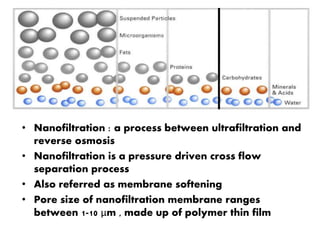
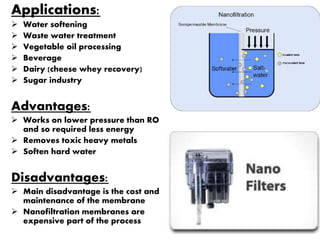
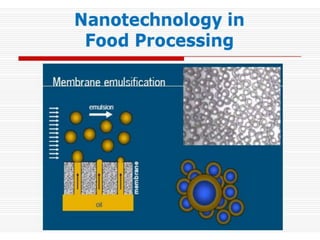
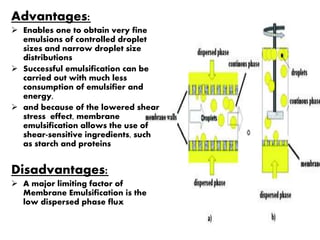
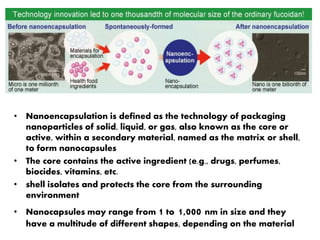
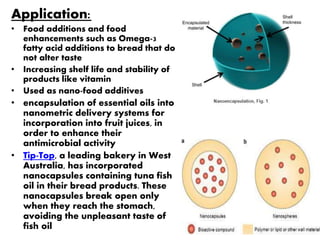
This document discusses three membrane-based separation processes: nanofiltration, membrane emulsification, and nanoencapsulation. It provides details on each process such as operating principles, pore sizes, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Nanofiltration is between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis used for softening and purifying water and fluids. Membrane emulsification uses microporous membranes to directly produce single or multiple emulsions with controlled droplet sizes. Nanoencapsulation packages nanoparticles within a shell or matrix 1-1000 nm in size to isolate, protect, and deliver active ingredients in applications like foods and nutraceuticals.