This document discusses antidepressant drugs and mood stabilizers. It begins by describing depression as one of the most common causes of ill health. Depression is characterized by emotional, biological, and manic symptoms. Depression affects 5-6% of the population and is more common in women.
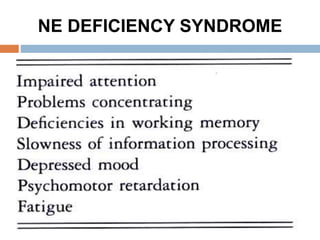
The document then discusses the diagnosis of different types of depressive disorders including unipolar depression, bipolar disorder, and others. It covers neurobiological theories of depression including the monoamine hypothesis of low neurotransmitter levels causing depression and the receptor hypothesis of changes in receptor sensitivity.
Finally, it discusses various classes of antidepressant drugs including SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs and others. It provides examples of SSRIs




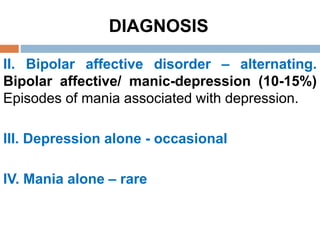
![DIAGNOSIS
Types of Depressive Mood (Affective) Disorders:
Unipolar (depressive) and Bipolar (manic-
depressive)
Unipolar (depressive) [reactive depression] in
which the patient swinging between normal mood
and depression caused by stressful life events.
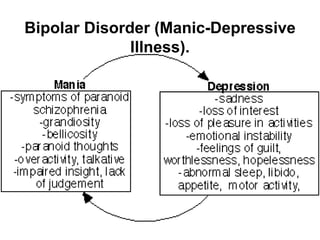
Bipolar depressive disorder (Manic-Depressive
Illness) in which the patient swinging between
mania and depression caused by hereditary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![NEUROBIOLOGICAL THEORY BASIS
OF DEPRESSION
I. Monoamine (catecholamine) theory or
Hypothesis (deficiency in 5-HT and/or NE
and/or DA) (1965):
The underlying biological or neuro-anatomical
basis for depression is a deficiency in the
amount of the monoamine neurotransmitters
[serotonin and/or norepinephrine and/or
dopamine] of the central noradrenergic and/or
serotonergic transmission in the brain [cortical
and limbic] including the frontal cortex,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-9-320.jpg)

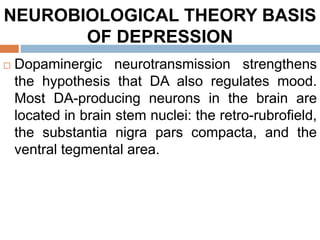
![NEUROBIOLOGICAL THEORY BASIS
OF DEPRESSION
A dysfunction of the mesocortical dopaminergic
pathway, innervating limbic structures including
the nucleus accumbens, amygdala, ventral
hippocampus and cortical areas may reduce
dopaminergic activity has been linked to
decreased motivation, anhedonia (loss of
pleasure) and loss of interest, whereas
increased dopaminergic transmission has been
linked to positive affect [to motivation, pleasure,
and reward, as well as interest in life].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-12-320.jpg)

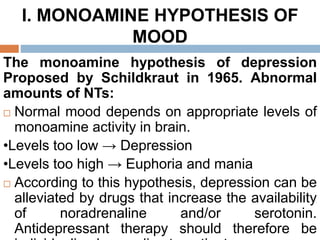
![II. RECEPTOR HYPOTHESIS OF
MOOD
[Supersensitivity pre-synaptic → down-
regulation receptors and Decreased post-
synaptic sensitivity → up-regulation of post-
synaptic receptors] leads to depression.
The antidepressant treatment increases the
amount of monoamines in CNS and gradually
normalize the density/sensitivity of their
receptors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-15-320.jpg)




