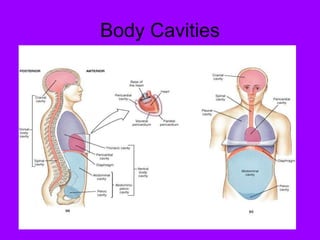
This document provides an introduction to human anatomy. It defines anatomy as the study of the structure of the human body and its parts and their relationships to one another. Anatomy is divided into gross anatomy, which studies structures visible to the eye, and microscopic anatomy, which requires a microscope. The human body is made up of cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and whole organisms. Anatomy can be studied regionally, focusing on one body region at a time, or systemically, focusing on one body system. The document outlines several body systems and describes planes used to divide the body, as well as body cavities and quadrants.