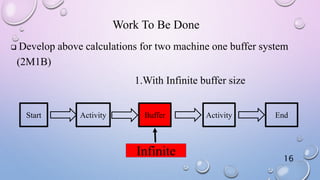
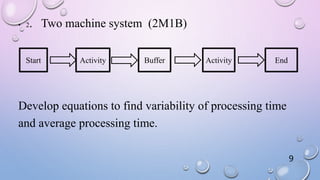
This document discusses analytical models of learning curves with variable processing times. It introduces the concept of learning curves where operators get faster at tasks over time. It presents the basic log-linear model used to mathematically represent learning curves. The objectives are to calculate processing times for single-machine and two-machine systems using different models that account for variability in processing times, like exponential and hypo-exponential distributions. Equations are developed and examples are shown for determining average and variability of processing times. Further work is identified to extend the calculations to two-machine systems with both infinite and finite buffer sizes.













![Results Using Other Models
Model Name Equation Mean Variance
Stanford-B
model
Y(x)=Y1(X+B)-b
1559.857 2813.13
Dejong’s
model
Y(x)=Y1[M+(1-M)X-b]
2428.25 6336.51
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e7535c0b-edd1-4f3e-aed2-1136f92ac11f-161008151110/85/Analytical-models-of-learning-curves-with-variable-processing-time-15-320.jpg)