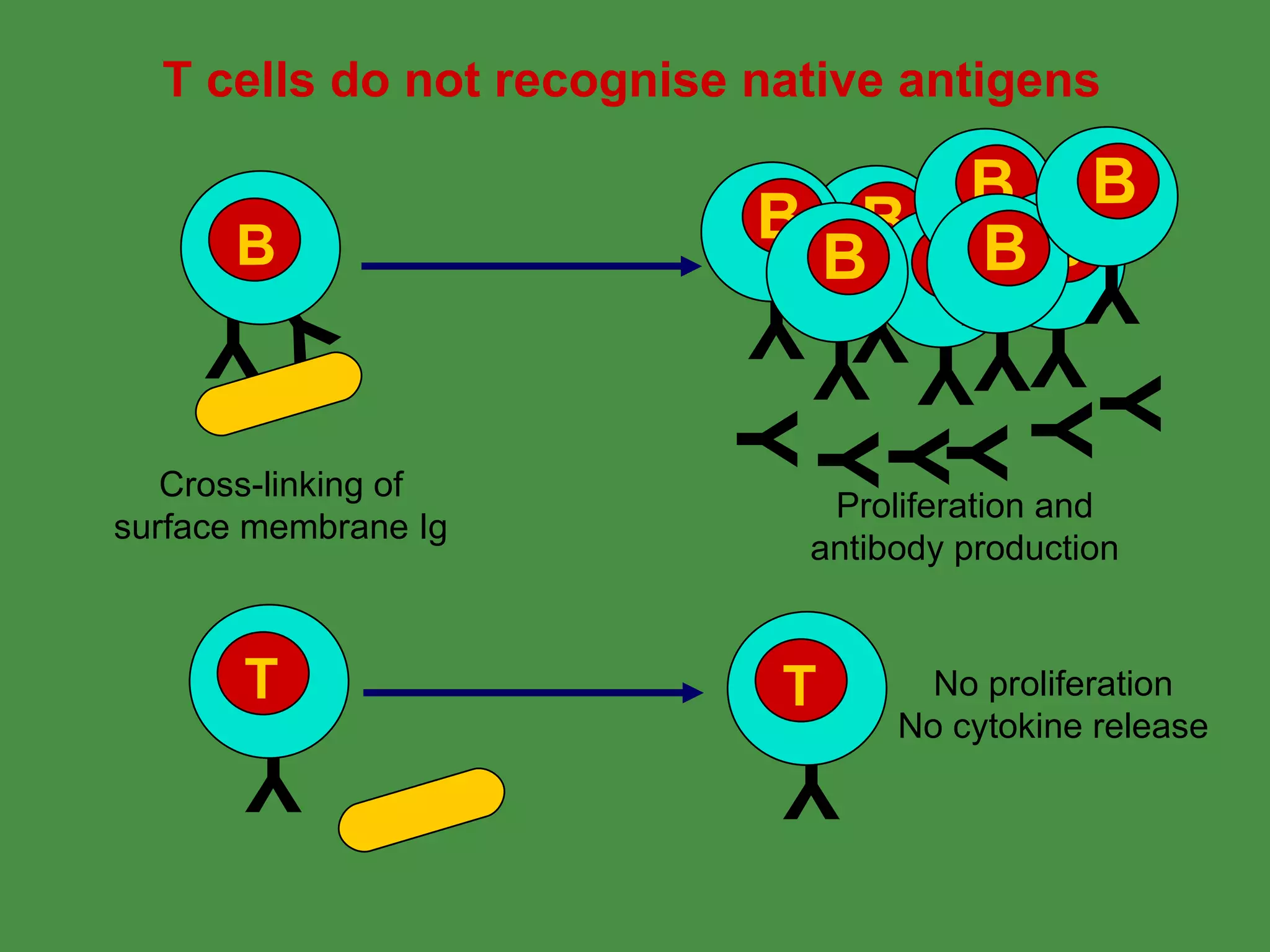
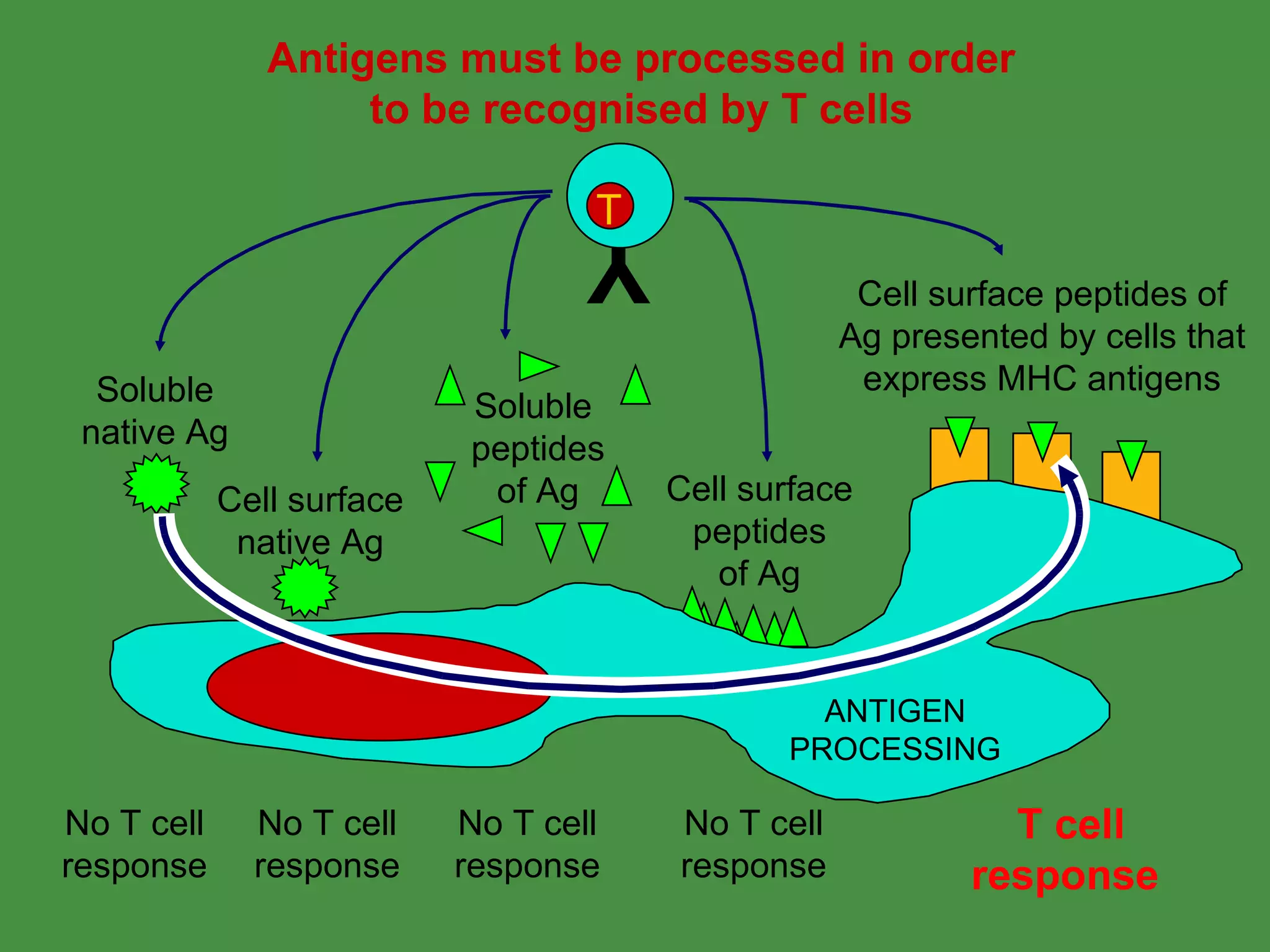
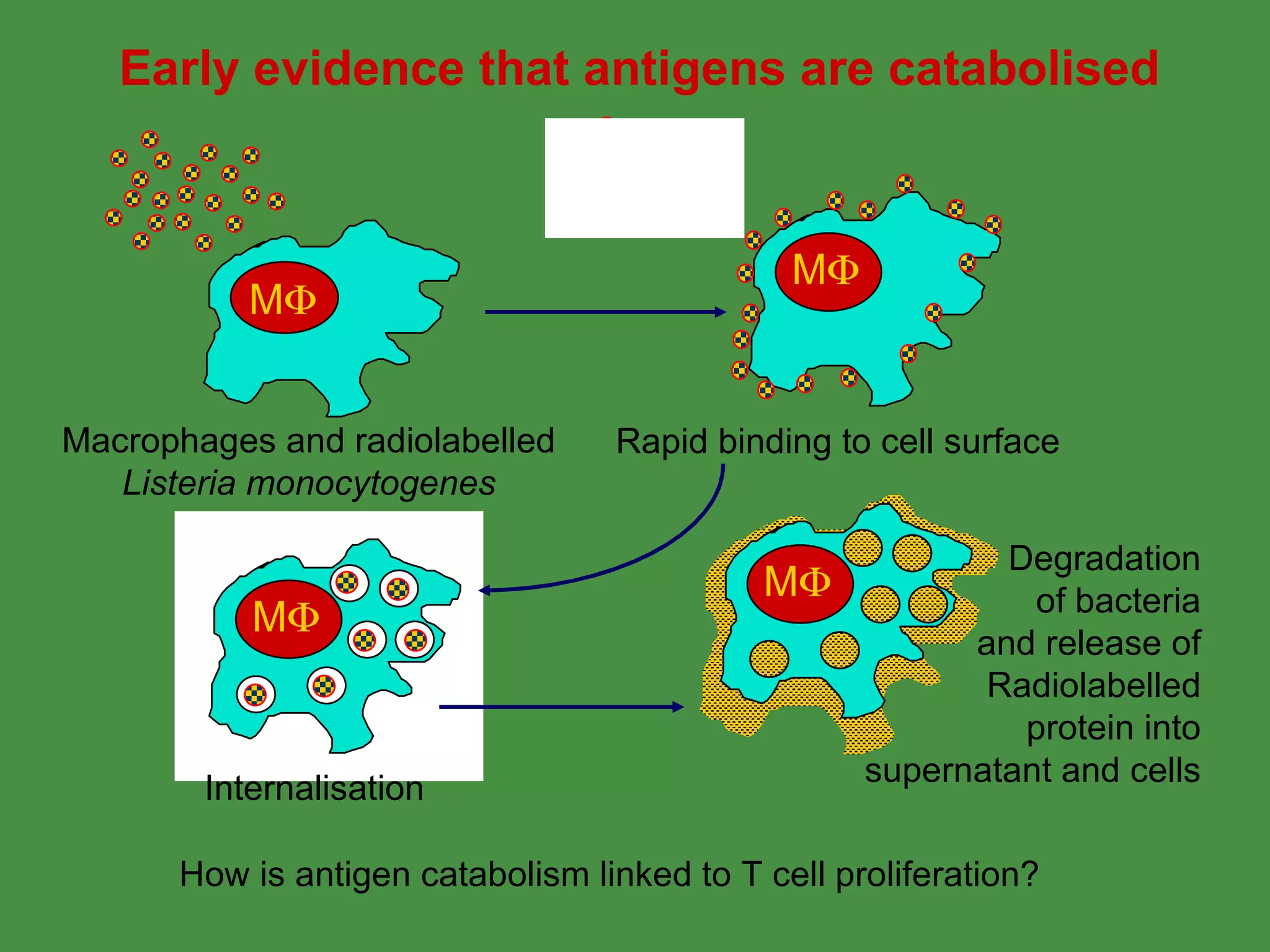
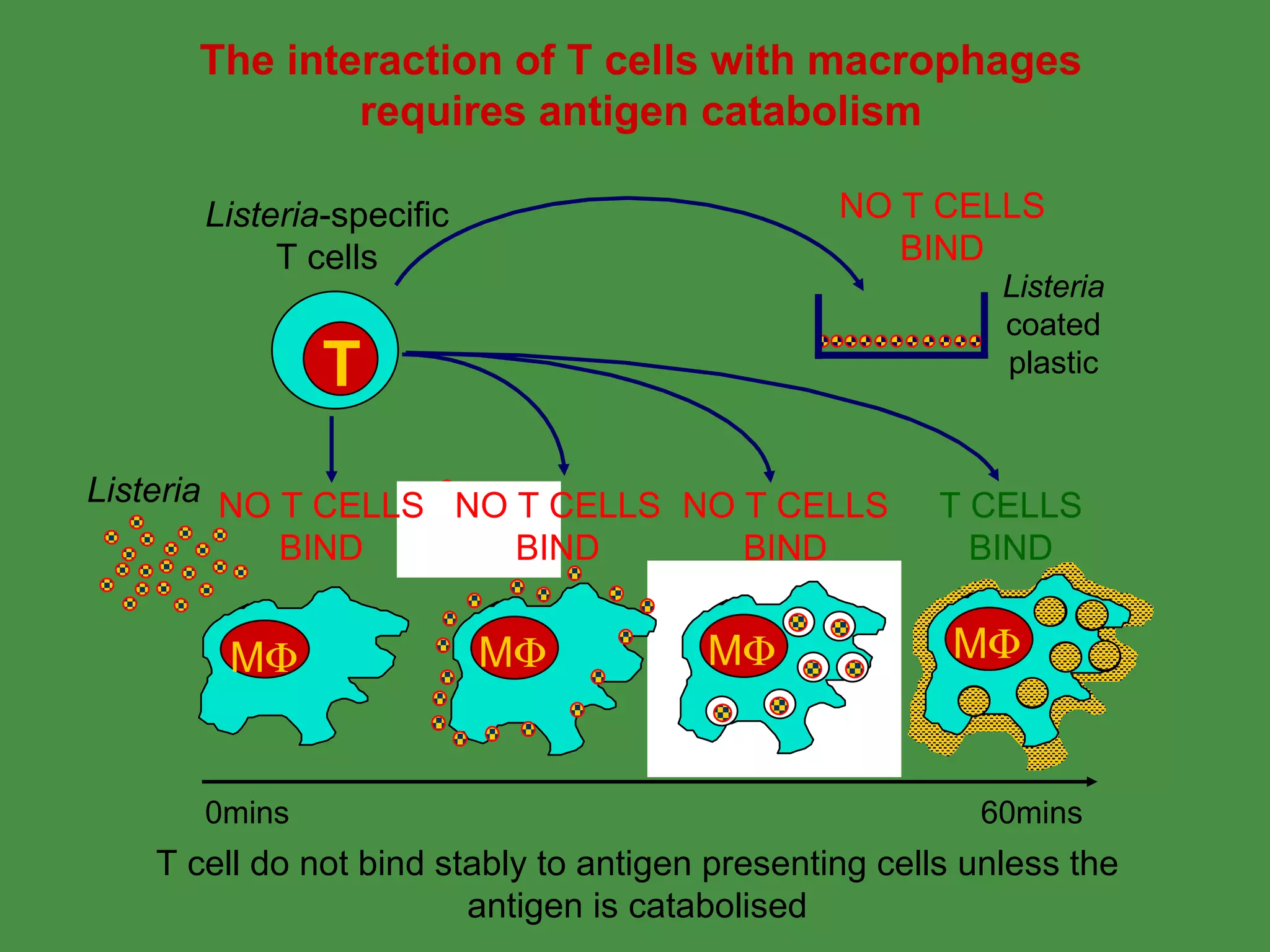
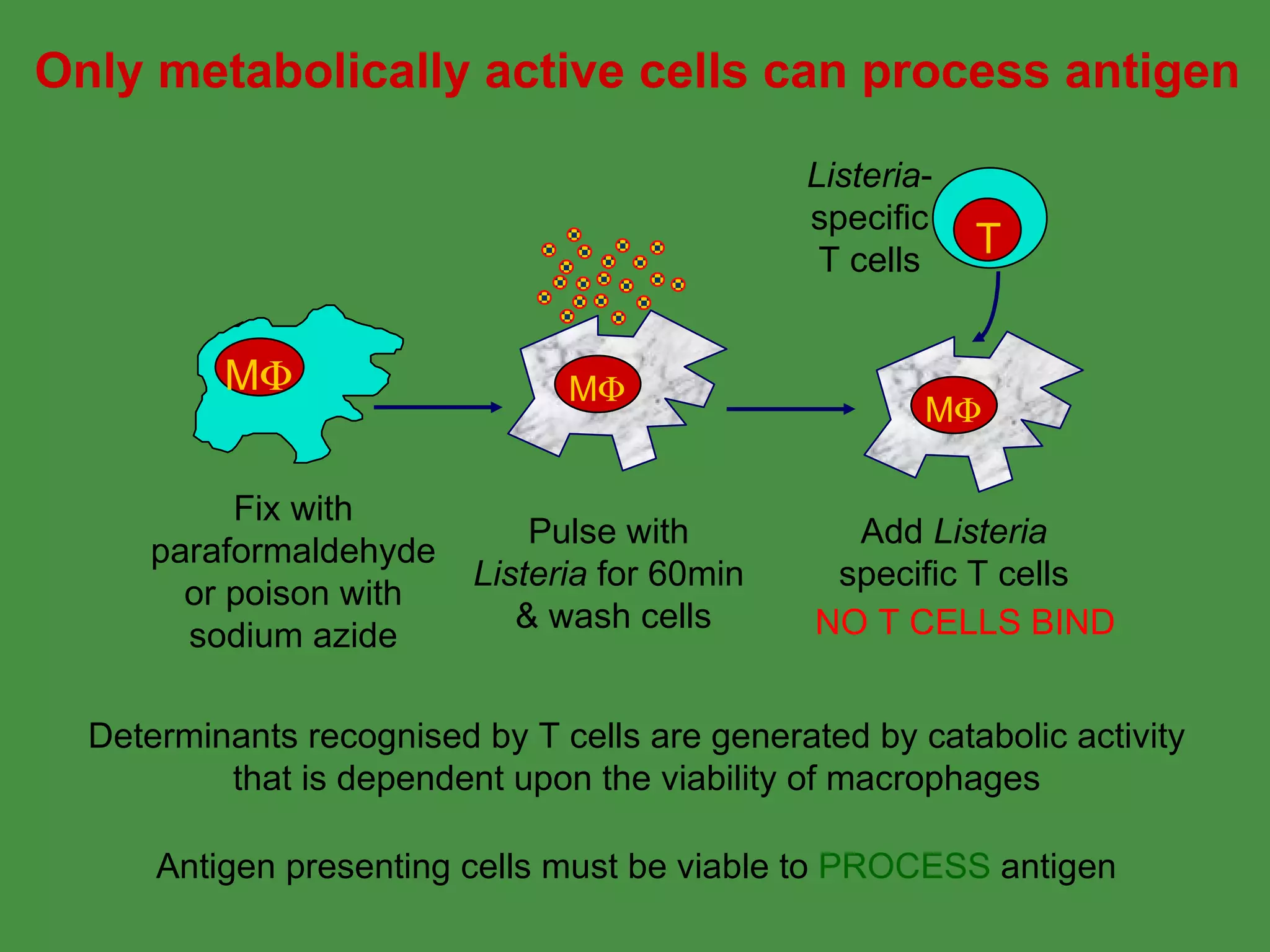
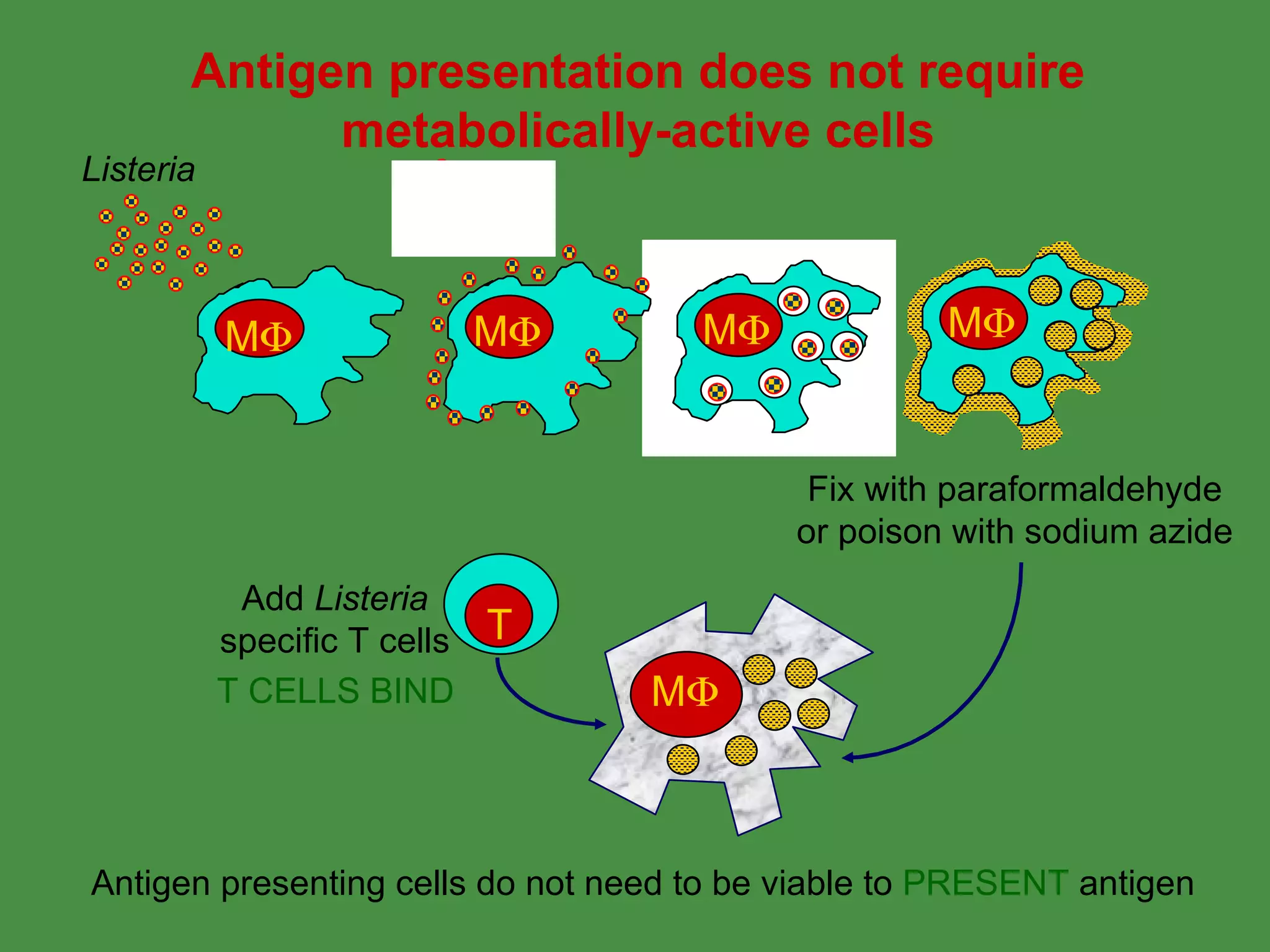
