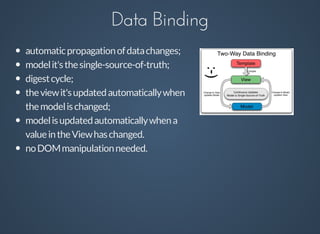
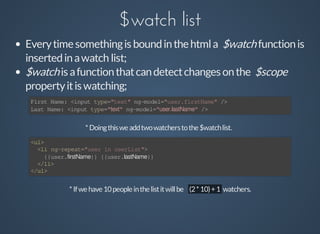
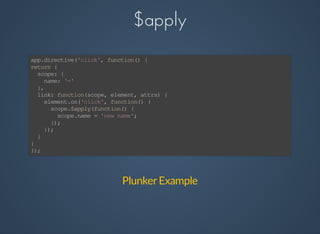
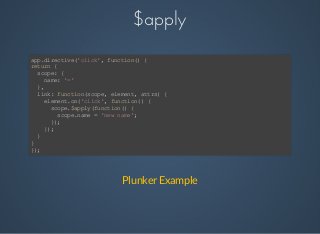
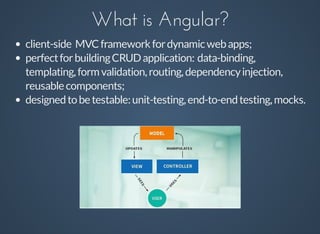
Angular is a client-side MVC framework designed for building dynamic web applications with features such as data-binding, templating, and reusable components. It facilitates easy testing and team development while using a clear architectural pattern. Angular implements two-way data binding through a digest cycle and utilizes components like $watch, $apply, and $digest to manage data updates seamlessly.



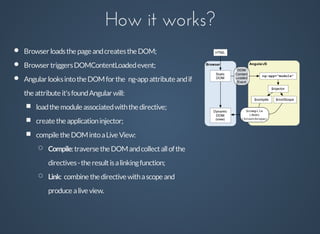
![How it works?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html ng-app="myApp">
<head>
<title>Angular app</title>
<script src="bower_components/angular/angular.js">
{{name}}
angular
.module('myApp', [])
.controller('MyCtrl', function($scope){
$scope.name = 'World';
});
Plunker Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-introduction-140808110013-phpapp02/85/AngularJS-introduction-how-it-works-5-320.jpg)