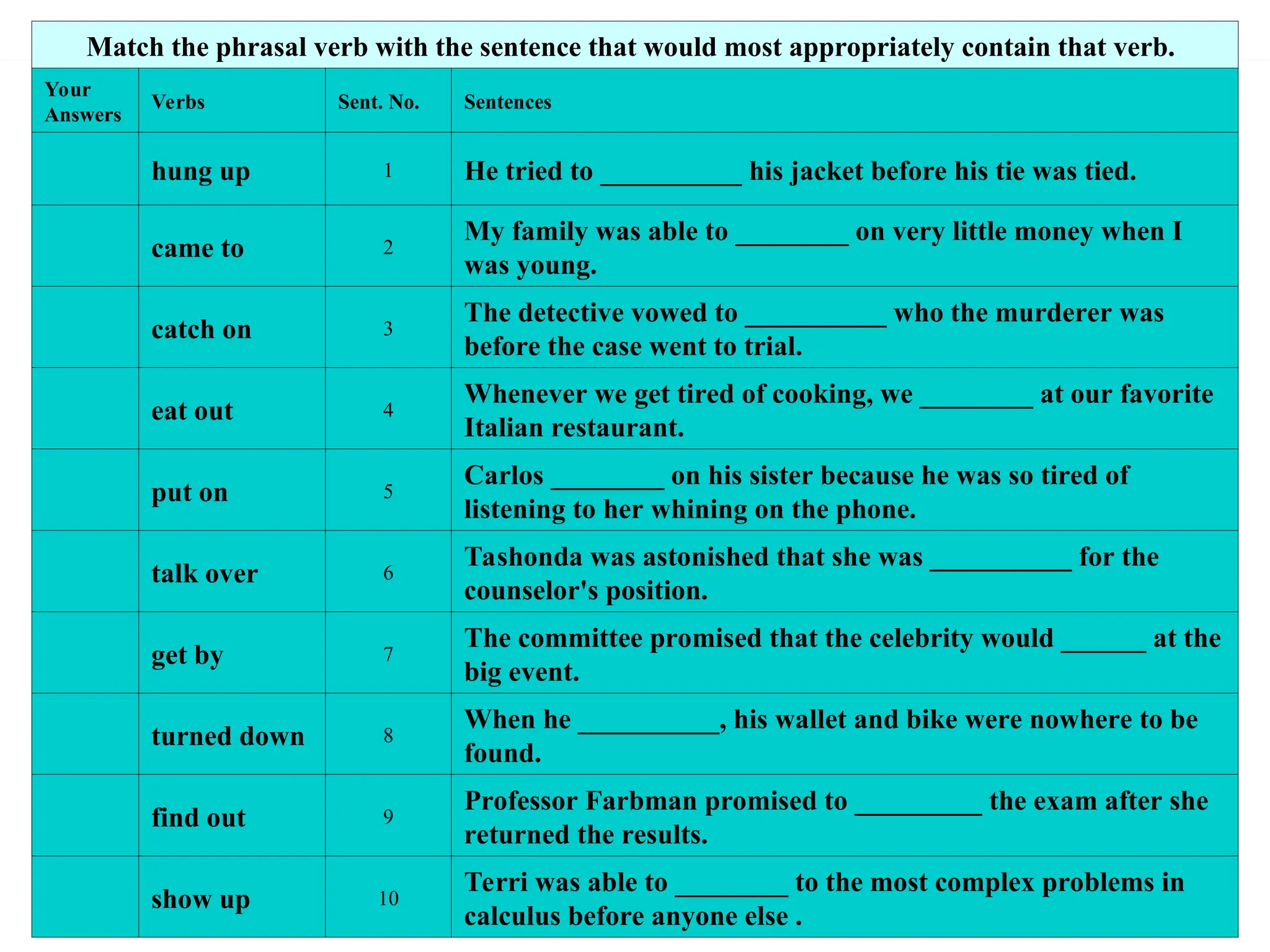
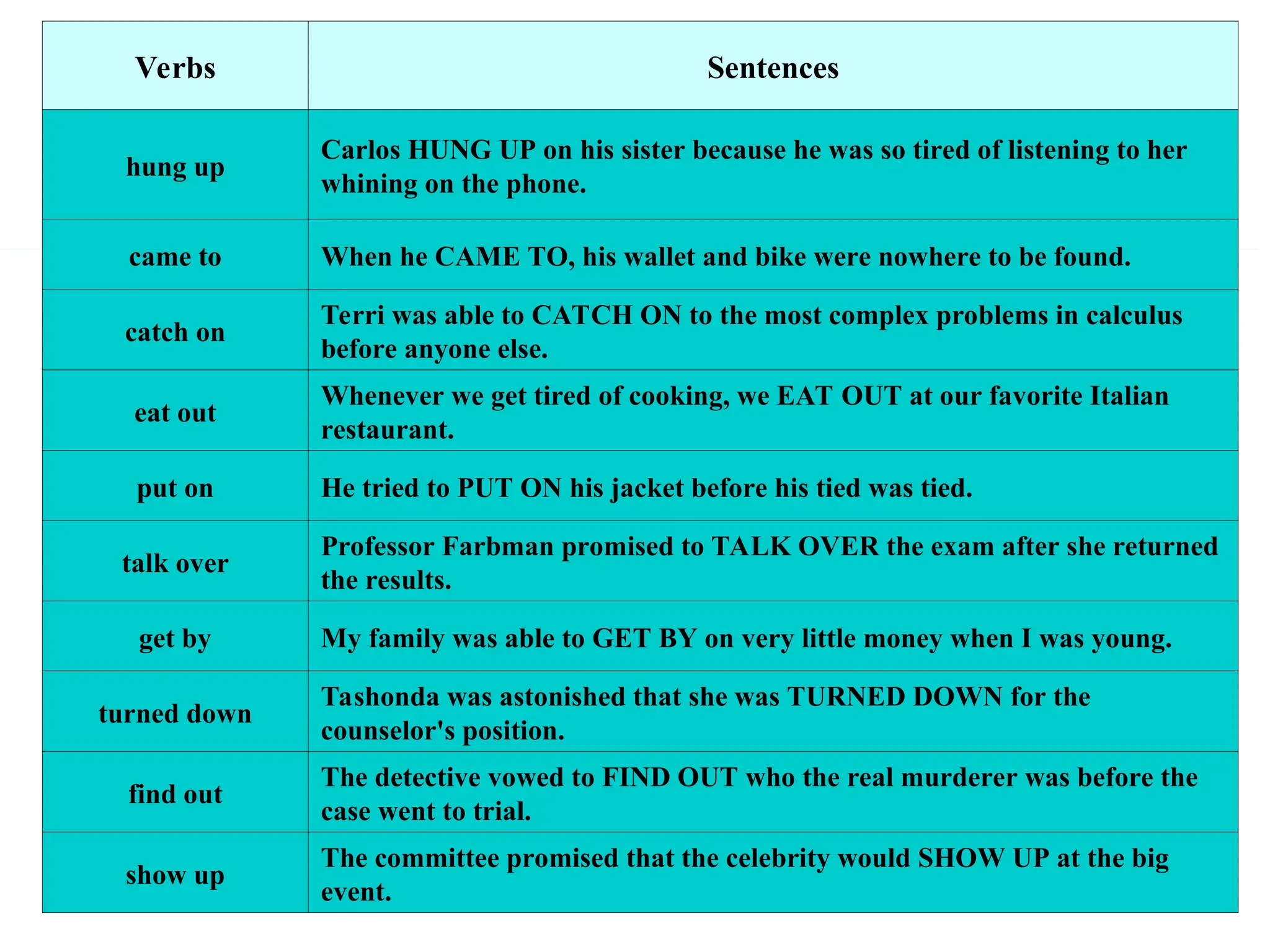
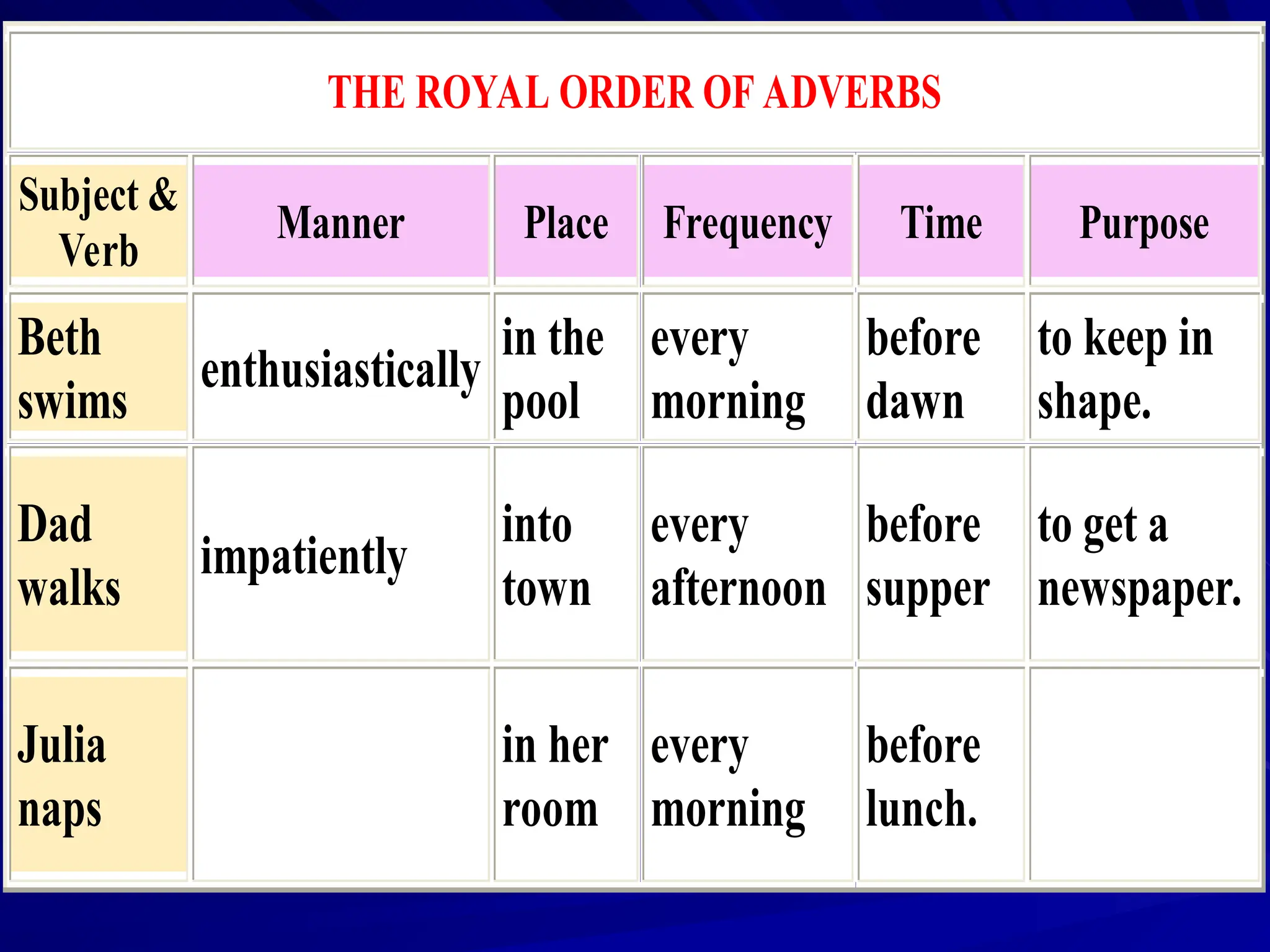
