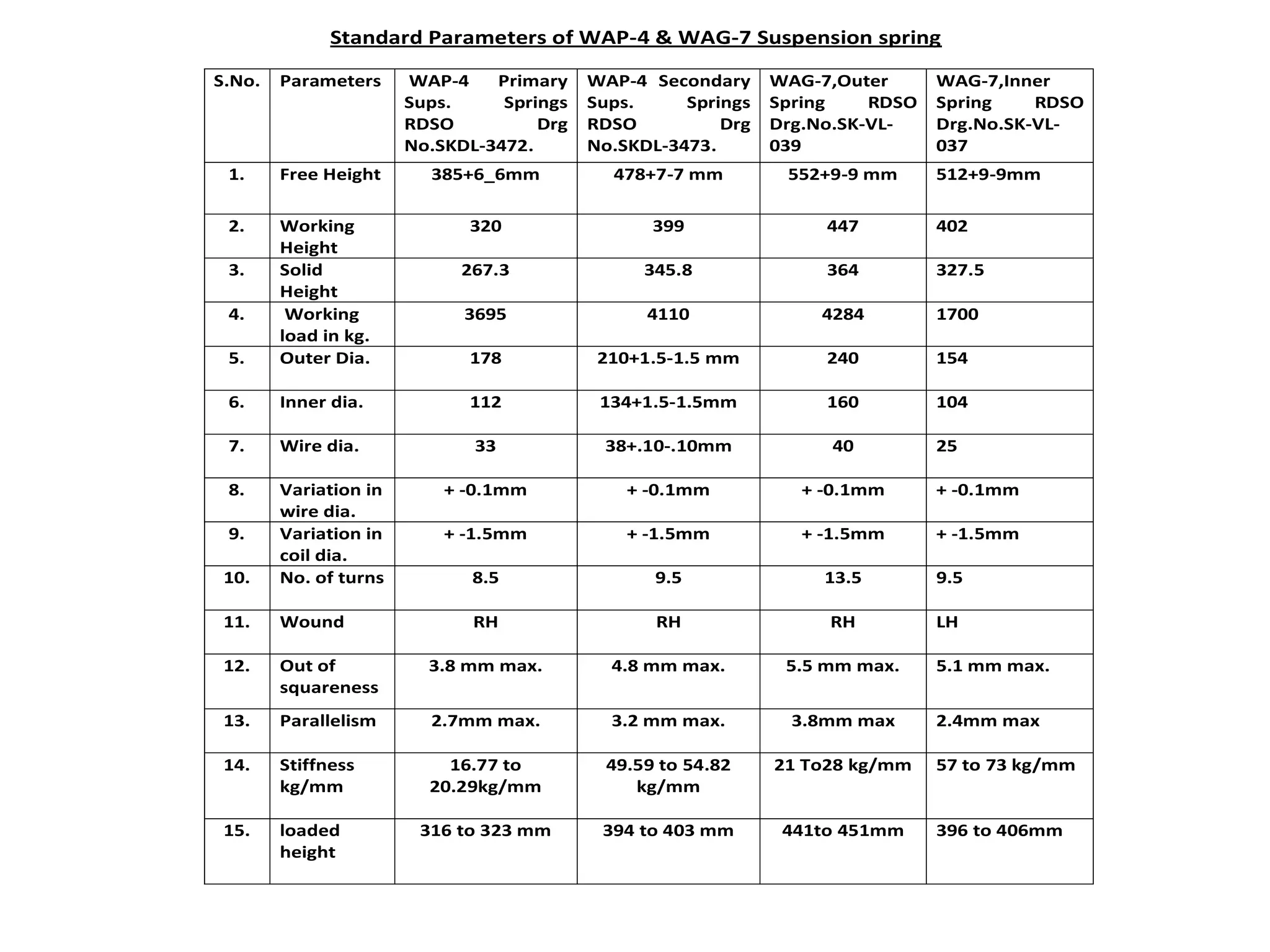
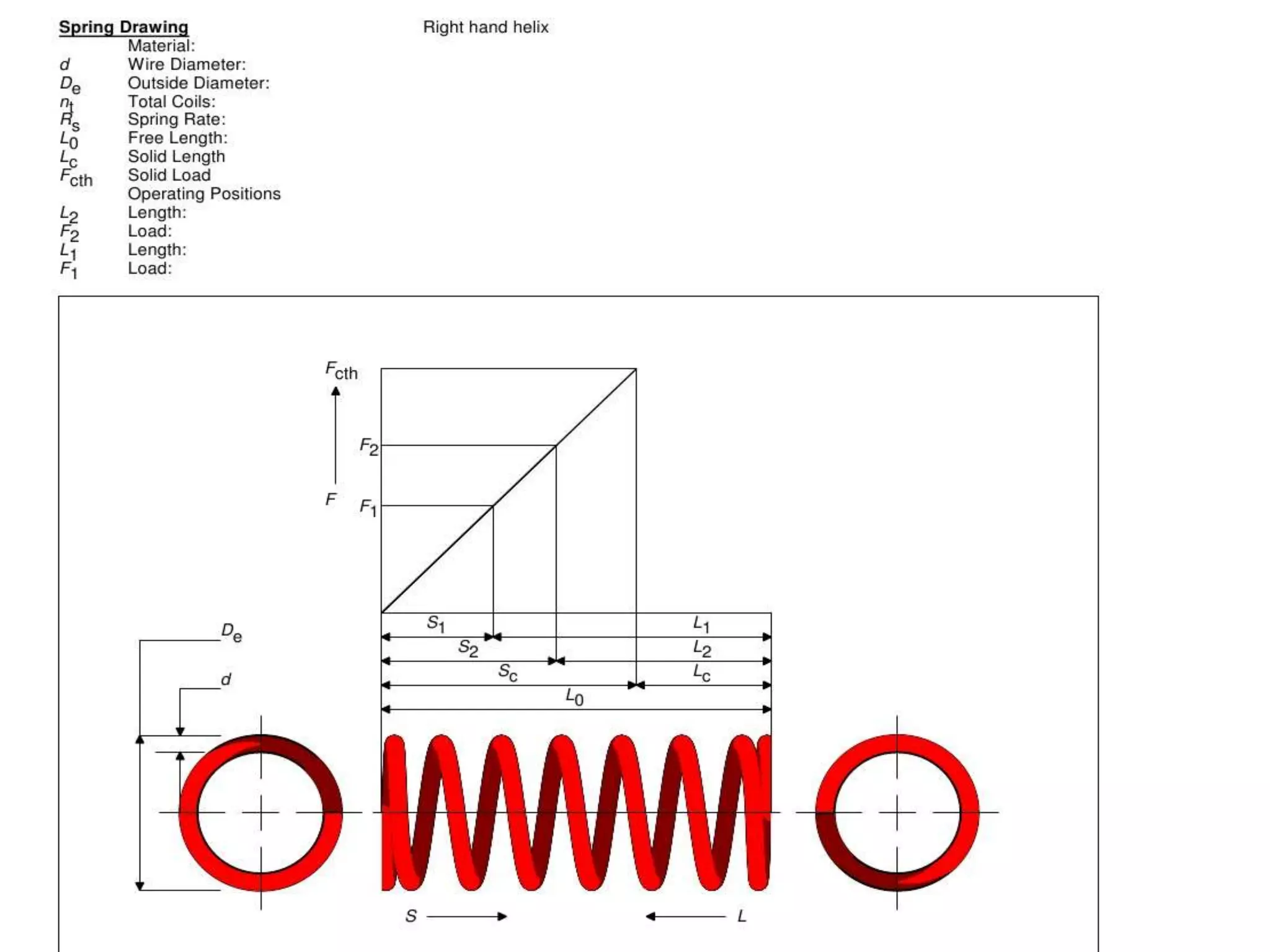
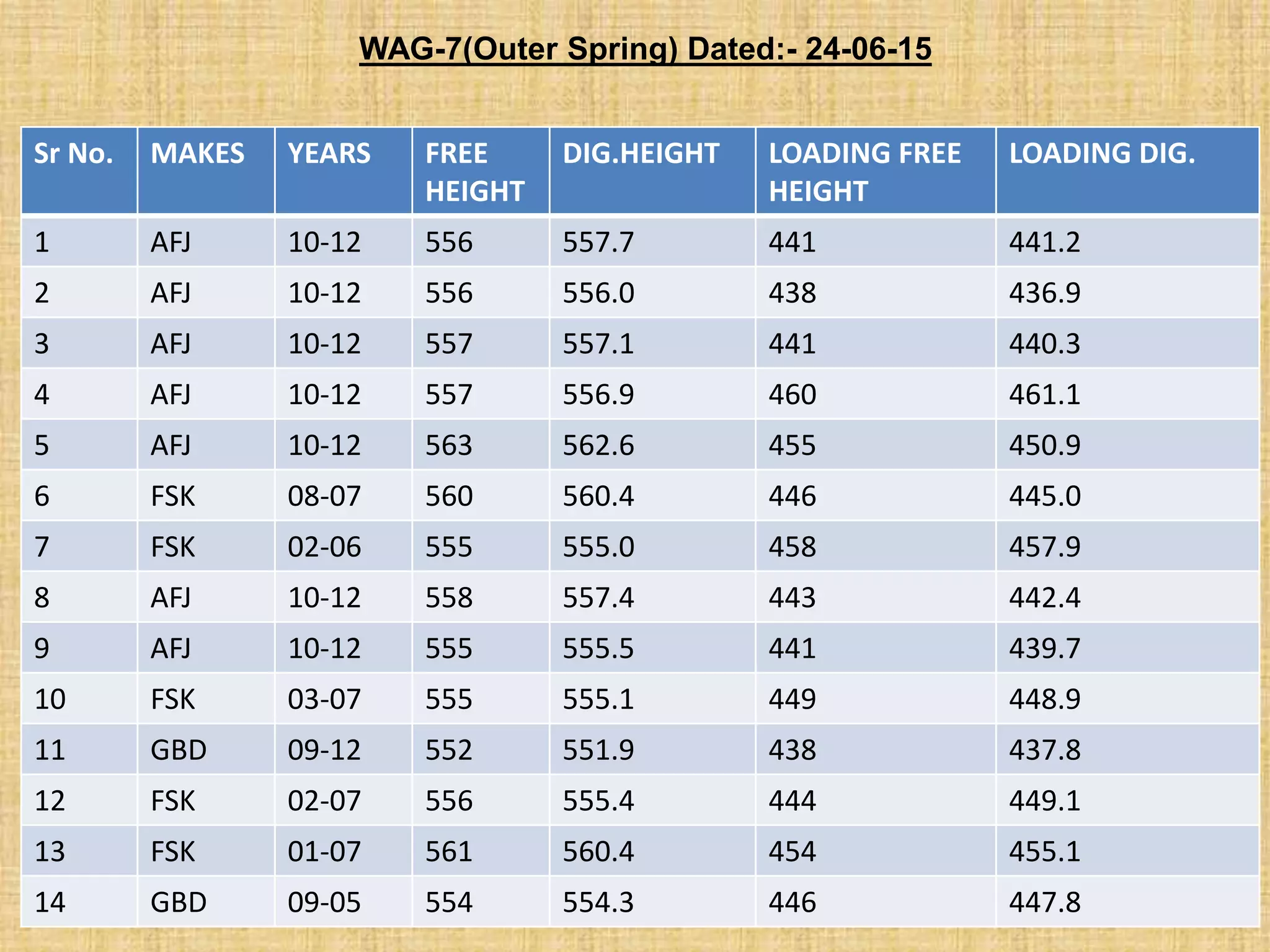
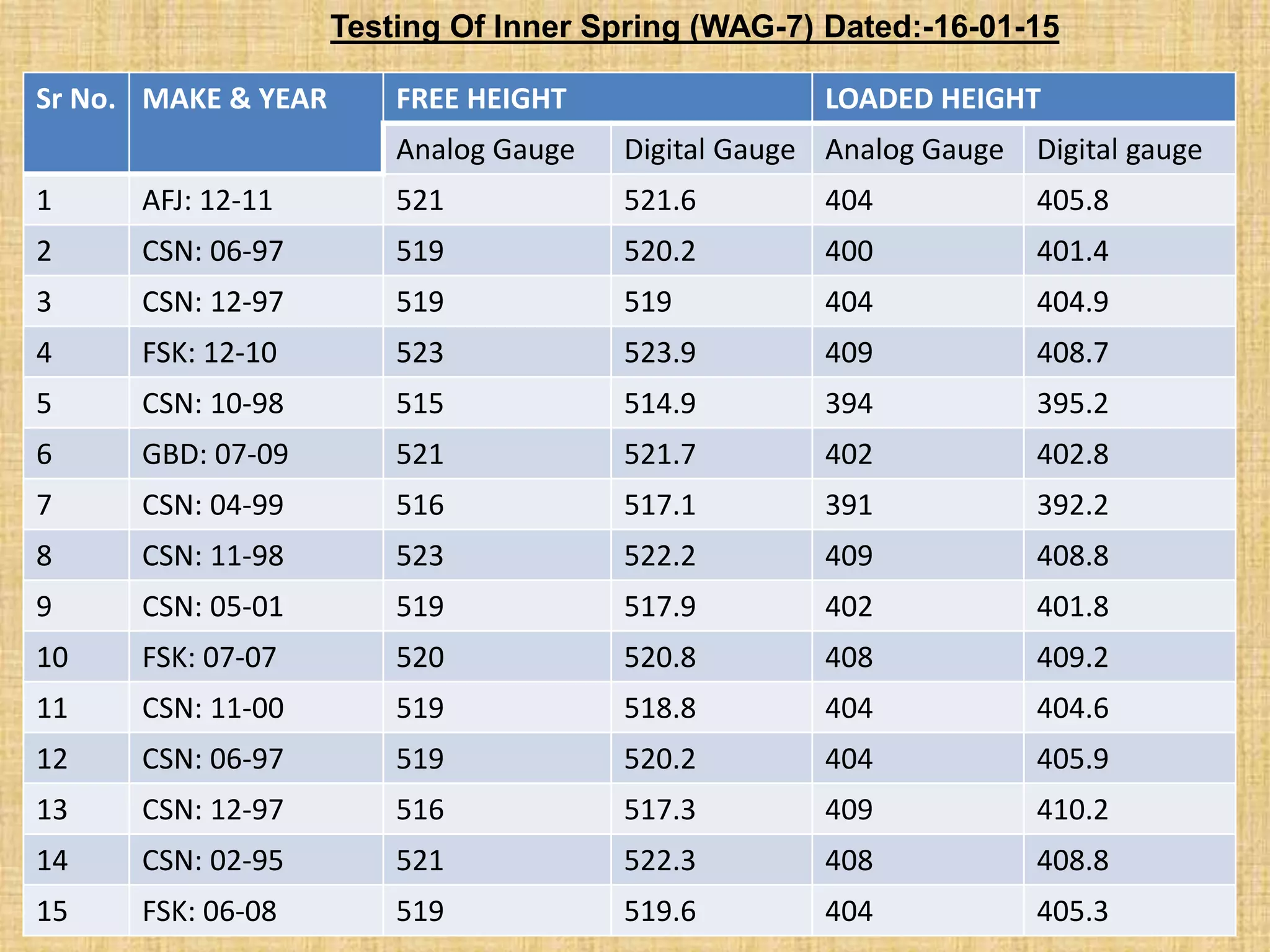