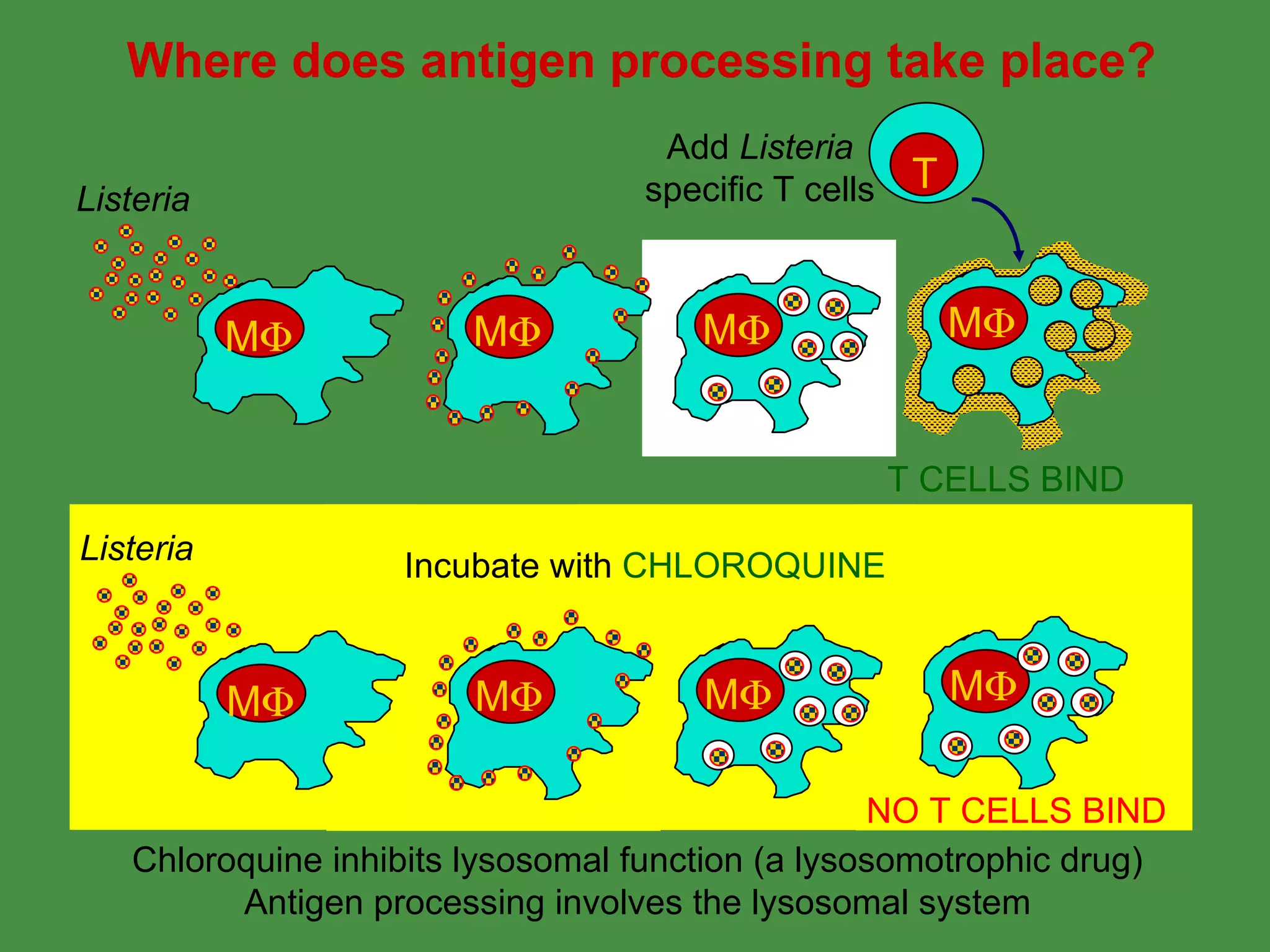
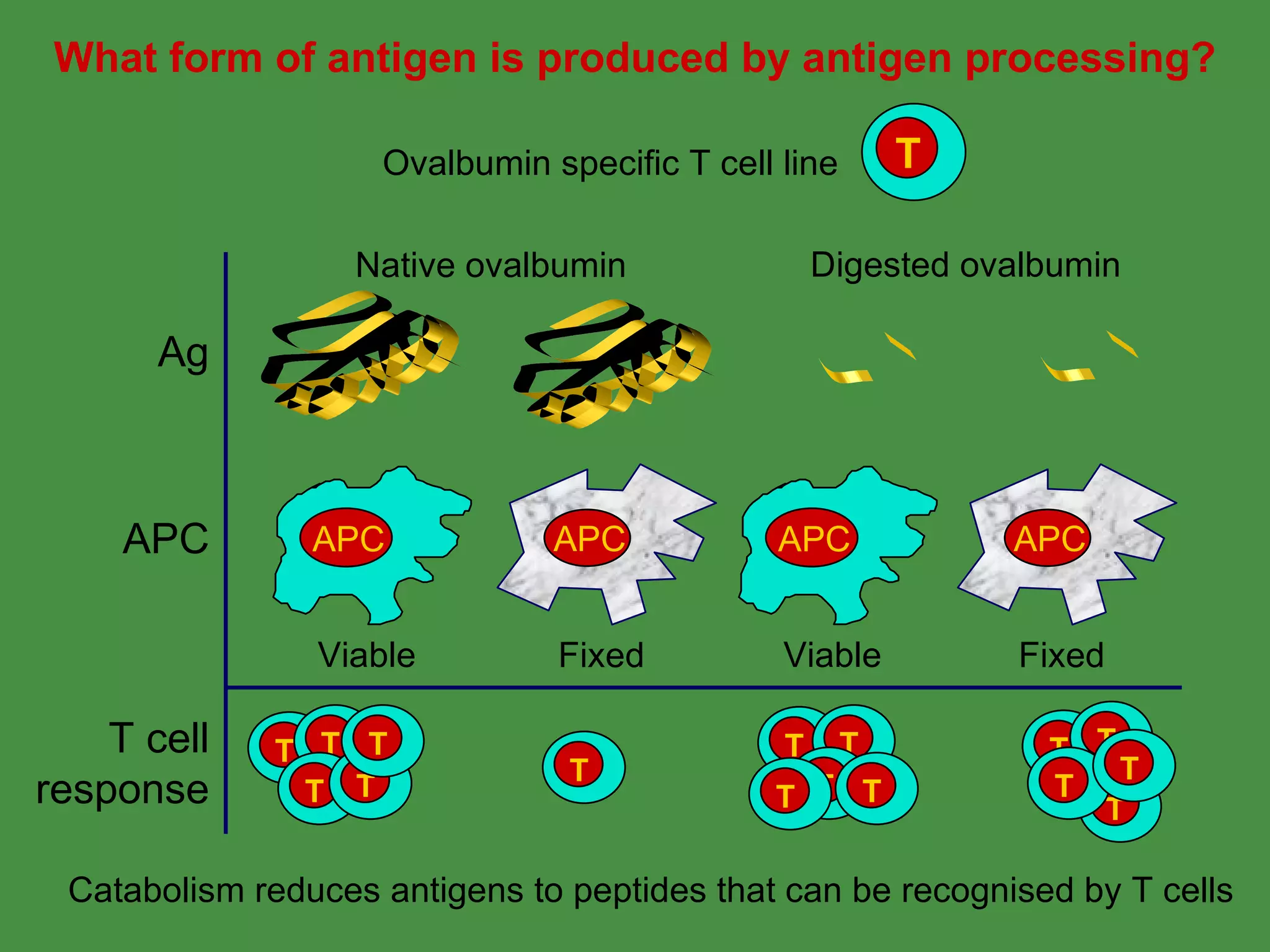
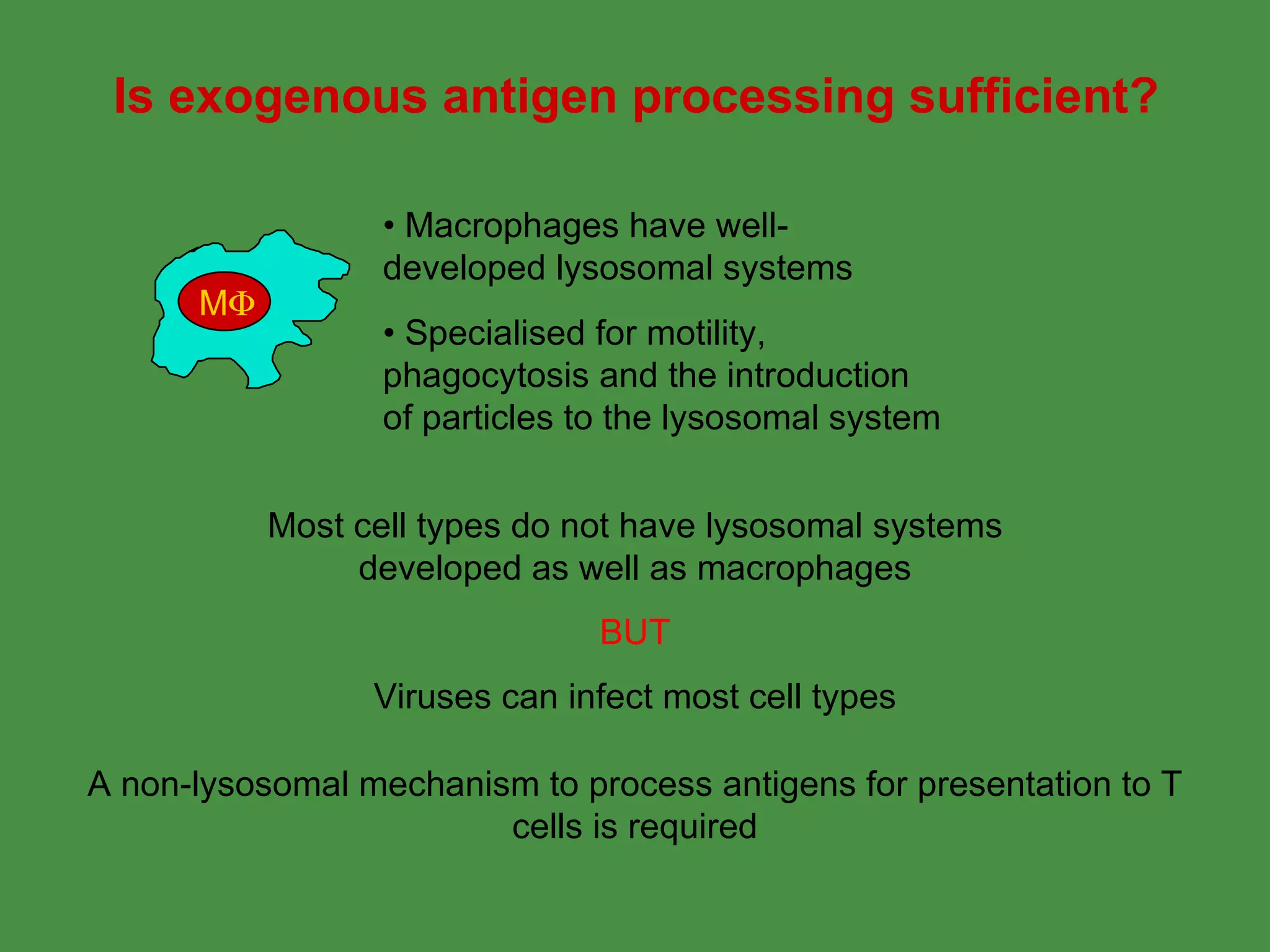
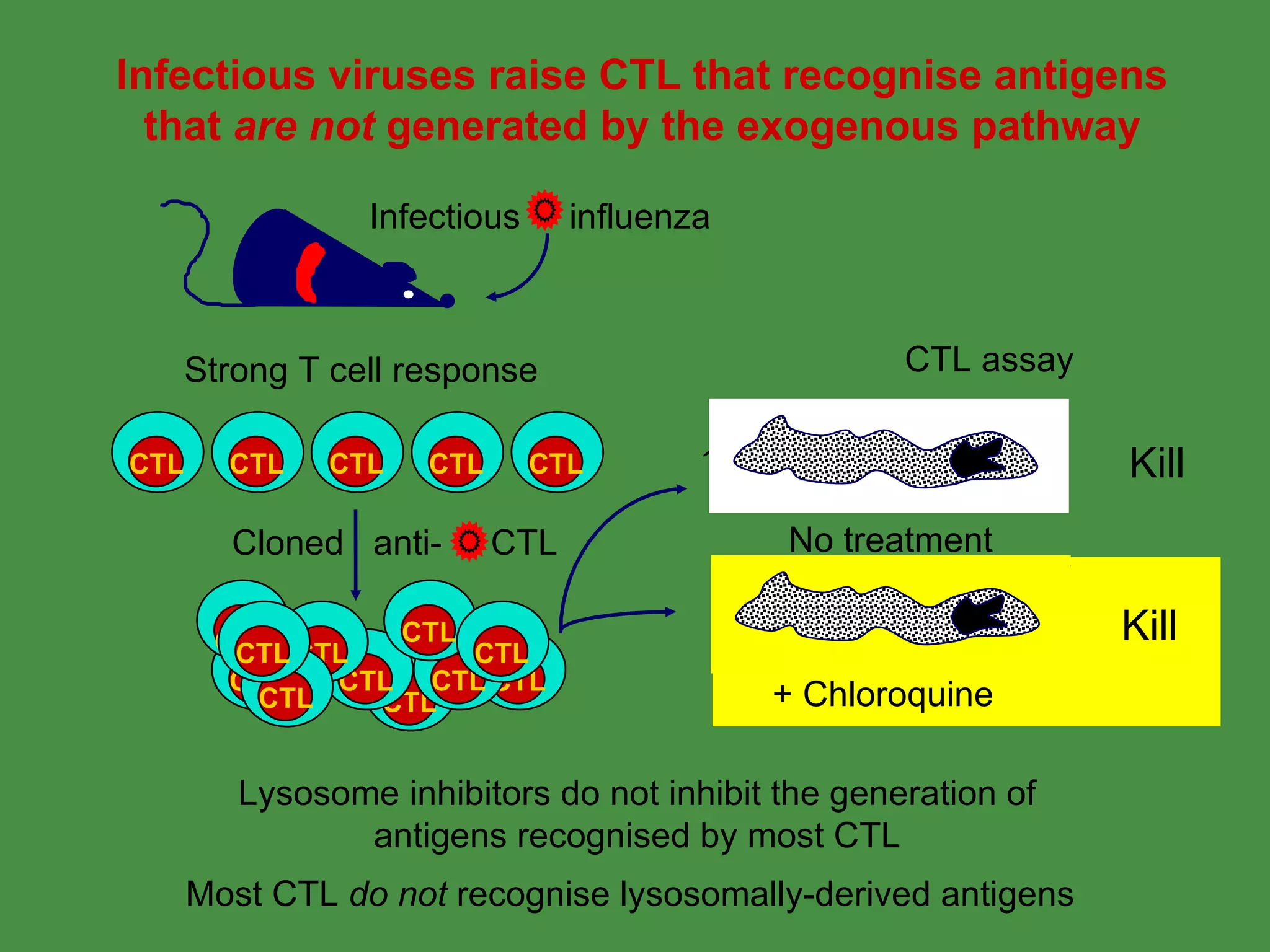
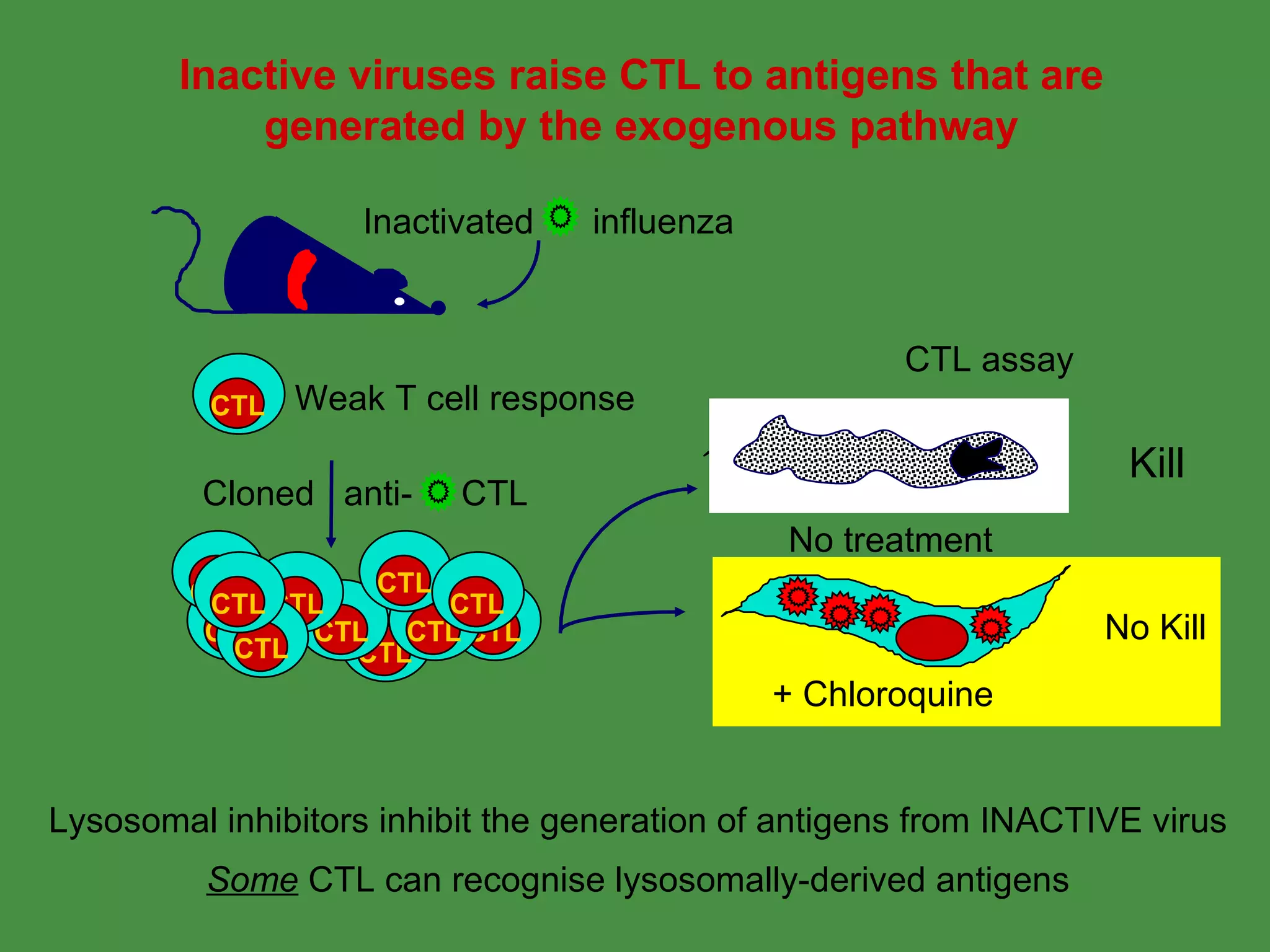
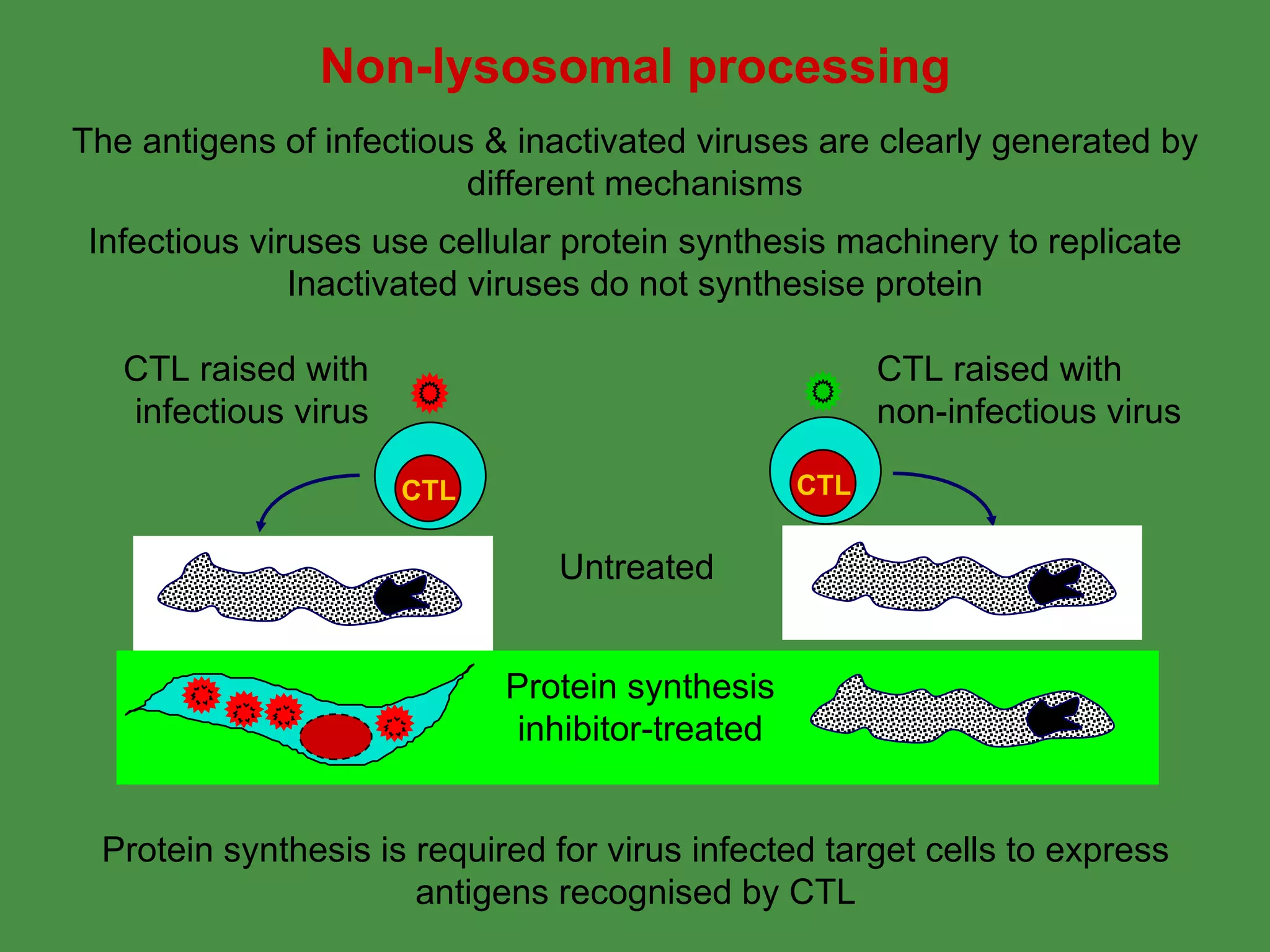