![PHARMACOTHERAPY
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
I. MONOAMINE UPTAKE INHIBITORS
1. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and
Heterocyclics (HCAs).[During the 1950s]
2. Selective Serotonin reuptake inhibitors
(SSRIs).[The beginning of the 1980s]
3. Serotonin-Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
(SNRIs). [During the 1990s]
4. Norepinephrine/Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitors
(NDRIs).
5. Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRIs).
6. The triple reuptake inhibitors (TRIs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![PHARMACOTHERAPY
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
II. MONOAMINE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS
[BLOCKERS]
1. Noradrenergic and Specific Serotonergic Antidepressant
(NaSSA)
2. Serotonin2A Antagonist/Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
(SARI)
III. MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS (MAOIS)[Two
isoforms: MAO-A and MAO-B].
1. Non-Selective Irreversible inhibition of MAO.
2. Selective Irreversible inhibition of MAO-B.
3. Selective Reversible MAO-A Inhibitors/Reversible
inhibitors of monoamine oxidase – A (RIMAs).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-22-320.jpg)
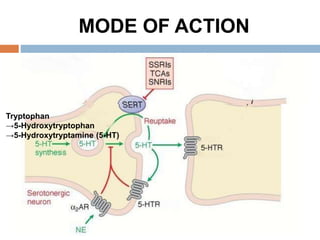
![2. SELECTIVE SEROTONIN
REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRI’s)
Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline,
Citalopram, Escitalopram.
Fluoxetine (Prozac) [Prototype]
2nd generation antidepressant category.
Selectively inhibits presynaptic reuptake of
serotonin (5-HT) leading to increased
concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft and
increased postsynaptic neuronal activity.
SSRIs: Most commonly first choice for unipolar
disorder; preferred for moderate depression and in
the elderly [Not as sedating as many of the tricylic
compounds]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-23-320.jpg)
![2. SELECTIVE SEROTONIN
REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRI’s)
No blockade of α1, histamine or M
cholinergic receptors or Na+ pump [Less
likely to cause anticholinergic side effects, no
cardiac effects, no postural hypotension].
Relatively safest antidepressant group in
overdose. [may be better tolerated and have a
wider safety margin].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-25-320.jpg)
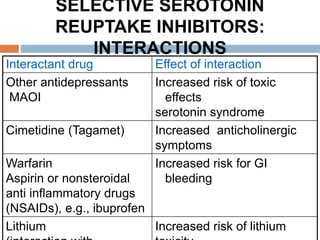
![2. SELECTIVE SEROTONIN
REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRI’s)
Lipophilic Well absorbed when given orally
Plasma half-lives of 18-24 h allowing once daily
dosage.
Metabolised by liver through CYP450 system
and most SSRIs inhibit some CYP450 isoforms
[may lead to drug interactions] and excreted in
urine.
Therapeutic effect is delayed for 2-12 weeks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-26-320.jpg)

![ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS
SSRI’S
Headache, Apathy, Insomnia, fatigue, increased
anxiety, irritability, Anorexia
Restlessness(akathisia), Extrapyramidal side
effects (EPSEs) Tremor.
Erectile dysfunction: Decreased libido,
anorgasmia, and ejaculatory delay.
Increased prolactin levels
Hyponatraemia.
GIT – nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, [Constipation
only with paroxetine].
Withdrawal syndrome
Serotonin syndrome upon intoxication or drug
interactions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-28-320.jpg)
![ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS
SSRI’S
Bruising and Bleeding disorders: Increased
risk of gastrointestinal bleeding with aspirin [5-
HT released from platelets causes local
vasoconstriction (5-HT2A, 5-HT1B) and platelet
aggregation (5-HT2A)] by a 5-HT transporter is
blocked by SSRI’s ]
SSRI’s reduce probability of new infarcts after
MI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-29-320.jpg)

![TCA’s vs. SSRI’s
SSRI’s low anticholinergic, antiadrenergic
activities. SSRI’s low or no affinity for
histaminergic and muscarinic receptors.
SSRI’s low cardiovascular side effects
SSRI’s low lethality in overdose [very low
suicide risk].
SSRI’s safer than Clomipramine for
serotonergic actions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antidepressantdrugs-230215222940-4962e20a/85/ANTIDEPRESSANT-DRUGS-pptx-32-320.jpg)