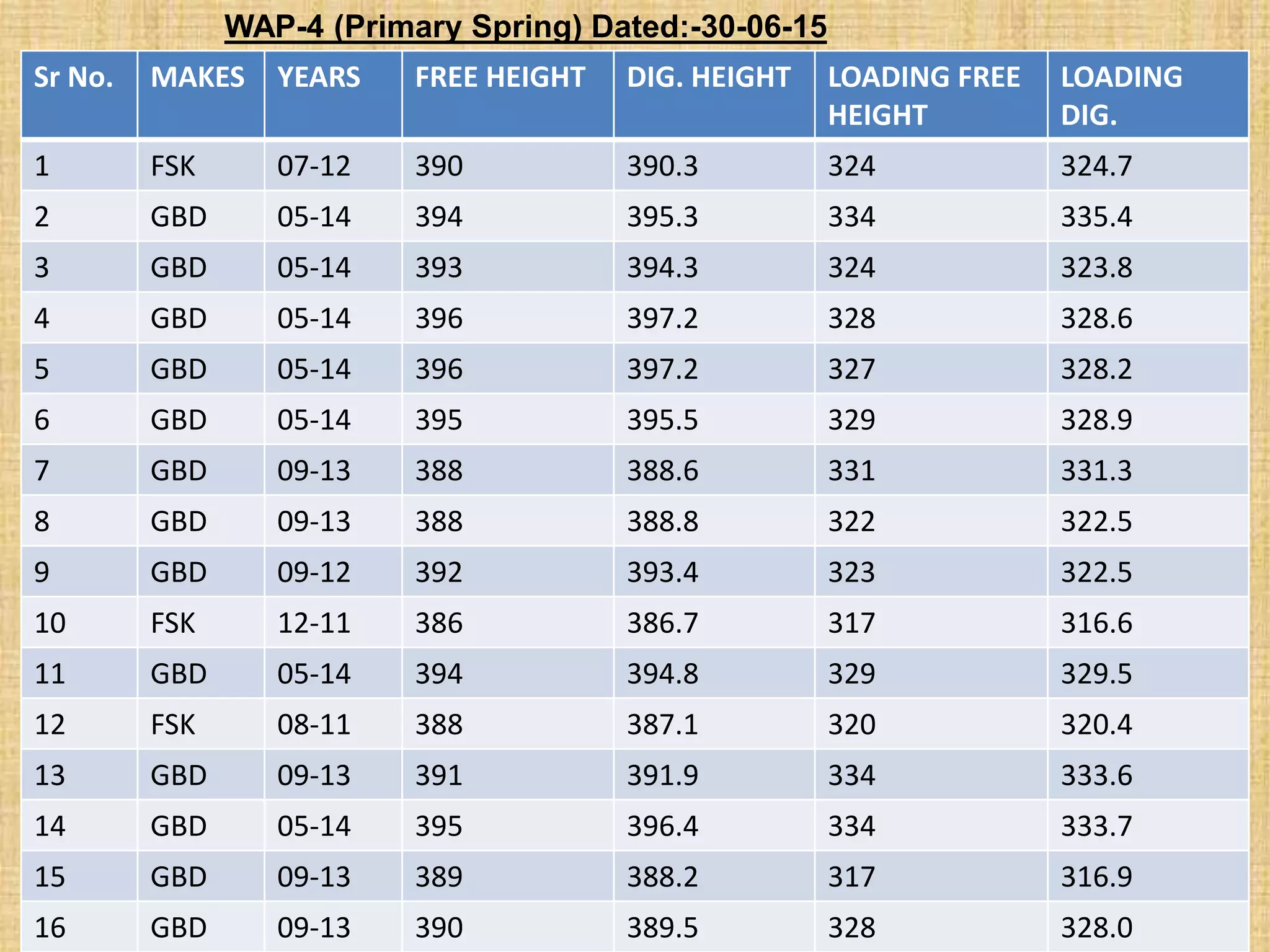
Spring failures in trains can occur due to material defects, metallurgical issues, or improper assembly. Common causes include lack of parallelism or squareness in springs, which affects how axial force is transferred. Biting, where coils contact each other, can cause breakage. Proper inspection and maintenance of parameters like stiffness, deflection, and end tapers is needed. Standards for suspension spring properties in WAP-4 and WAG-7 trains are provided. Testing data on springs removed from trains confirms dimensions and loads. Past failure rates of primary and secondary springs are reported.