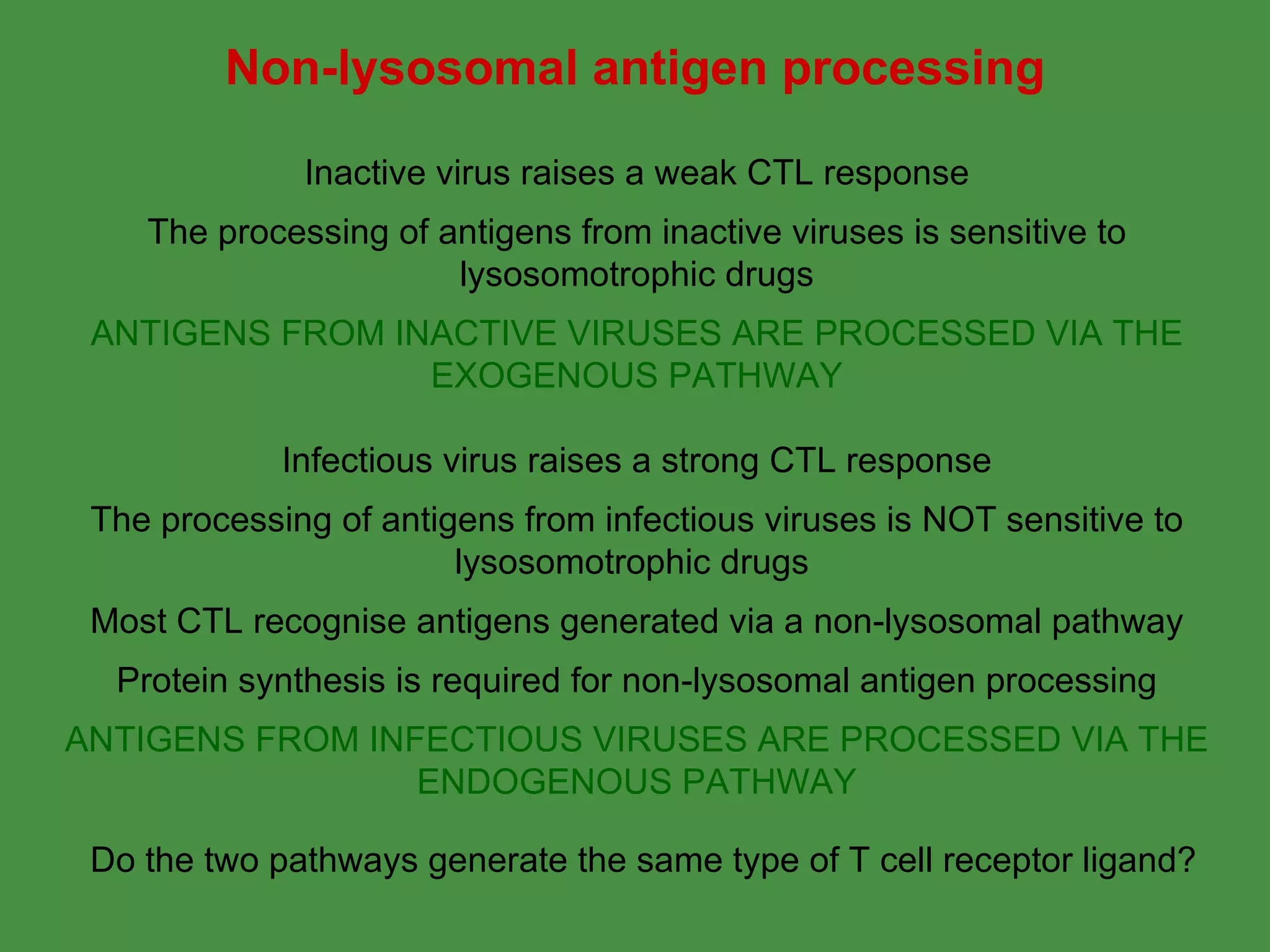
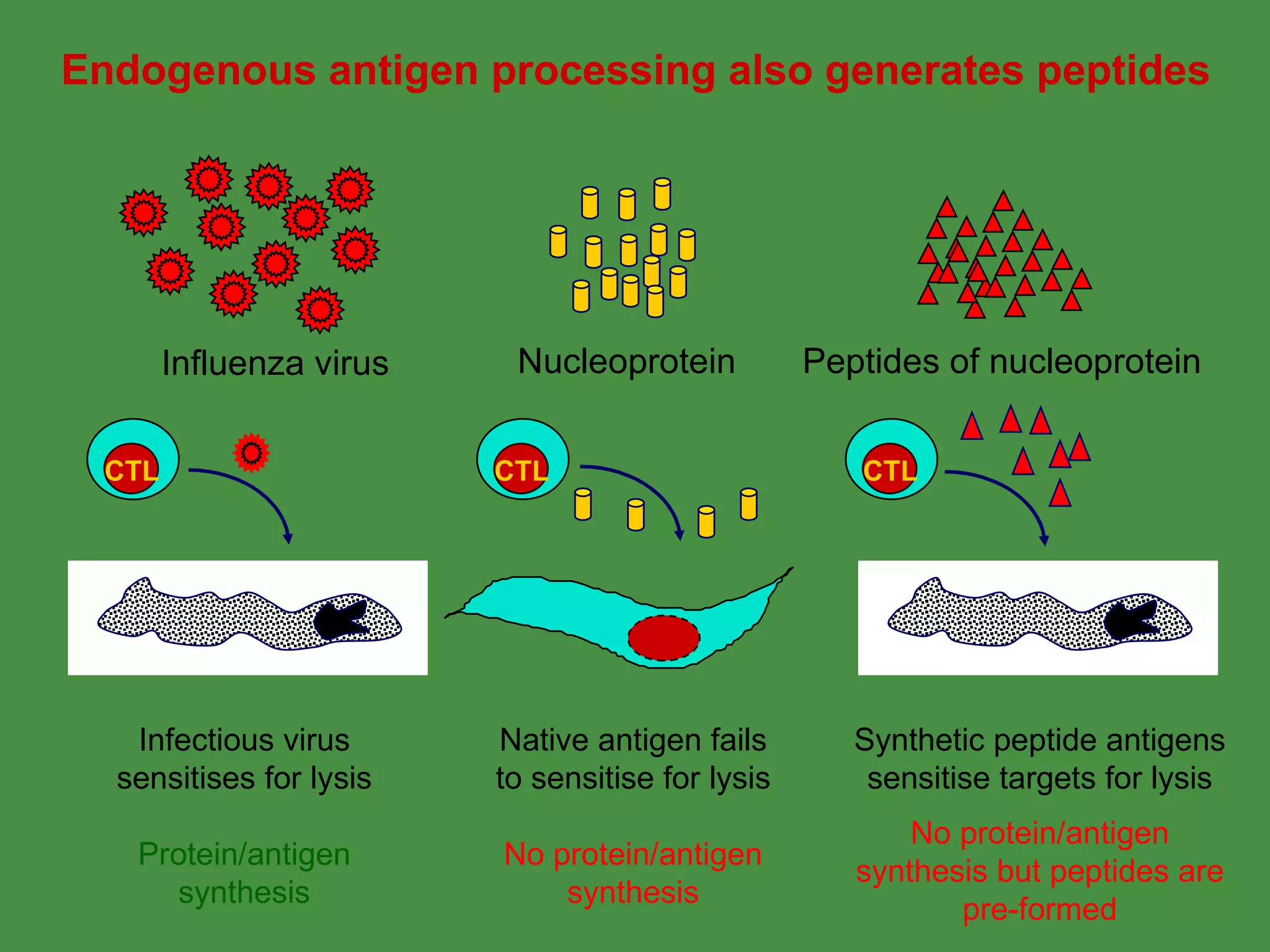
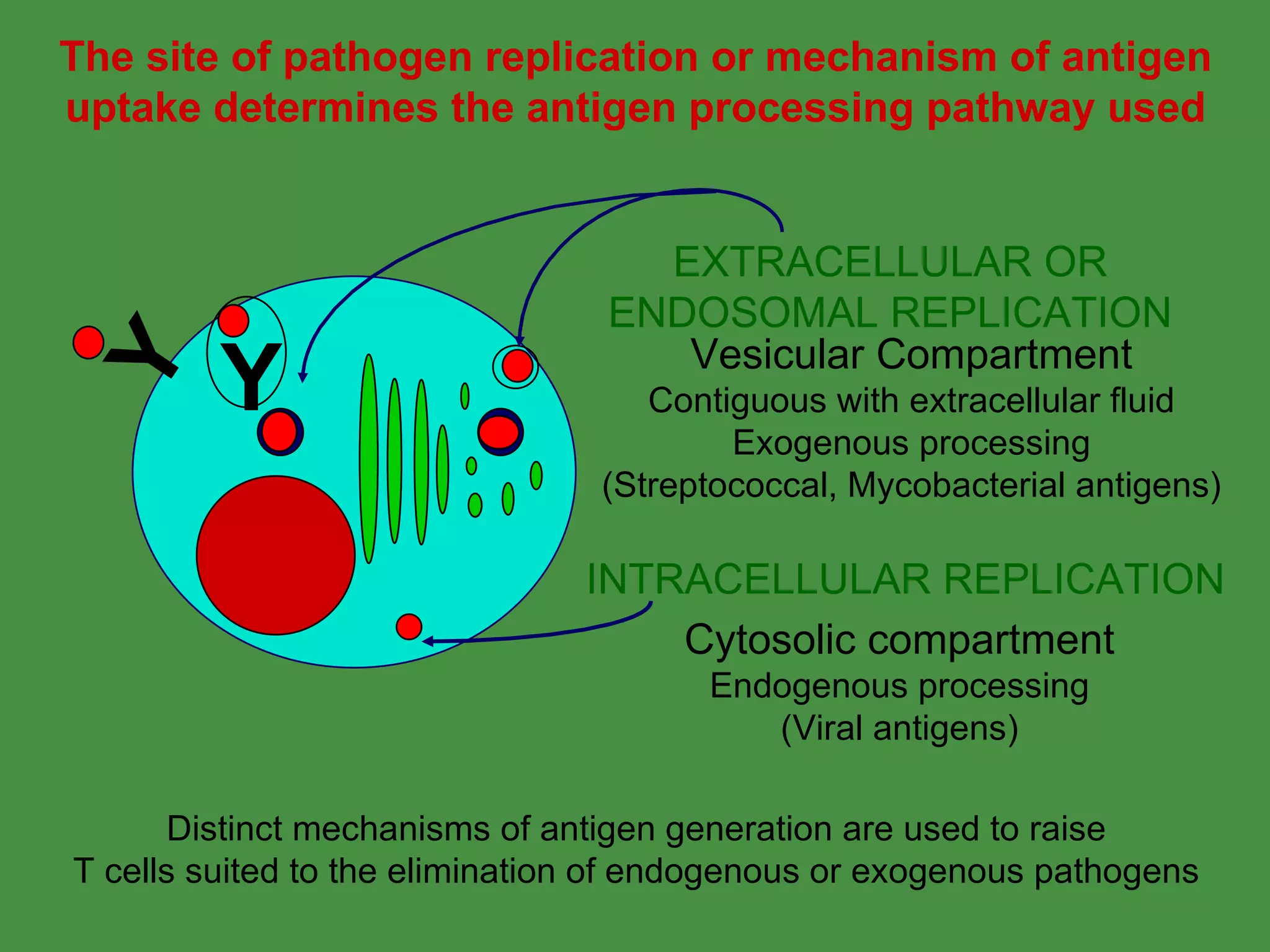
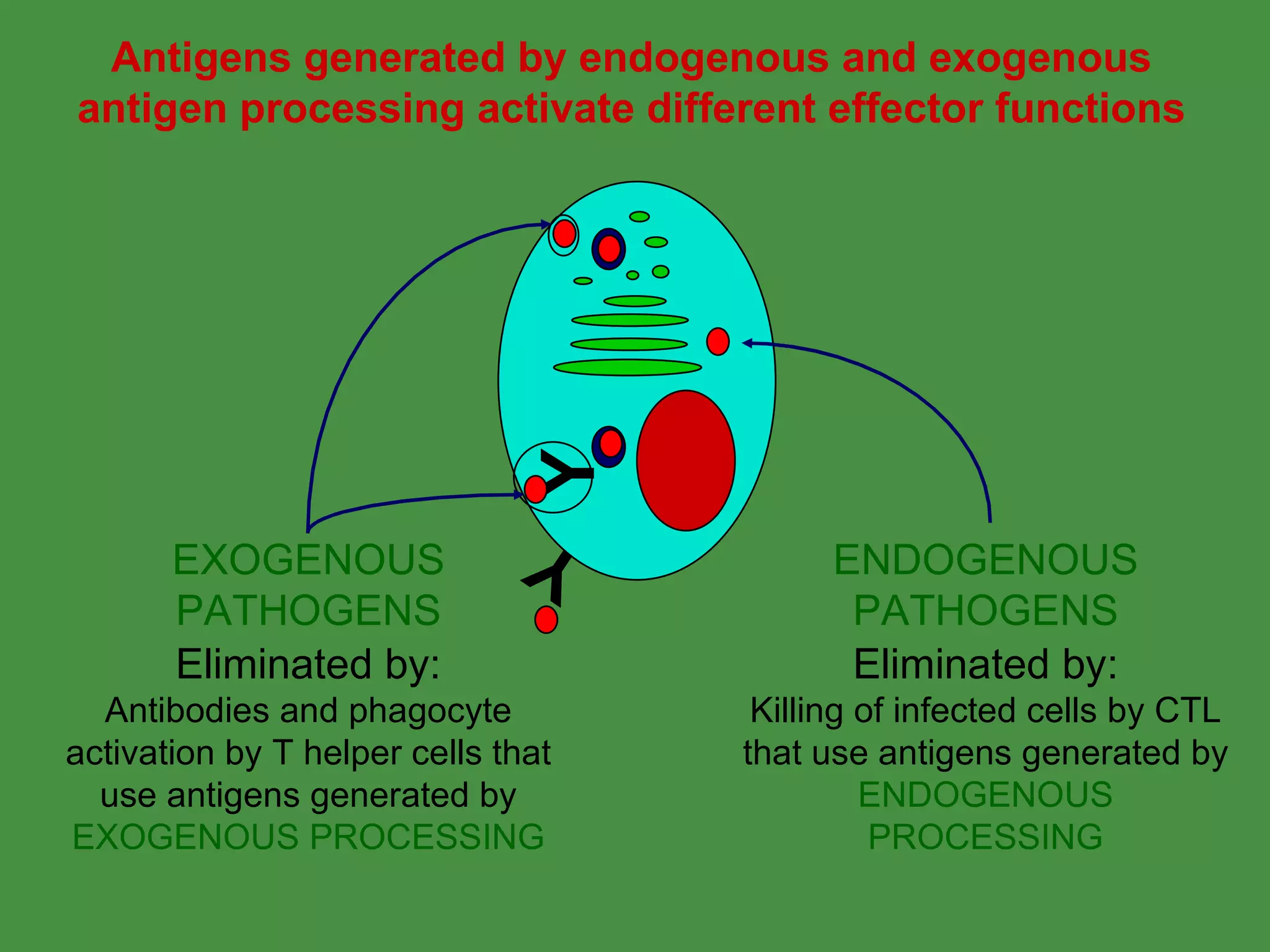
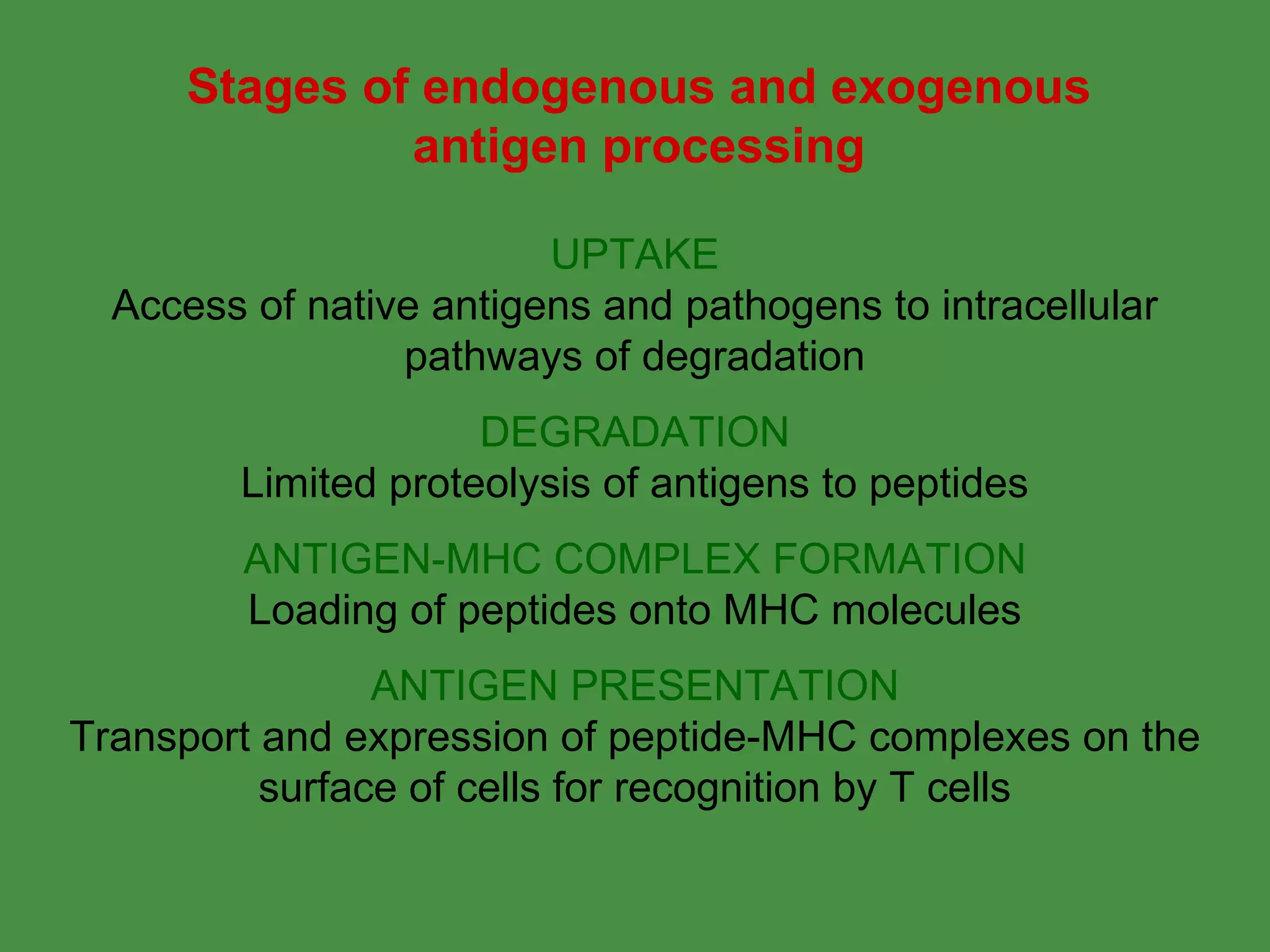
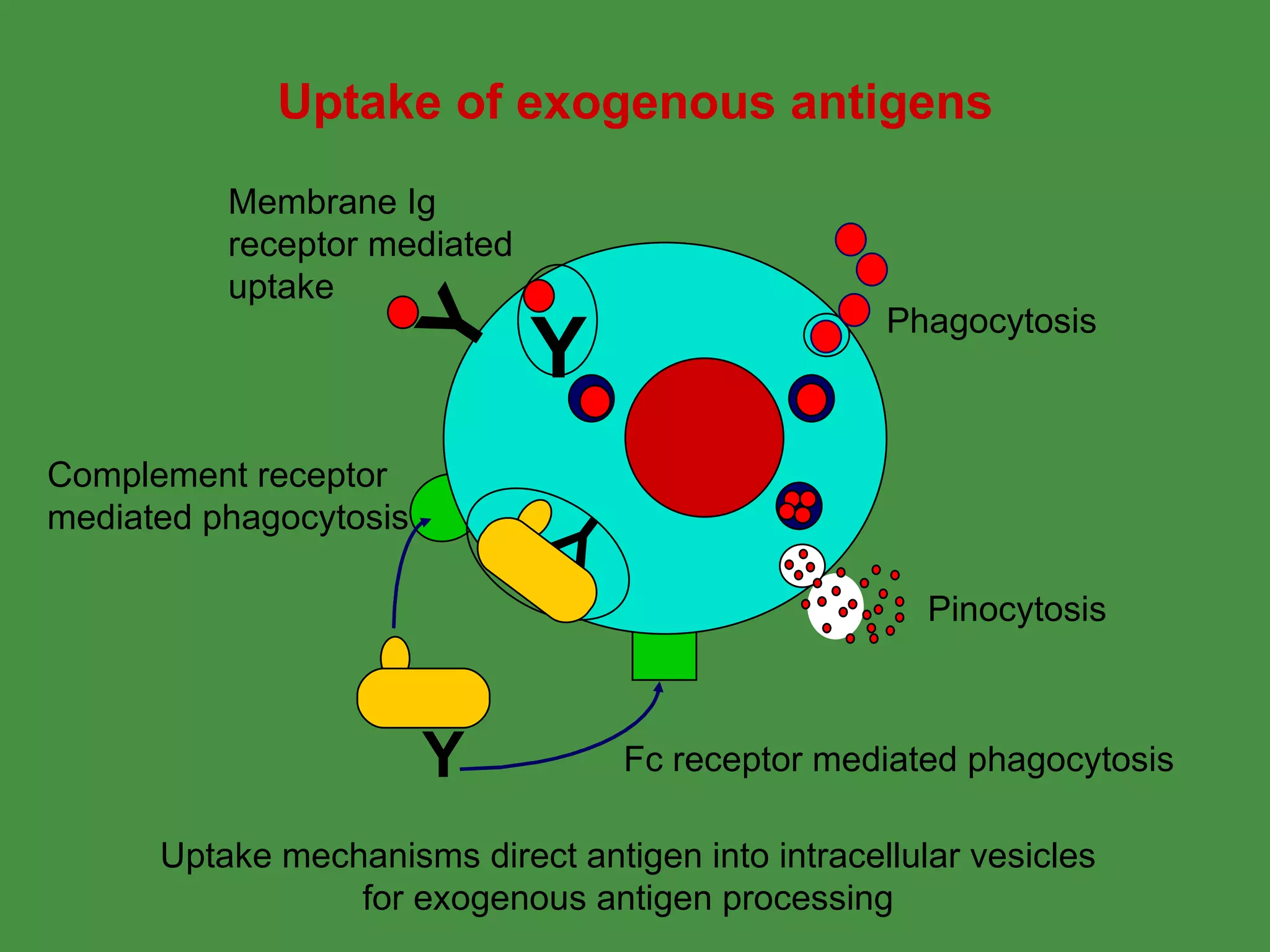