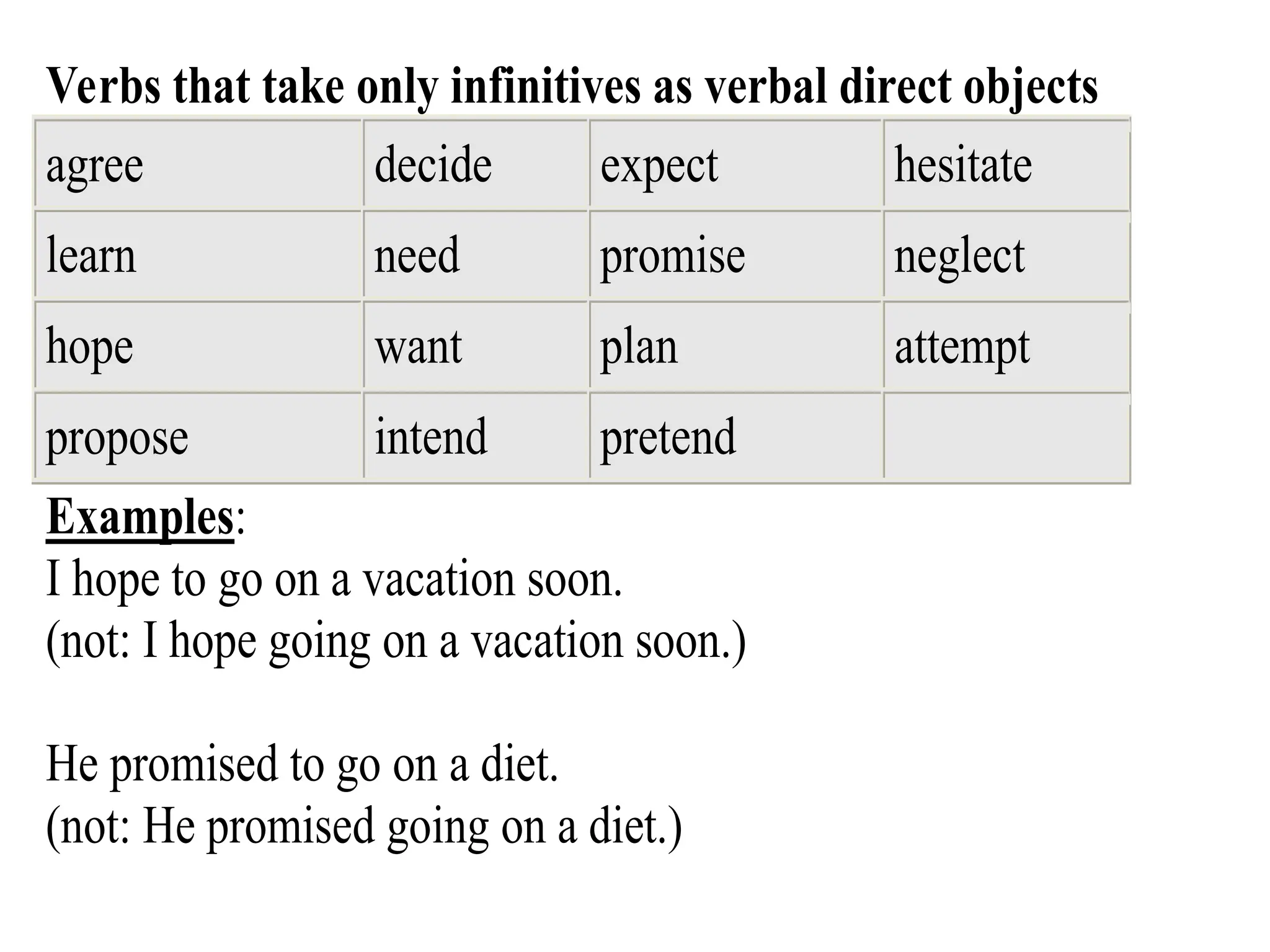
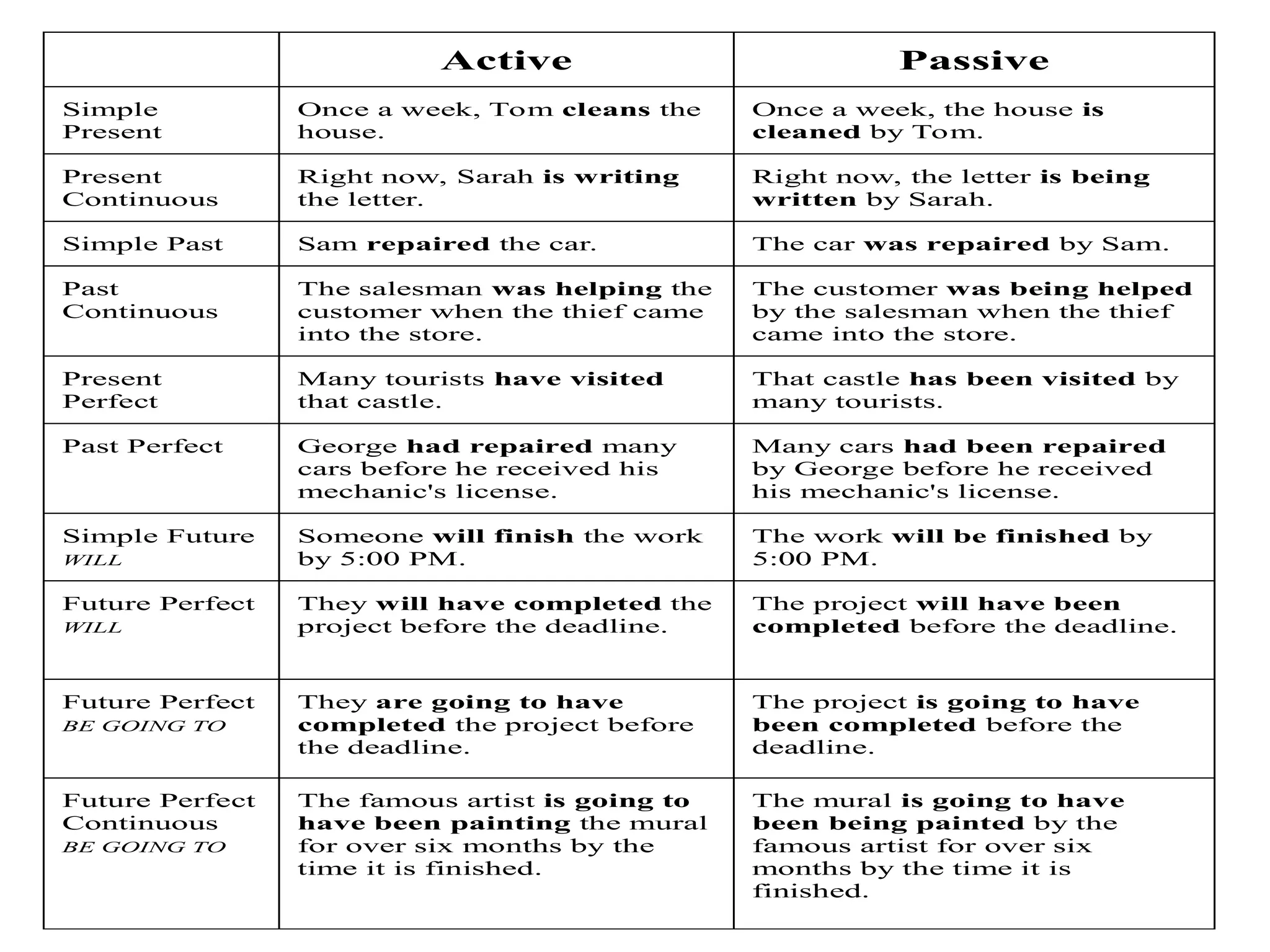
The document outlines the structure and requirements for a standardized English proficiency test for admission to Kuwait University, detailing its components: grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension. It explains the objectives of each section and provides examples of questions and topics covered. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of standardized tests, such as TOEFL, in predicting a student's future academic achievements.