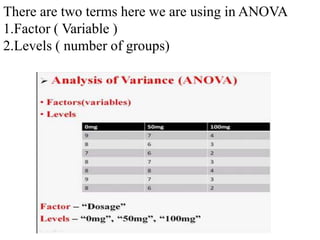
ANOVA (analysis of variance) is a statistical method used to compare the means of two or more groups. It divides the variation in a data set into distinct components. The two main types of ANOVA are one-way and repeated measures. One-way ANOVA has one independent factor with at least two levels, while repeated measures has one dependent factor with at least two levels. To perform ANOVA, null and alternative hypotheses are defined along with the significance level. Degrees of freedom, sum of squares, mean squares, and the F-statistic are calculated to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.