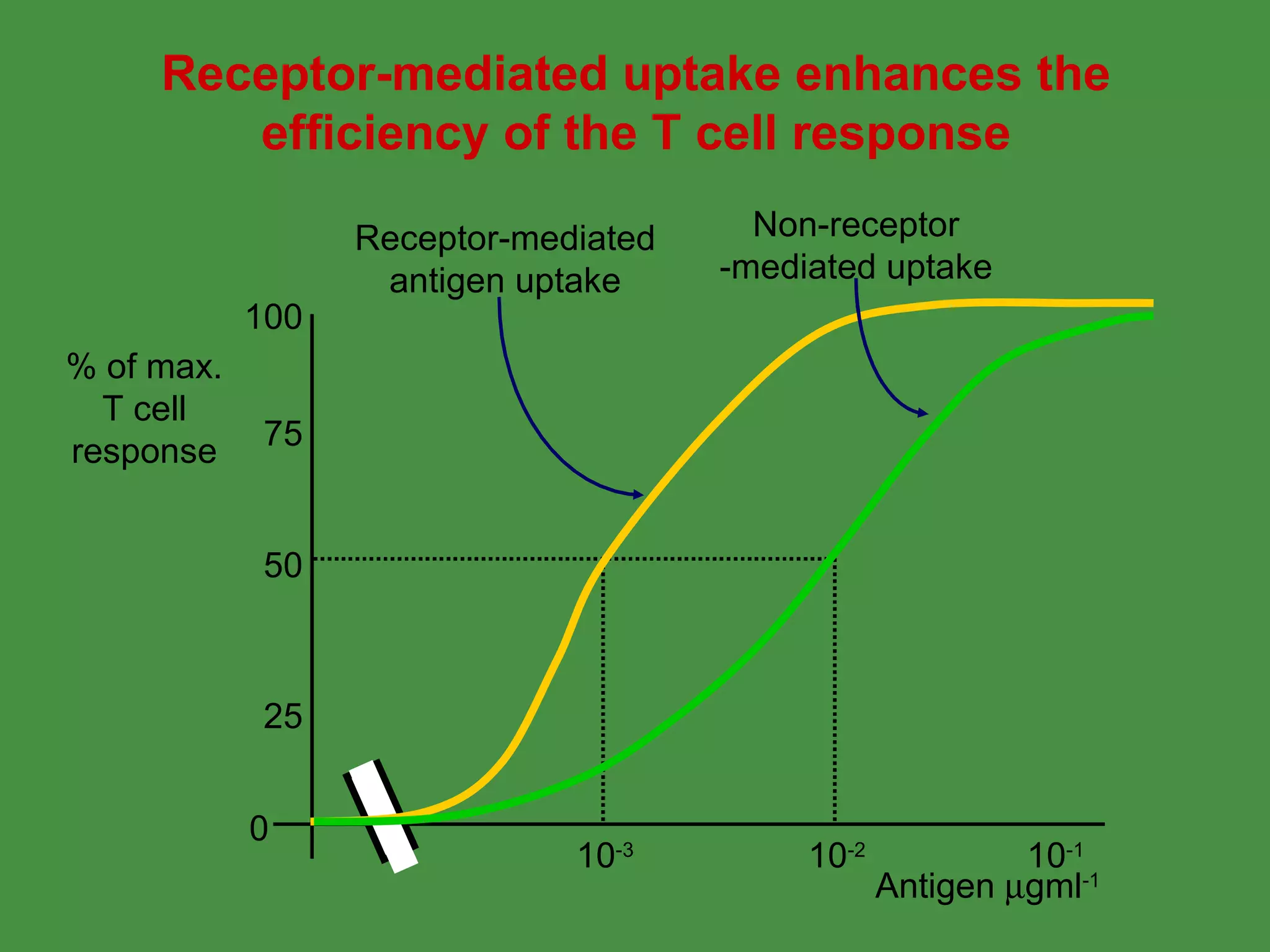
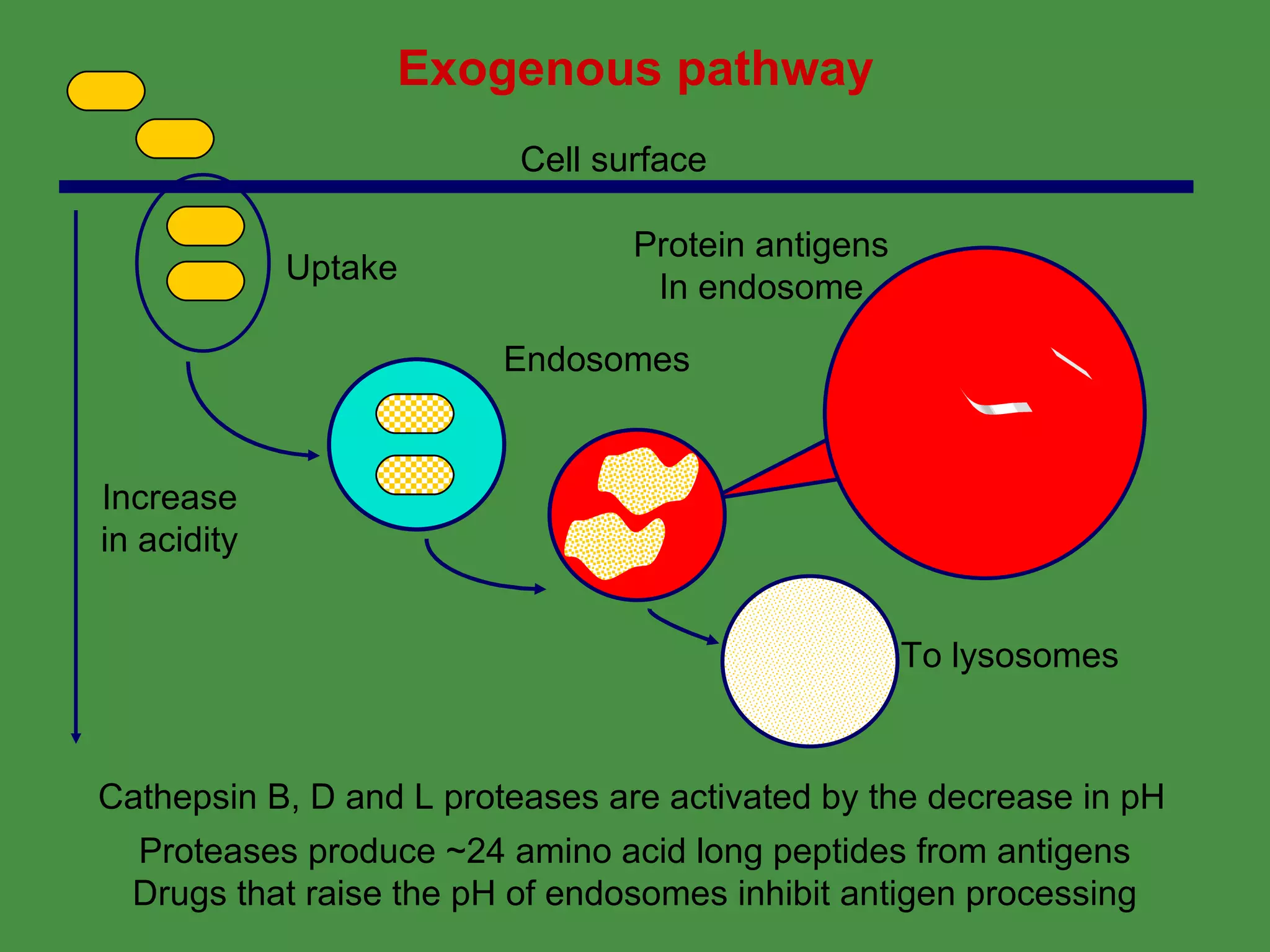
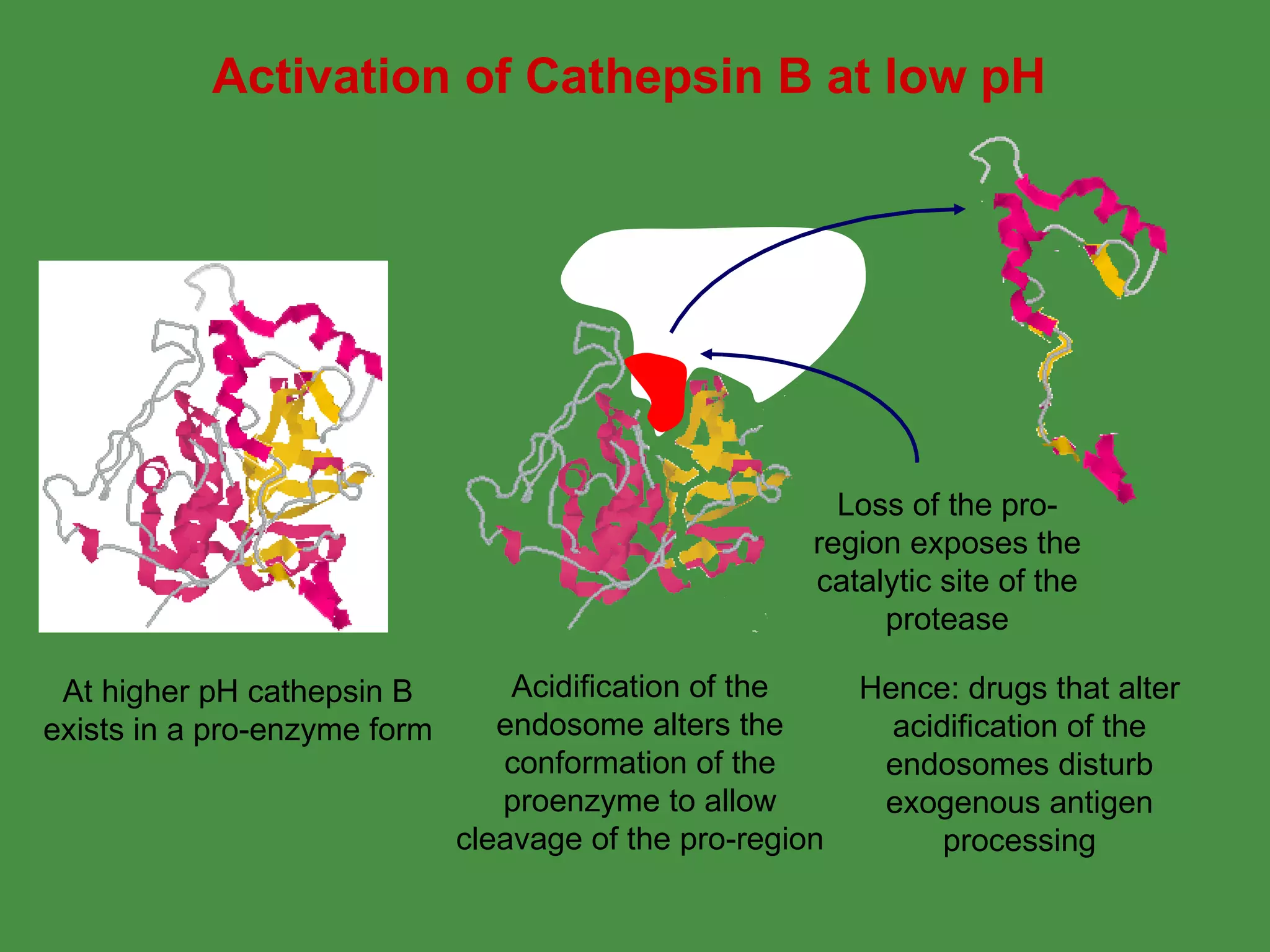
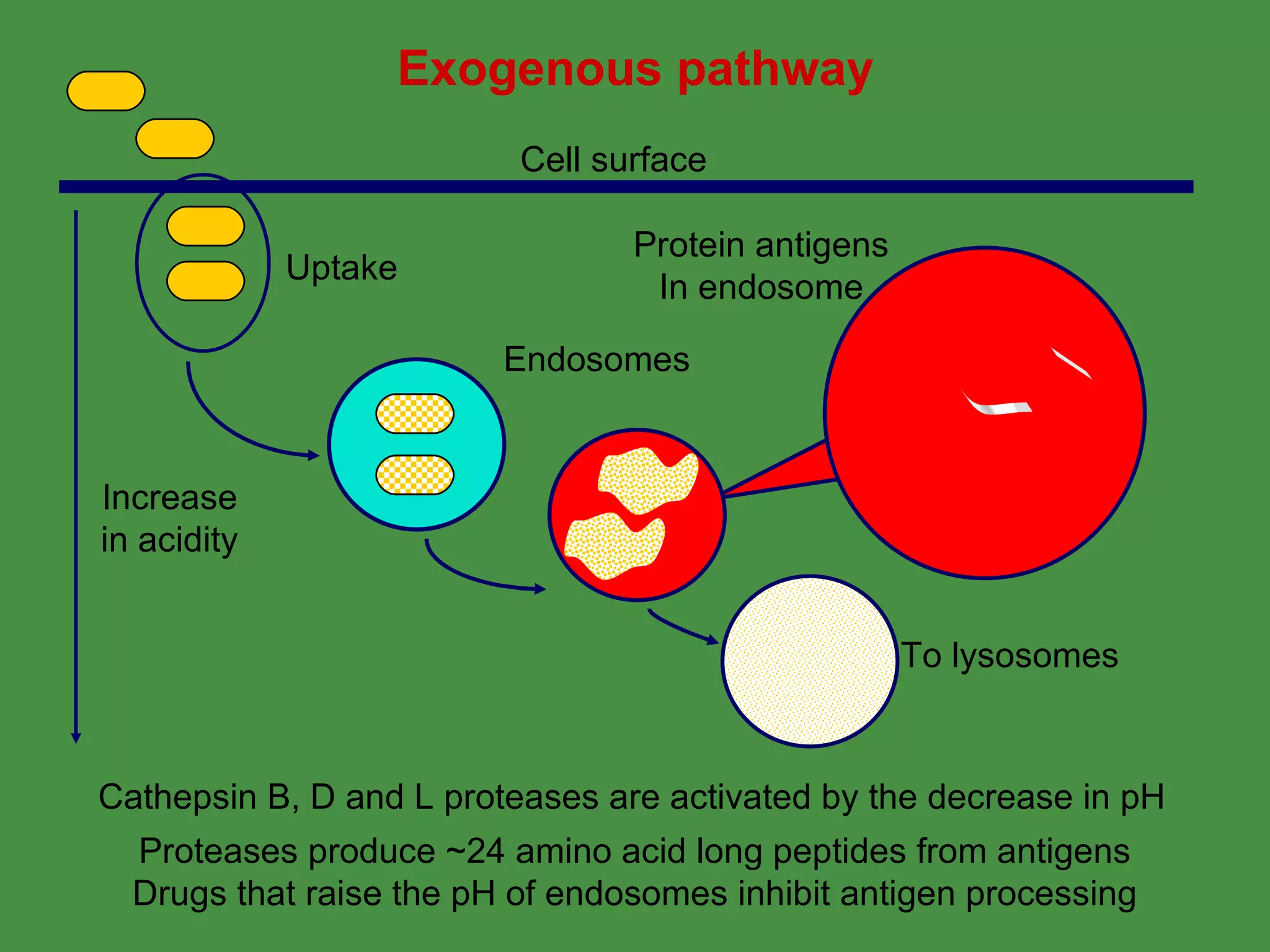
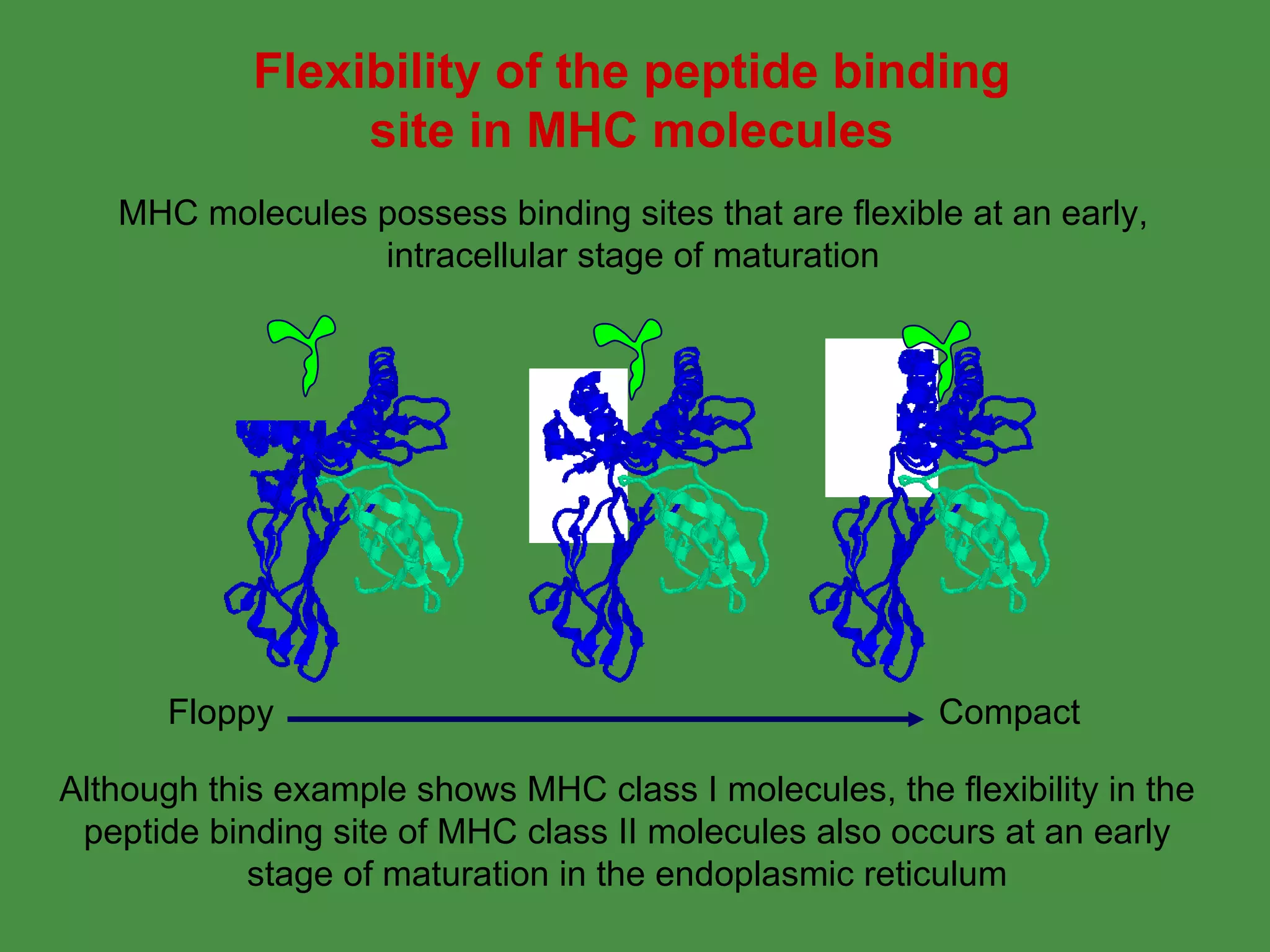
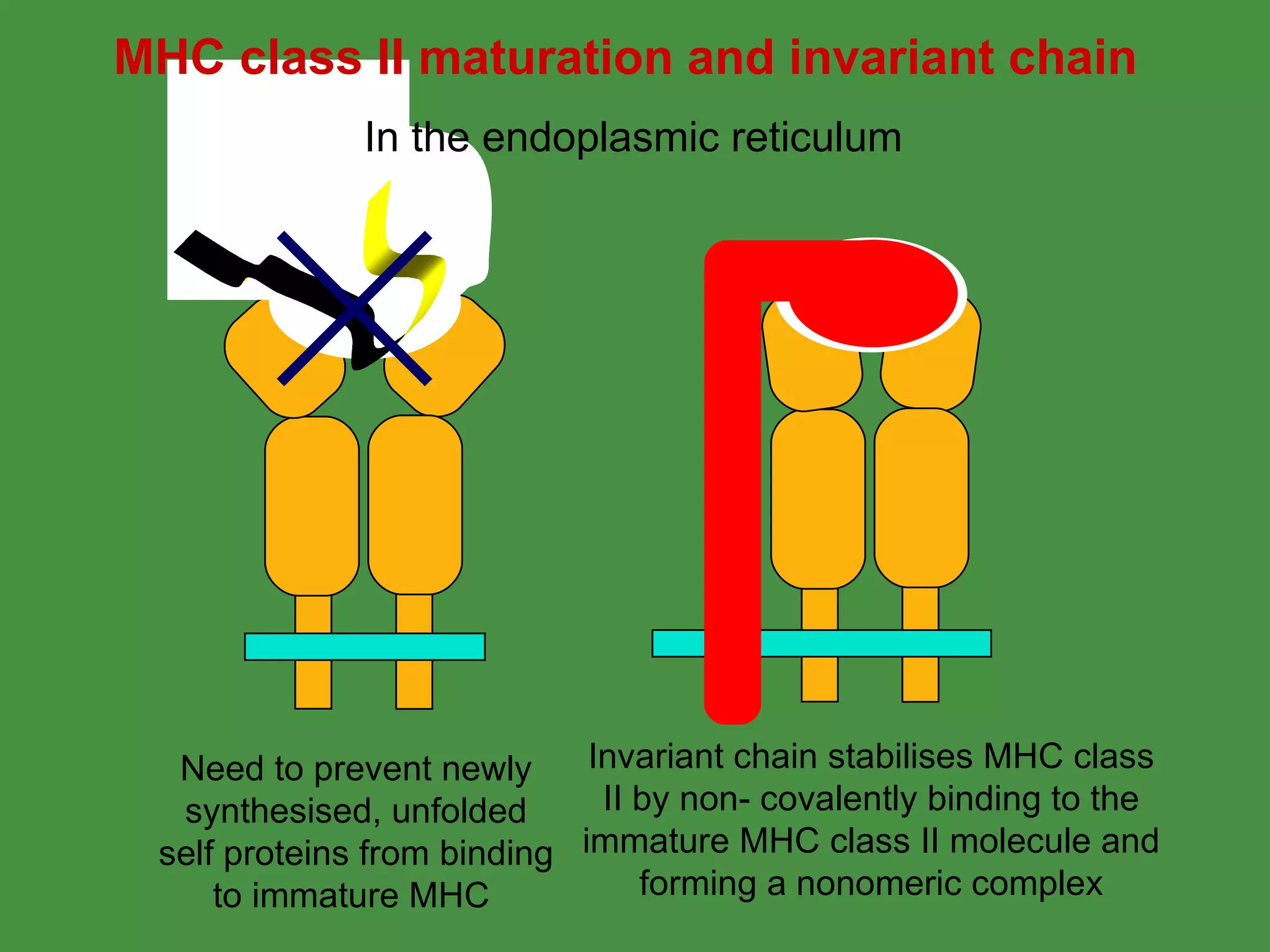
