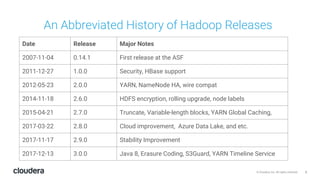
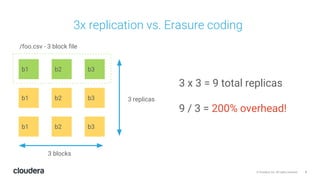
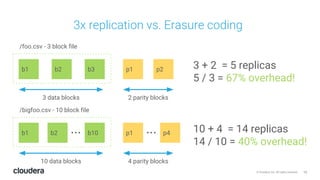
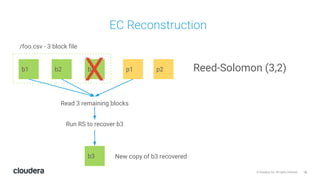
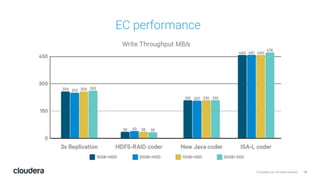
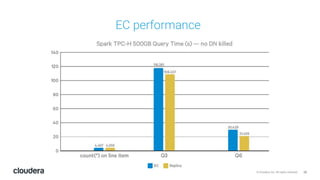
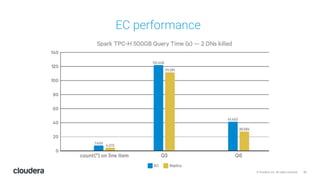
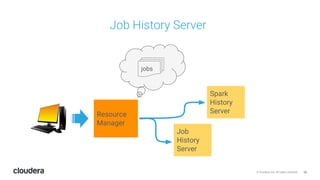
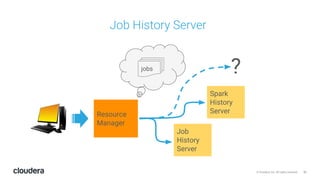
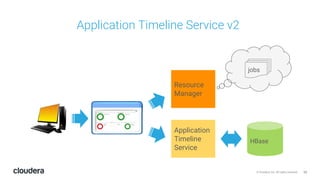
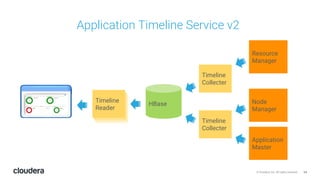
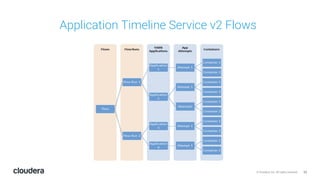
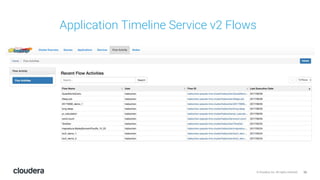
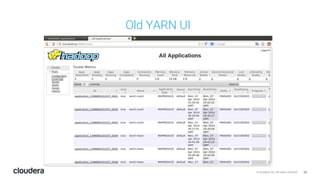
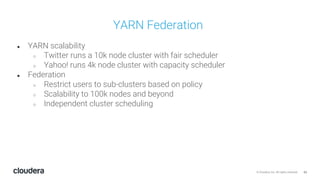
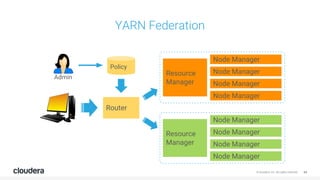
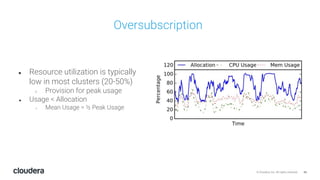
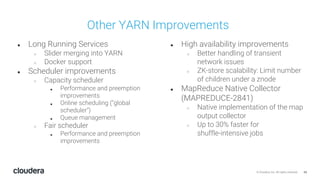
The document discusses the release and key features of Hadoop 3.0, which includes enhancements such as HDFS erasure coding for improved storage efficiency, and a new YARN UI for better visibility into cluster operation. It highlights the motivation for this upgrade, the timeline of its development, and mentions compatibility with previous versions. Additionally, it covers various optimizations and improvements in resource management and operational efficiency.