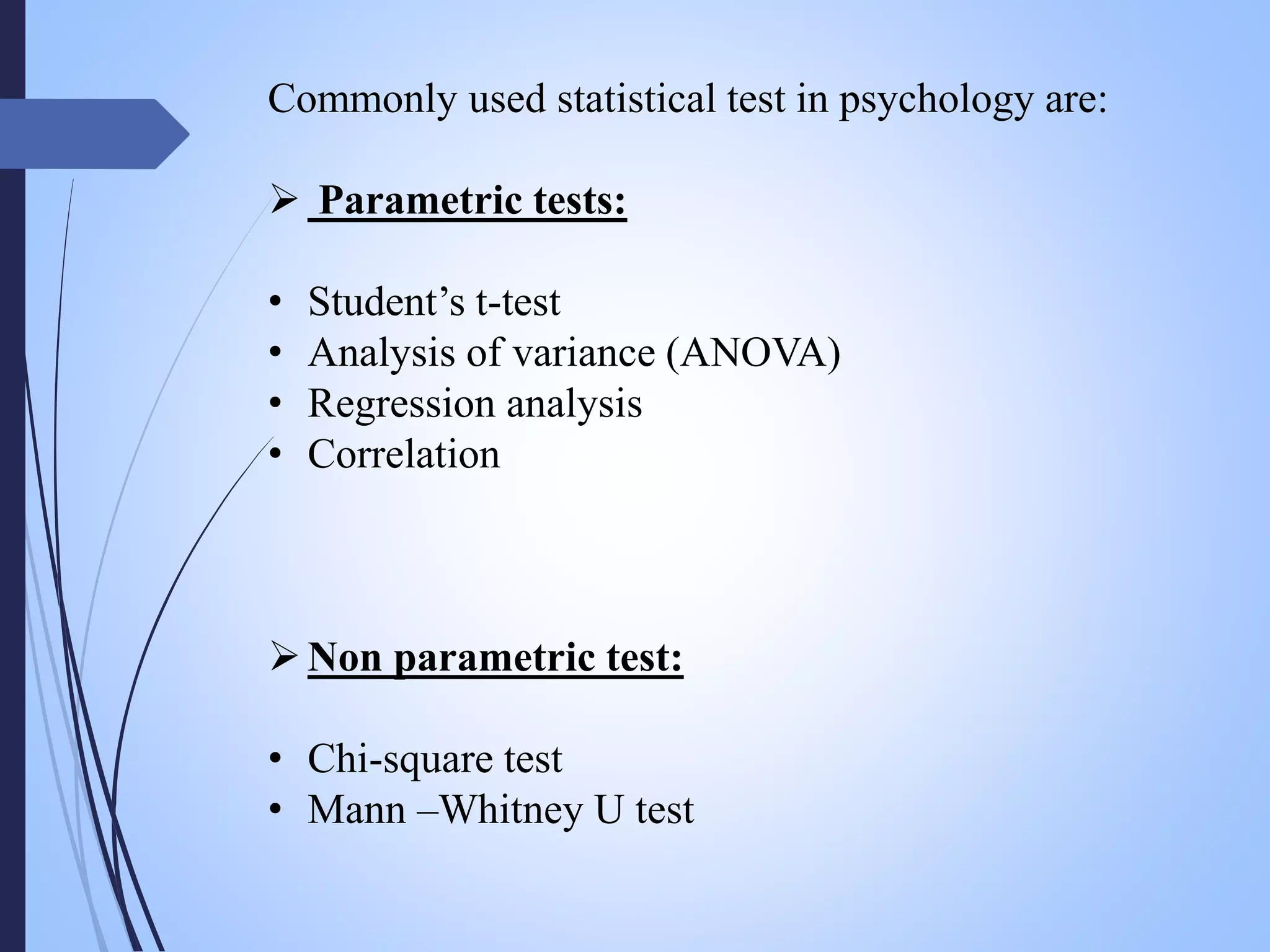
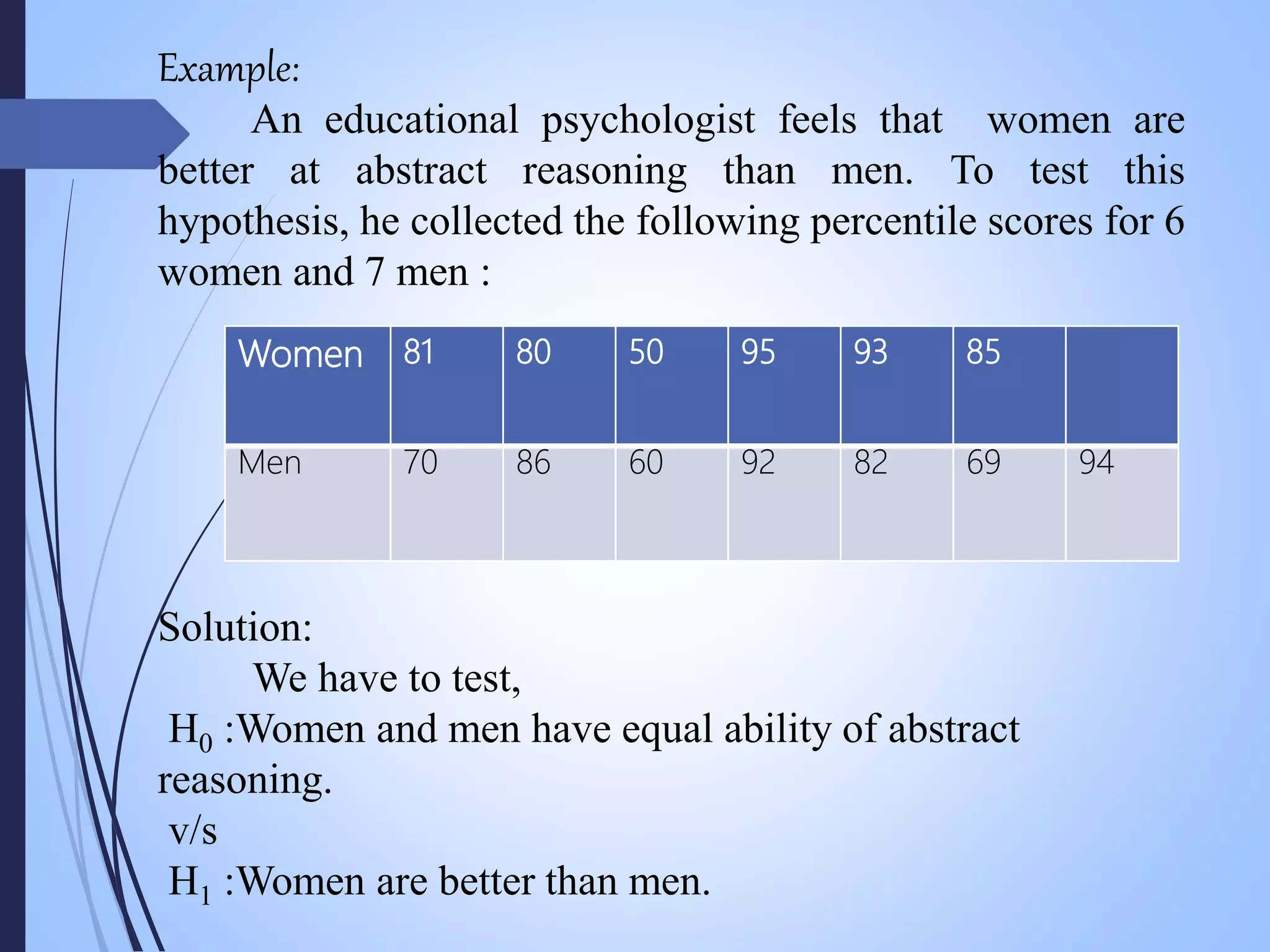
The document presents a seminar on the applications of statistics in psychology, highlighting the importance of statistical methods in analyzing psychological data. It covers fundamental concepts of psychology, types of statistical tests used, and a specific example involving a hypothesis test comparing abstract reasoning between men and women. References to key resources are also provided to support the content discussed.