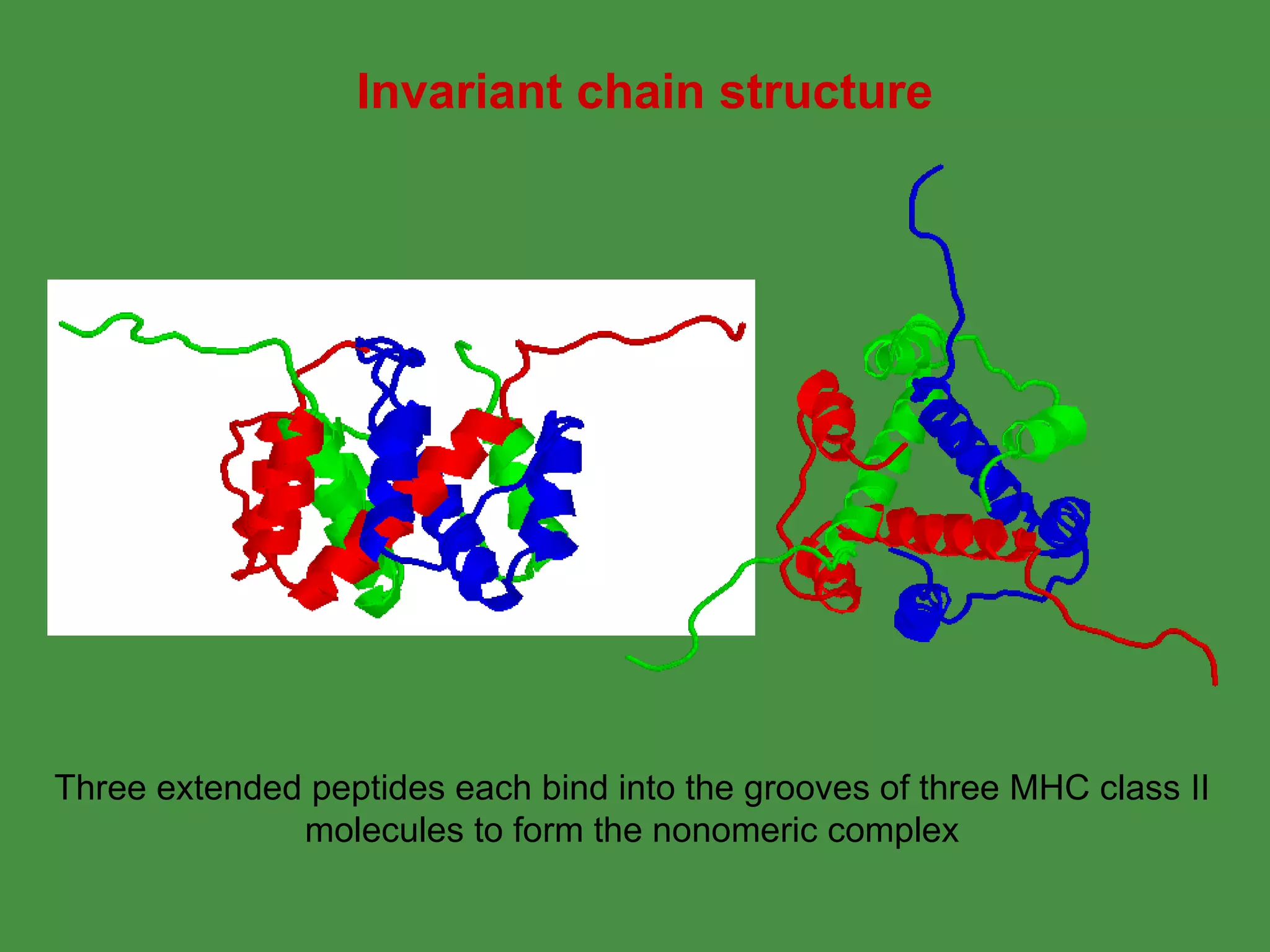
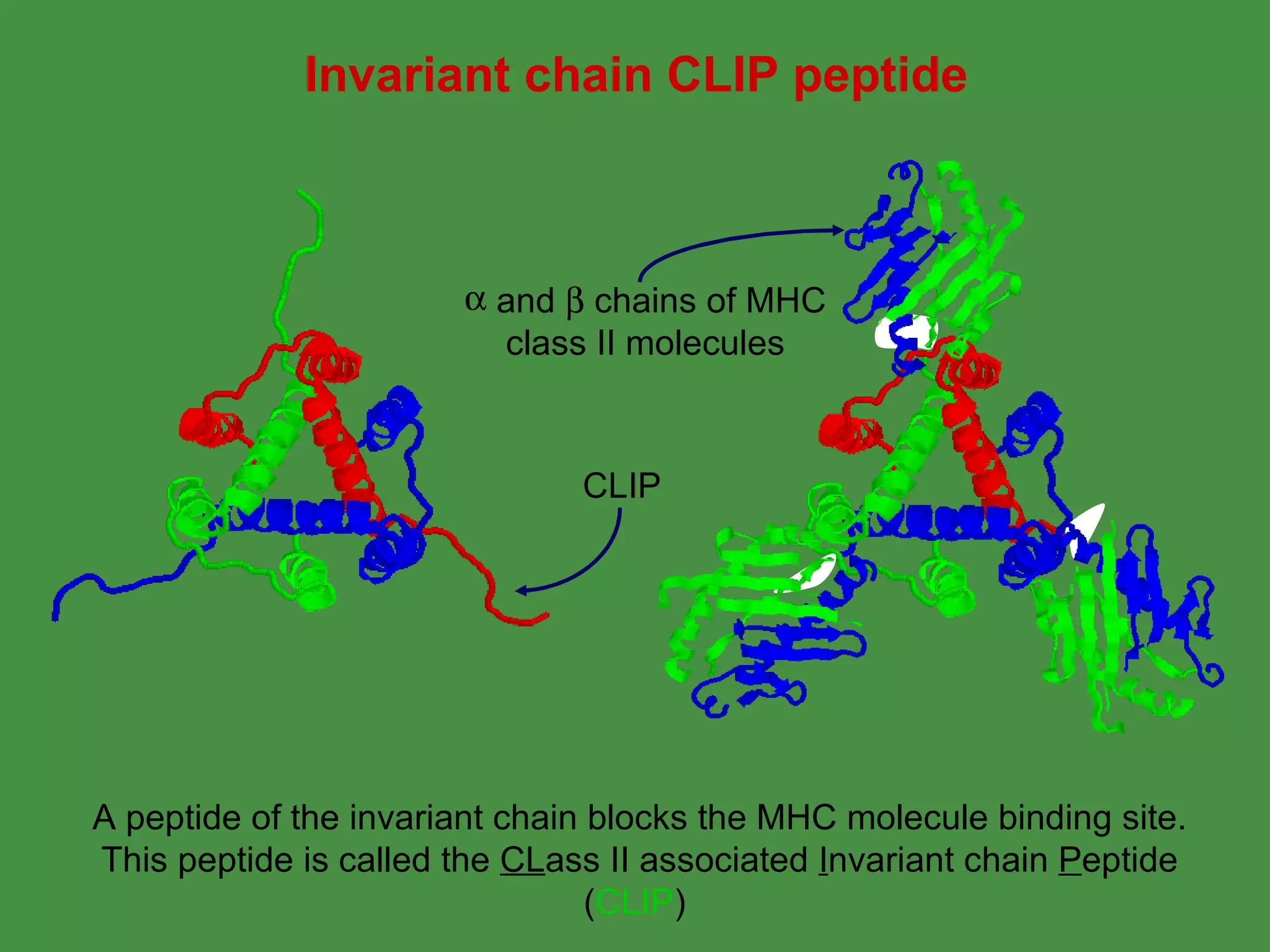
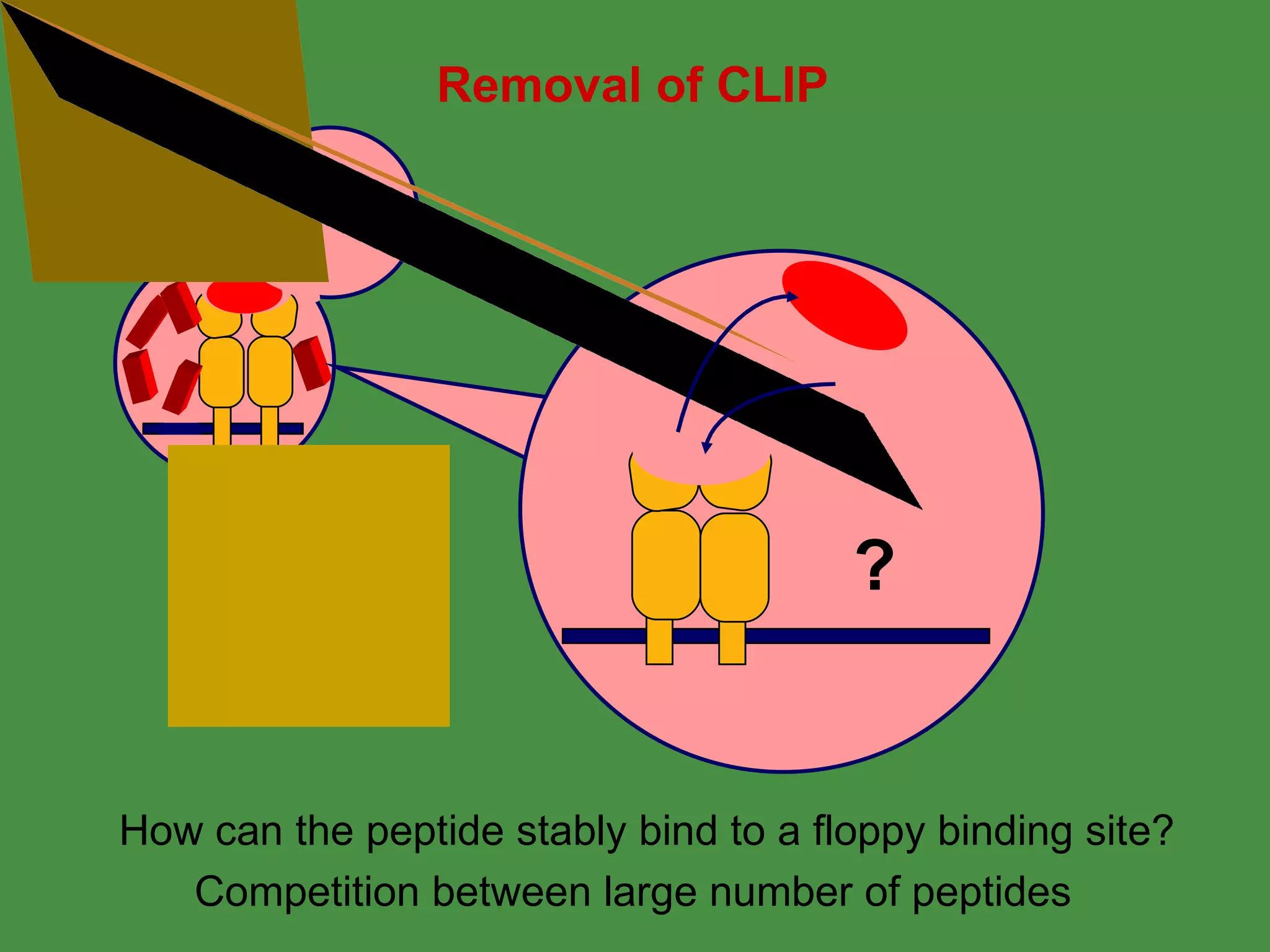
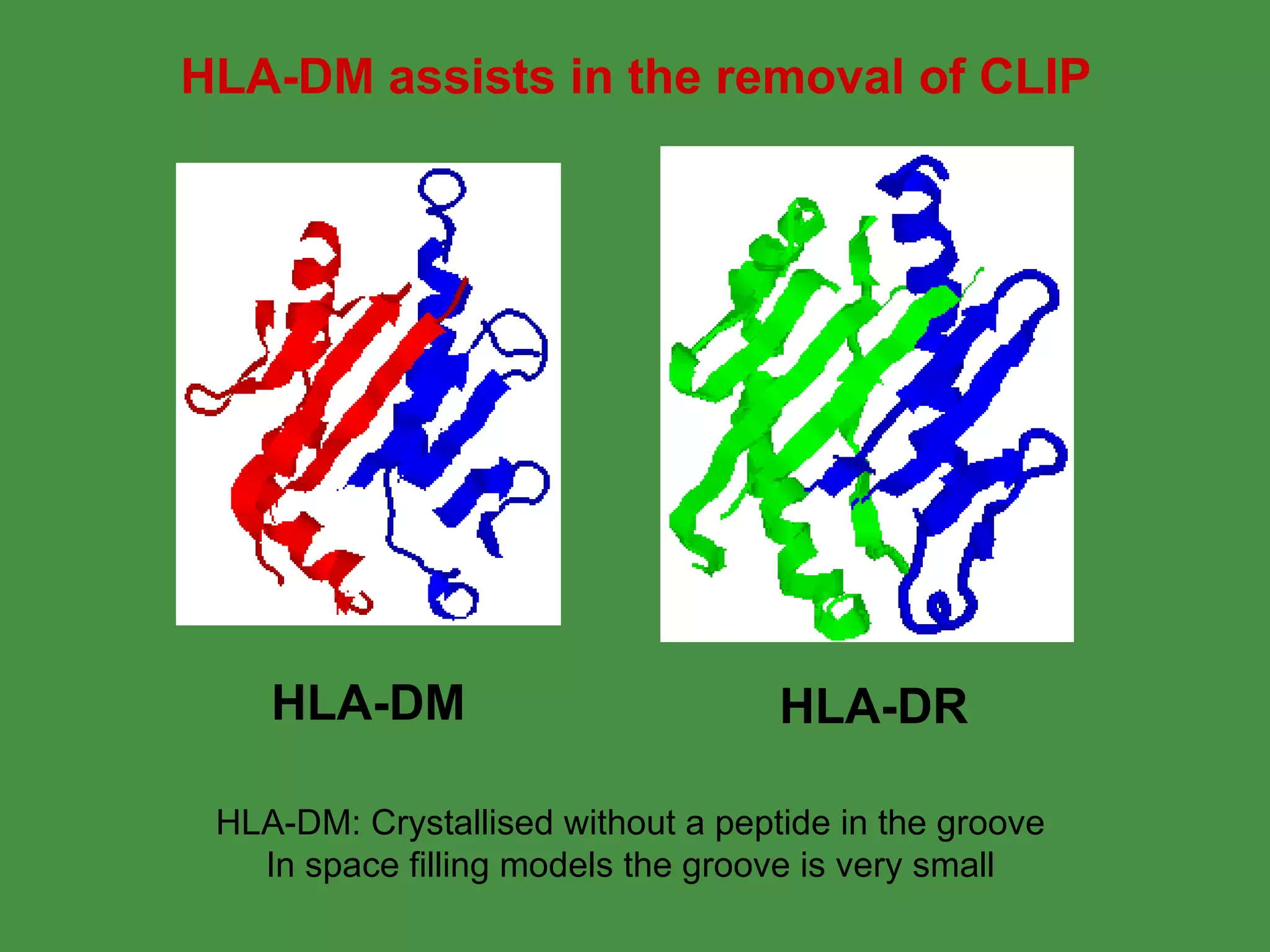
Antigen processing involves two main pathways:
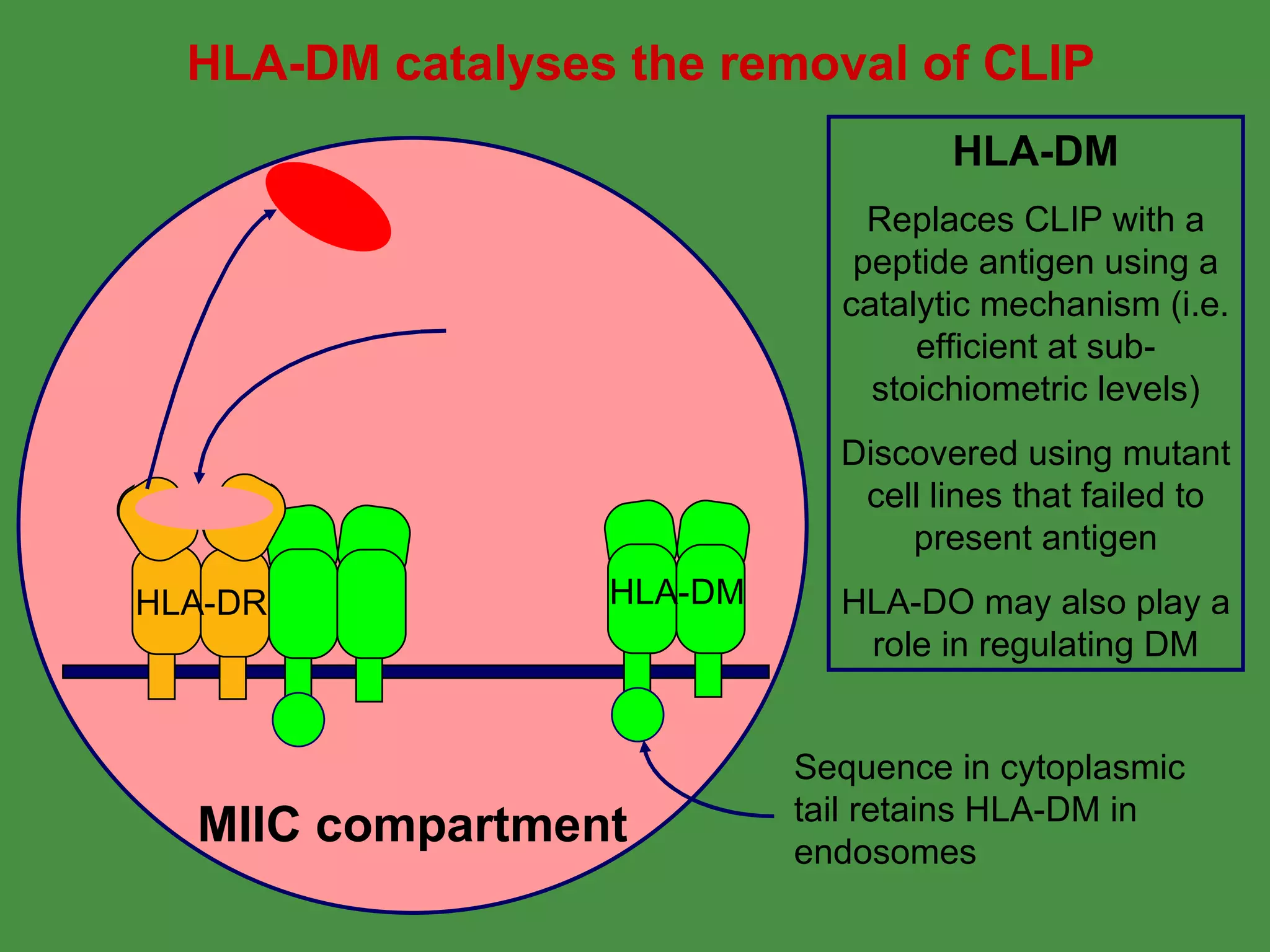
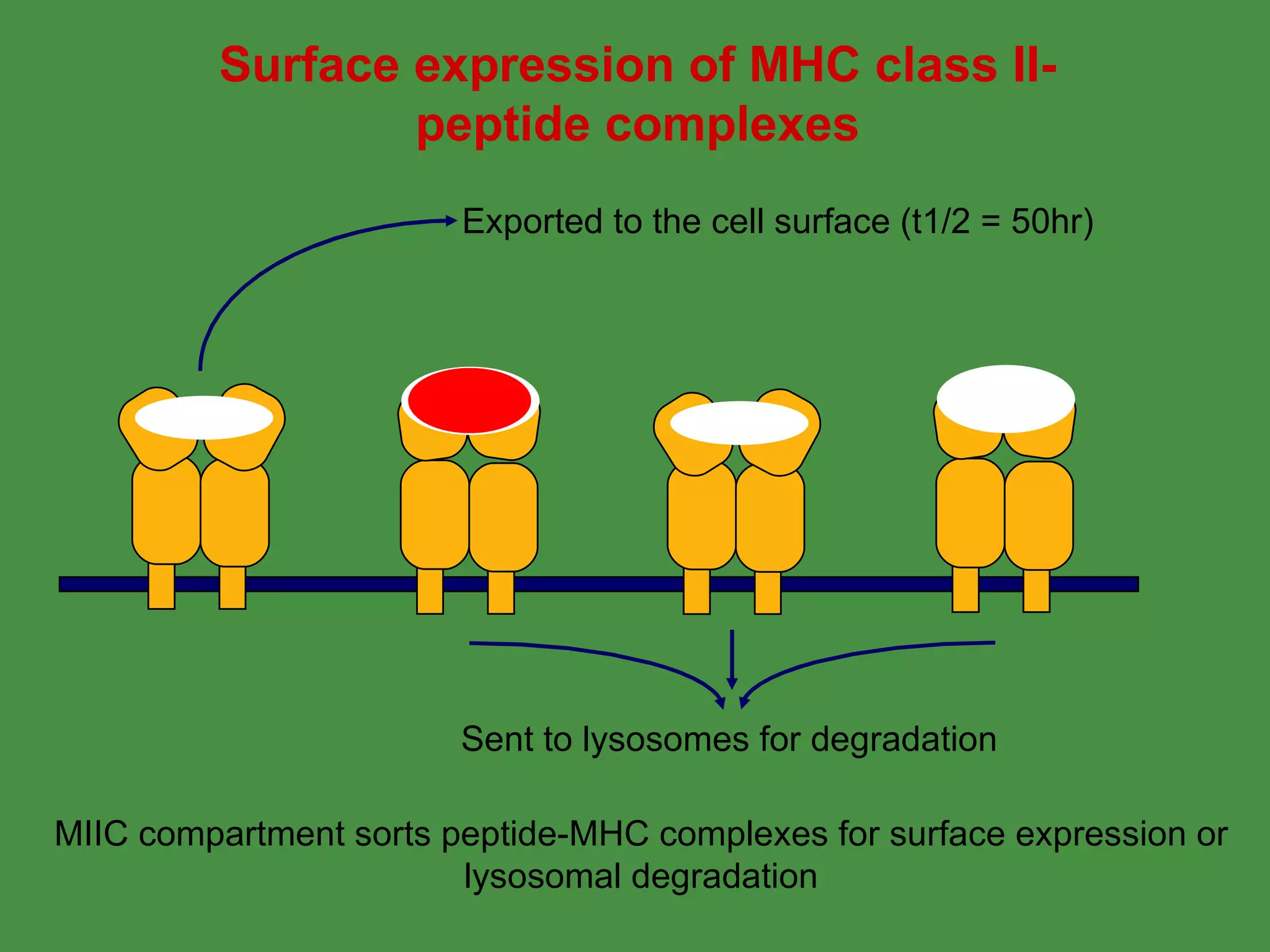
1. Exogenous antigens are processed in the lysosomes by proteases and presented on MHC class II molecules. This involves uptake, degradation, complex formation and presentation.
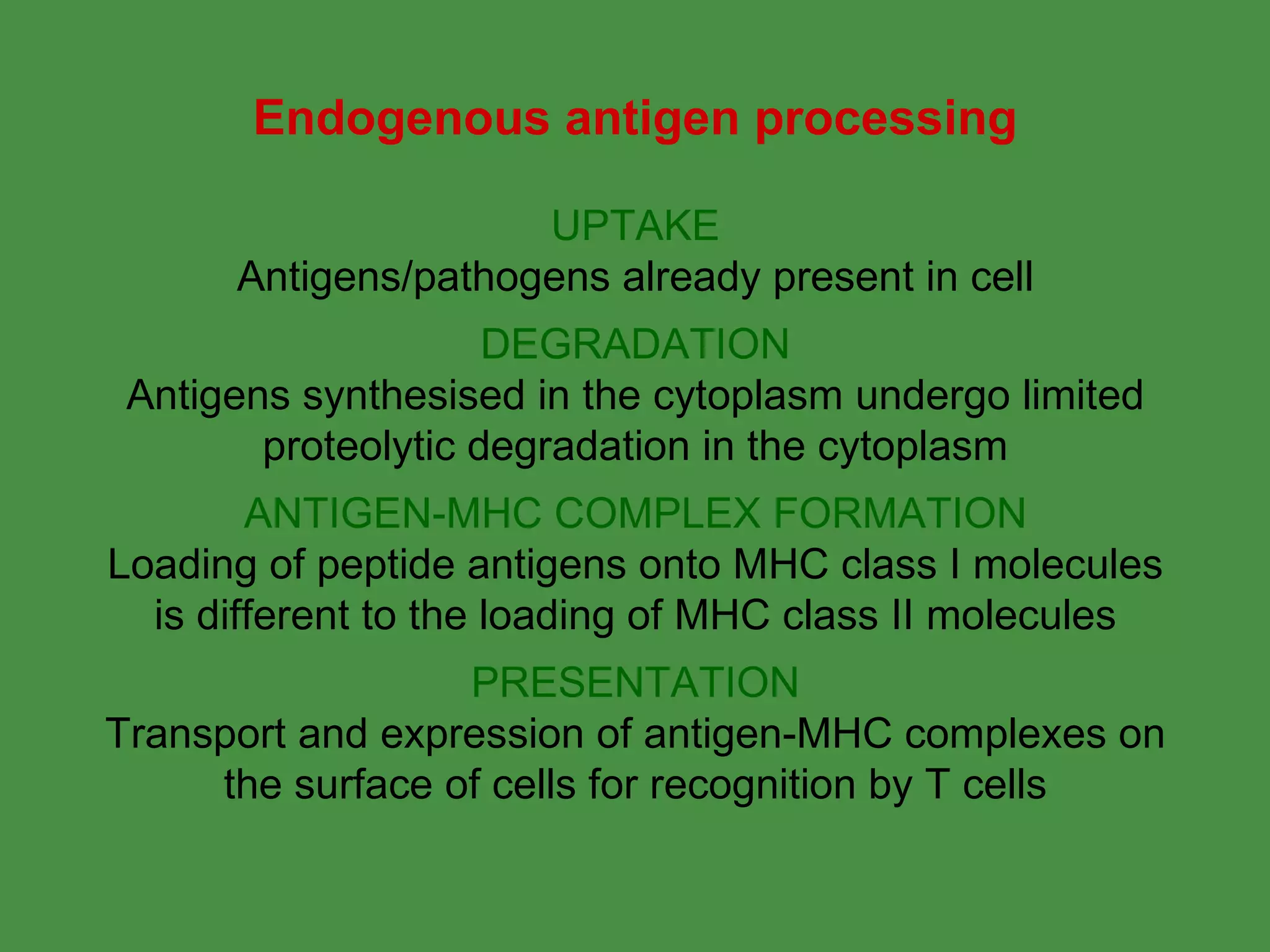
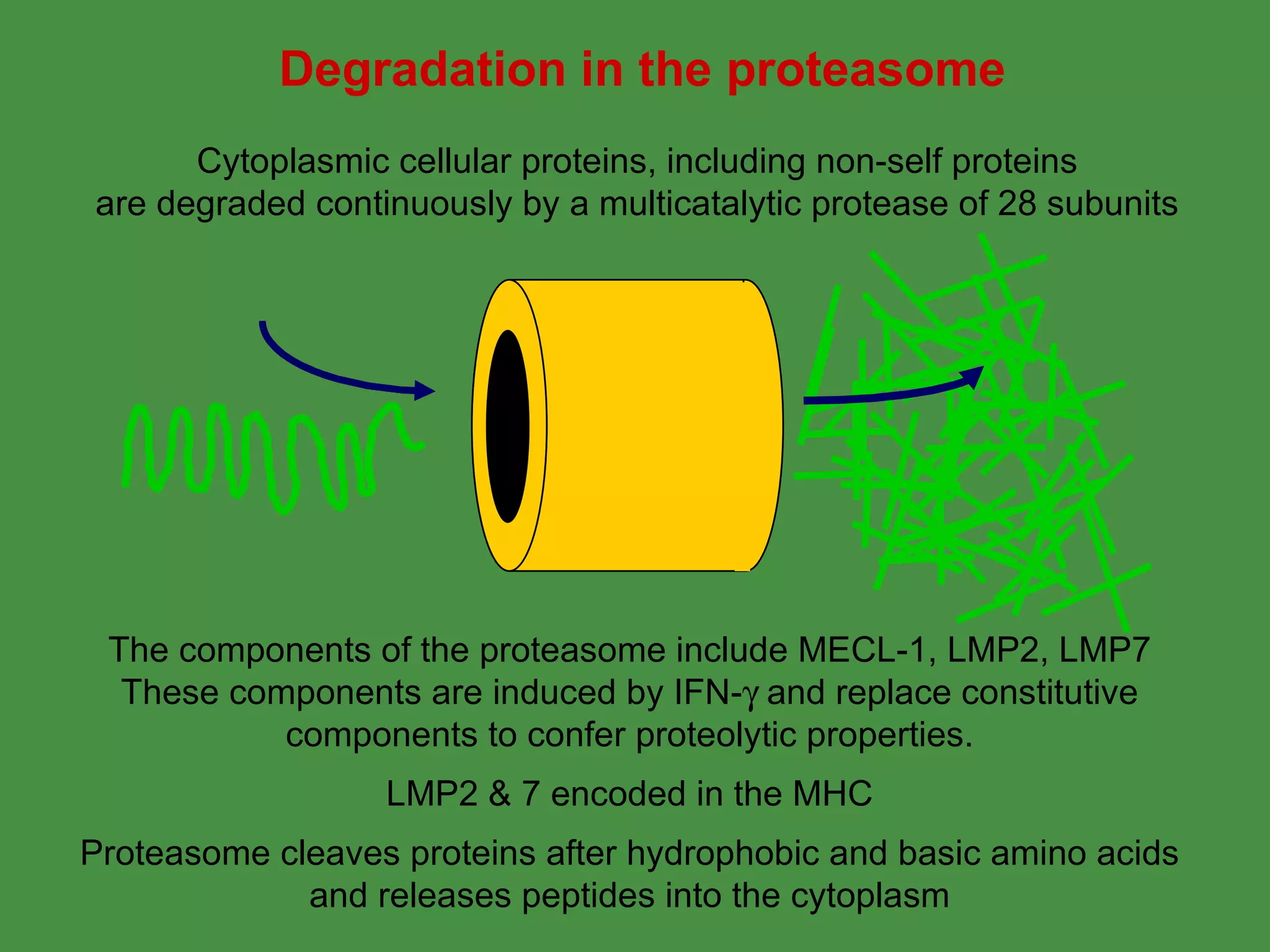
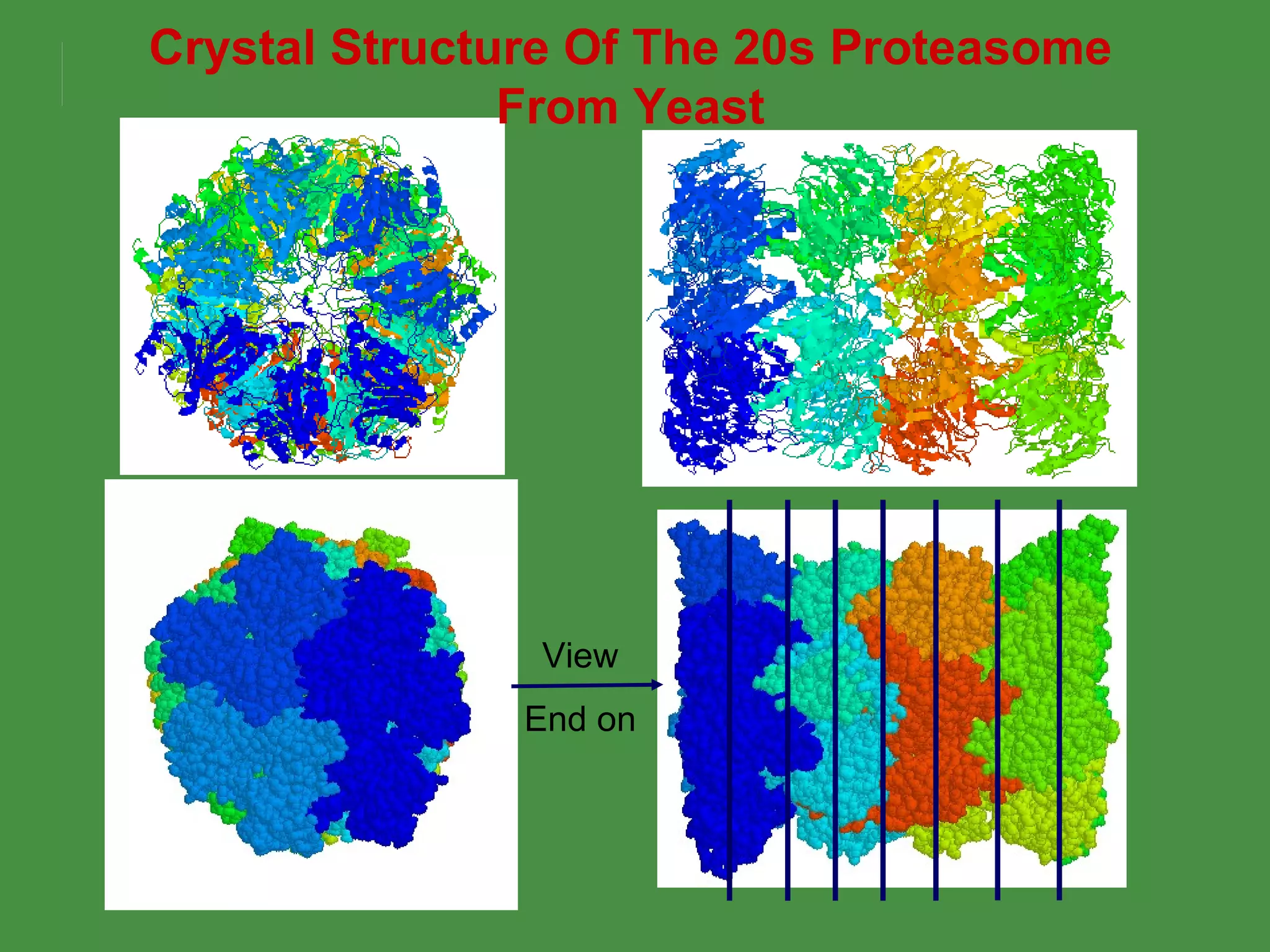
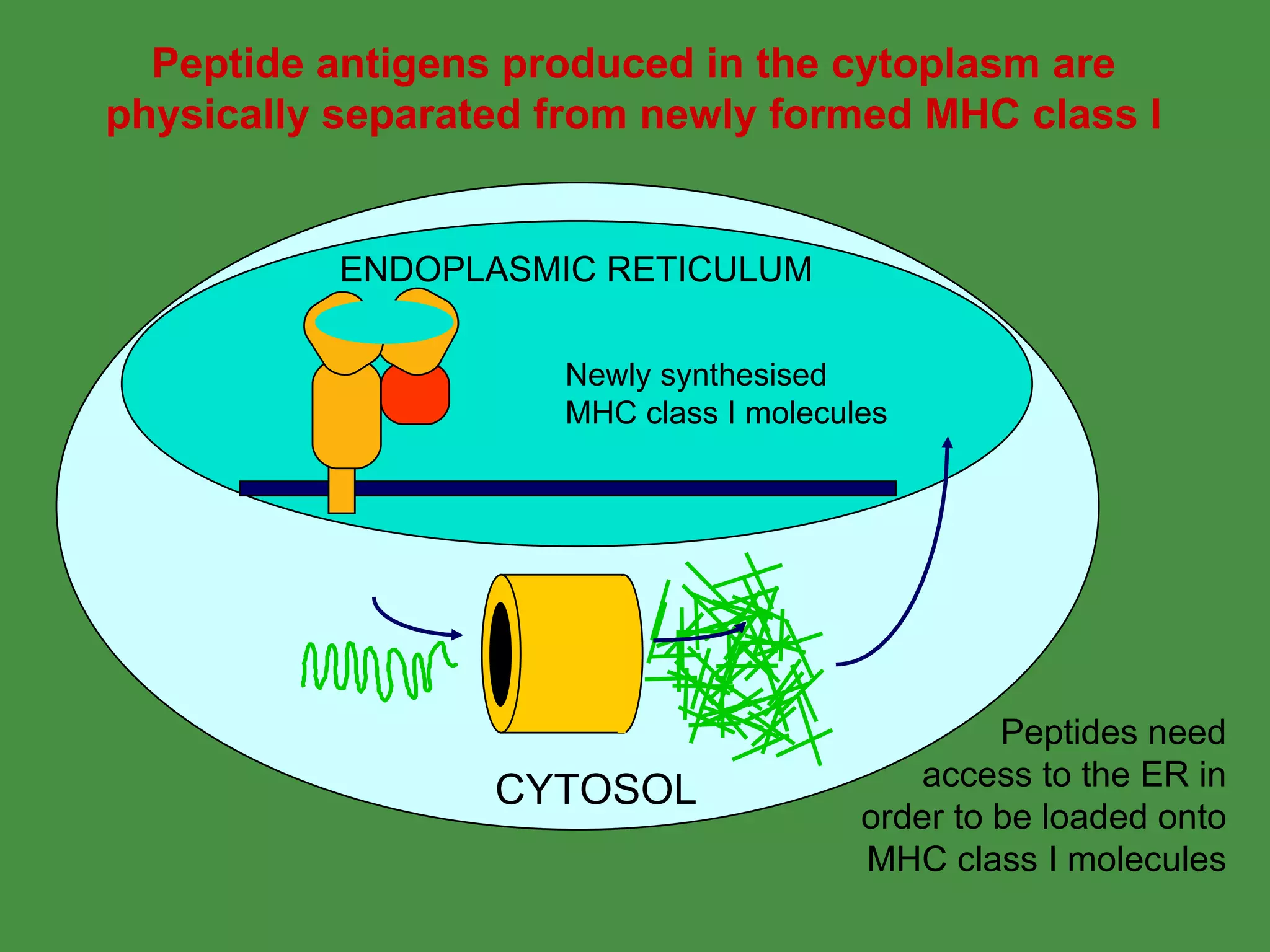
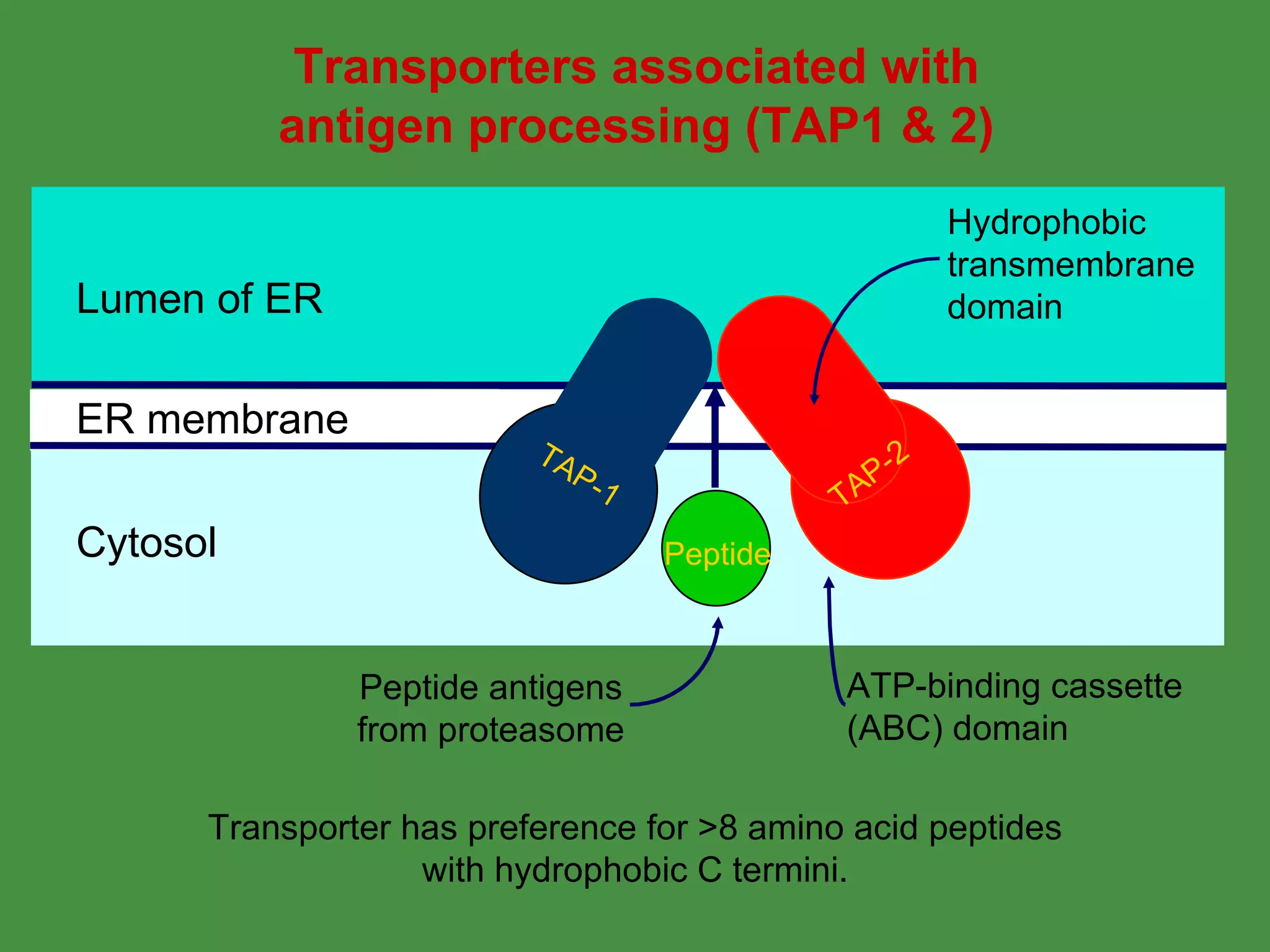
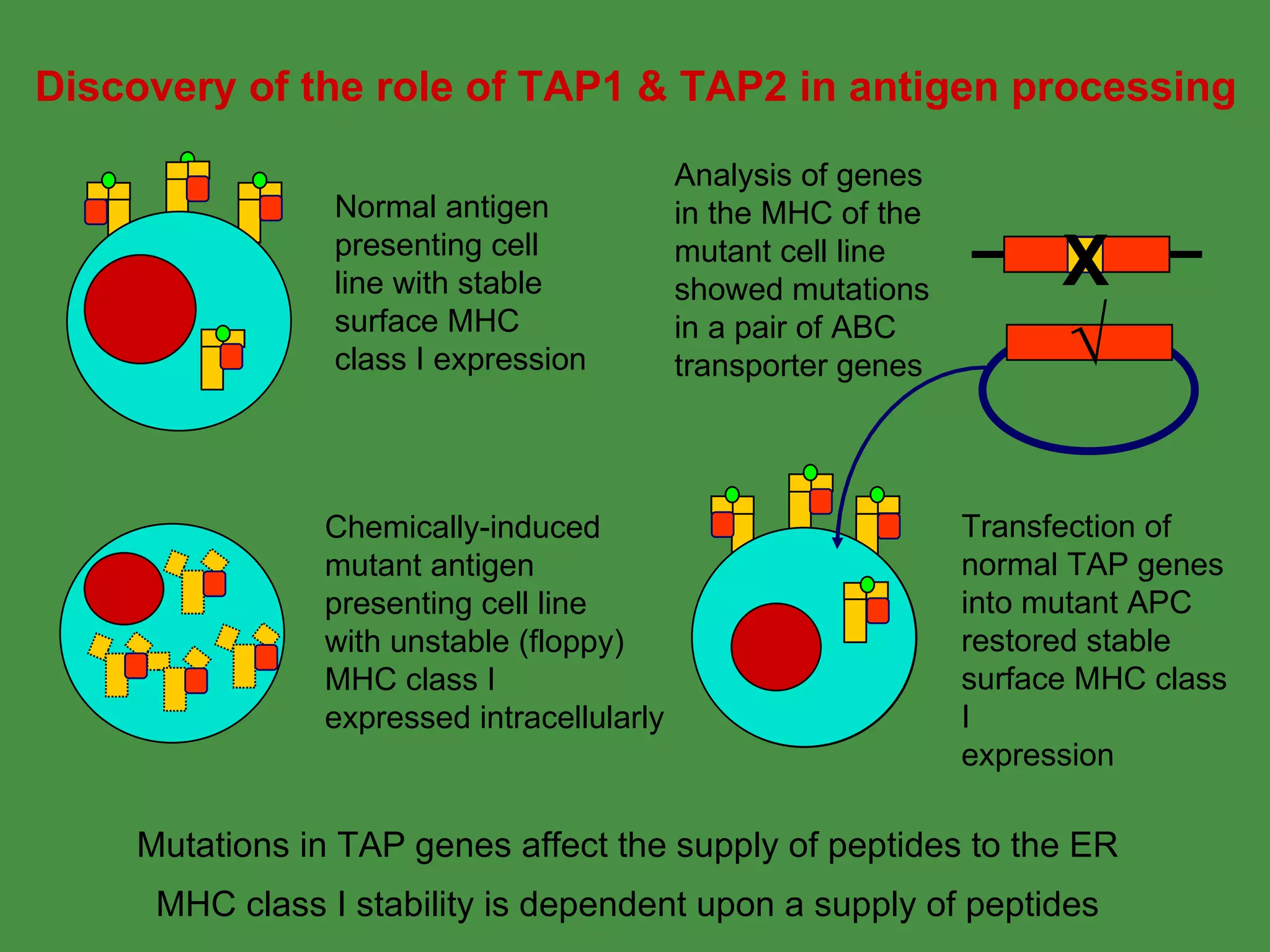
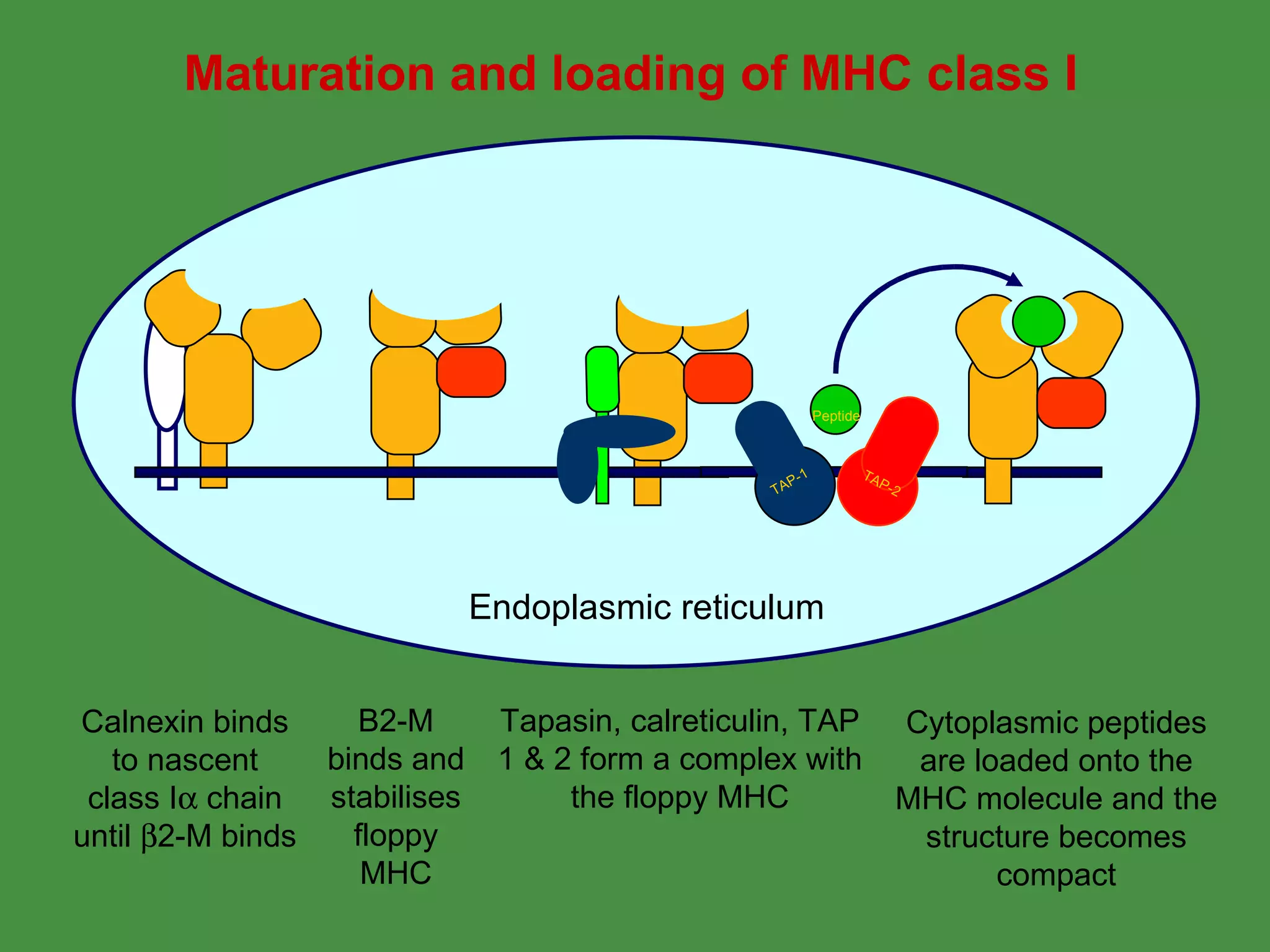
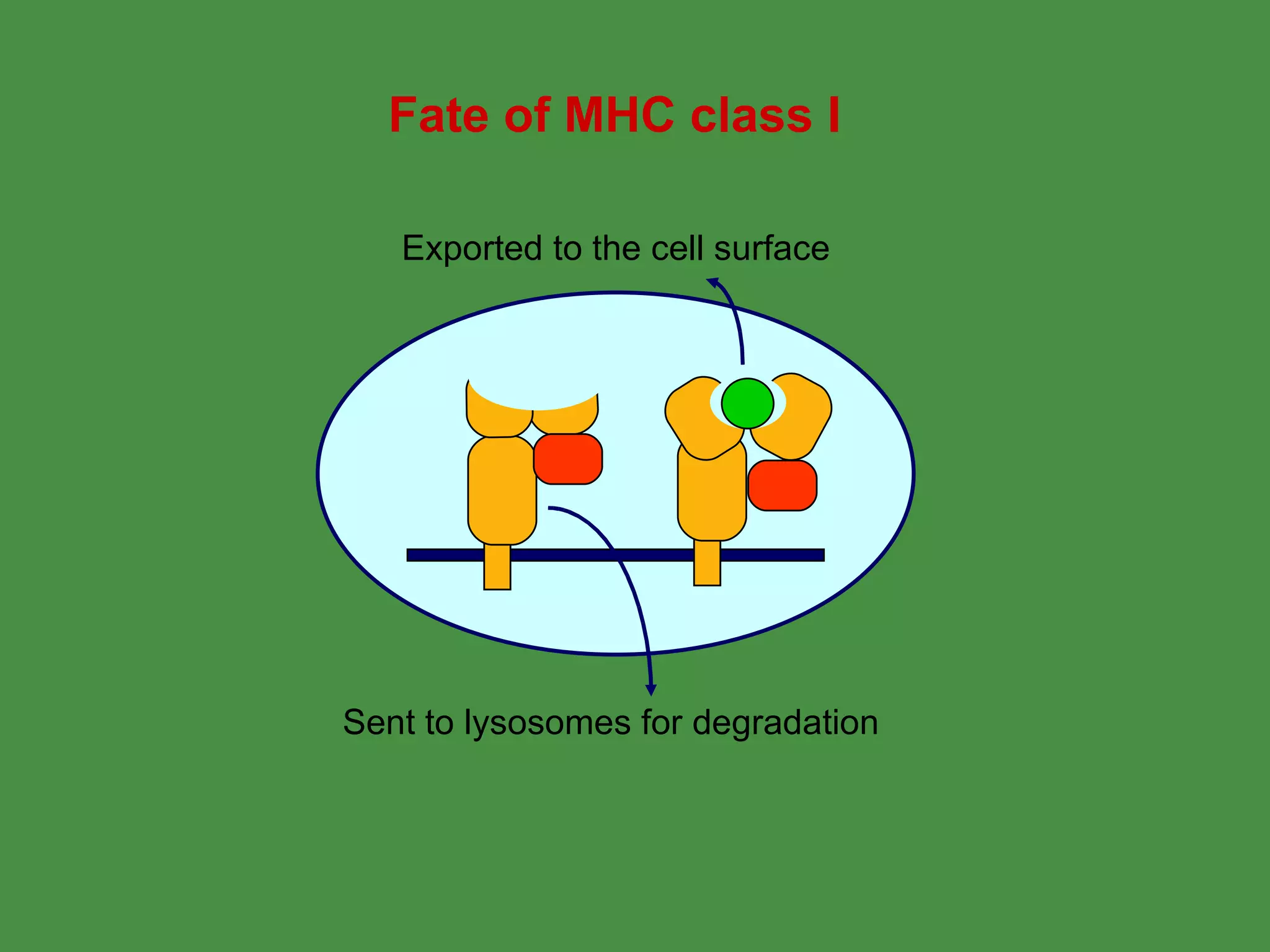
2. Endogenous antigens from cytosolic pathogens are processed by the proteasome and transported into the ER by TAP for loading onto MHC class I. This non-lysosomal pathway generates peptides for CTL response.
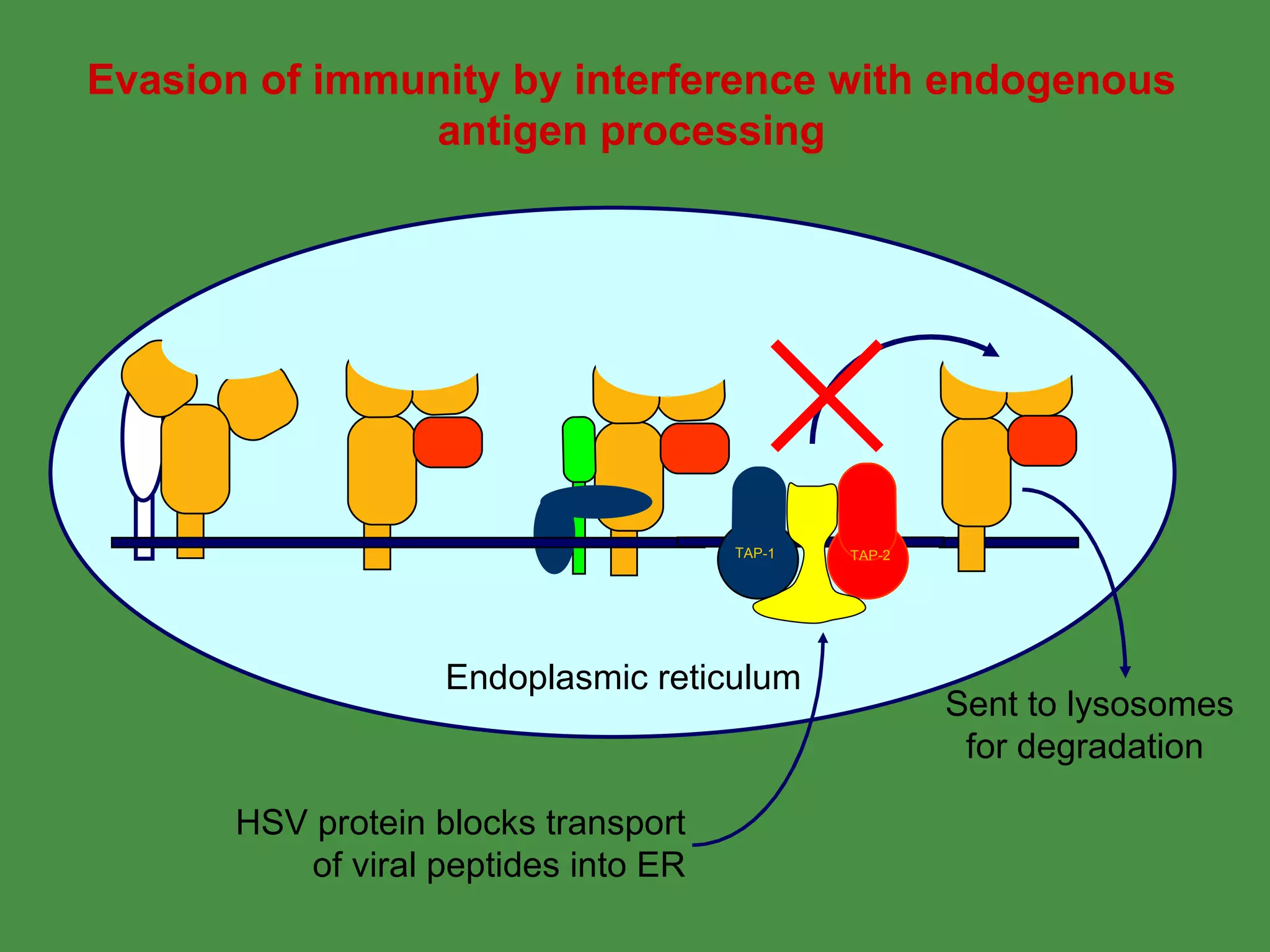
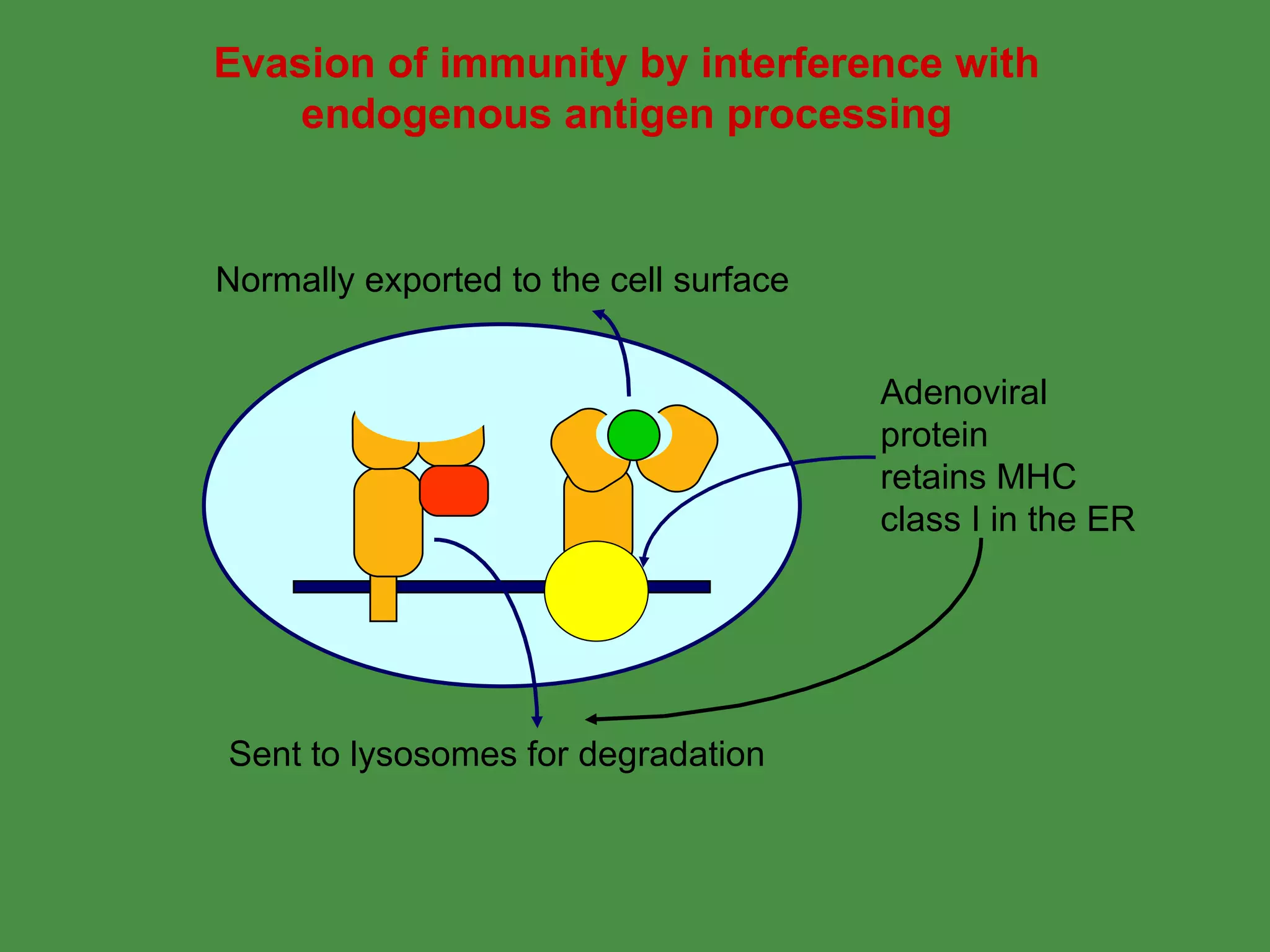
Pathogens can evade immunity by interfering with these antigen processing pathways, such as by blocking transporter function or retaining MHC in the ER. Proper antigen processing is essential for generating effective T cell immunity.