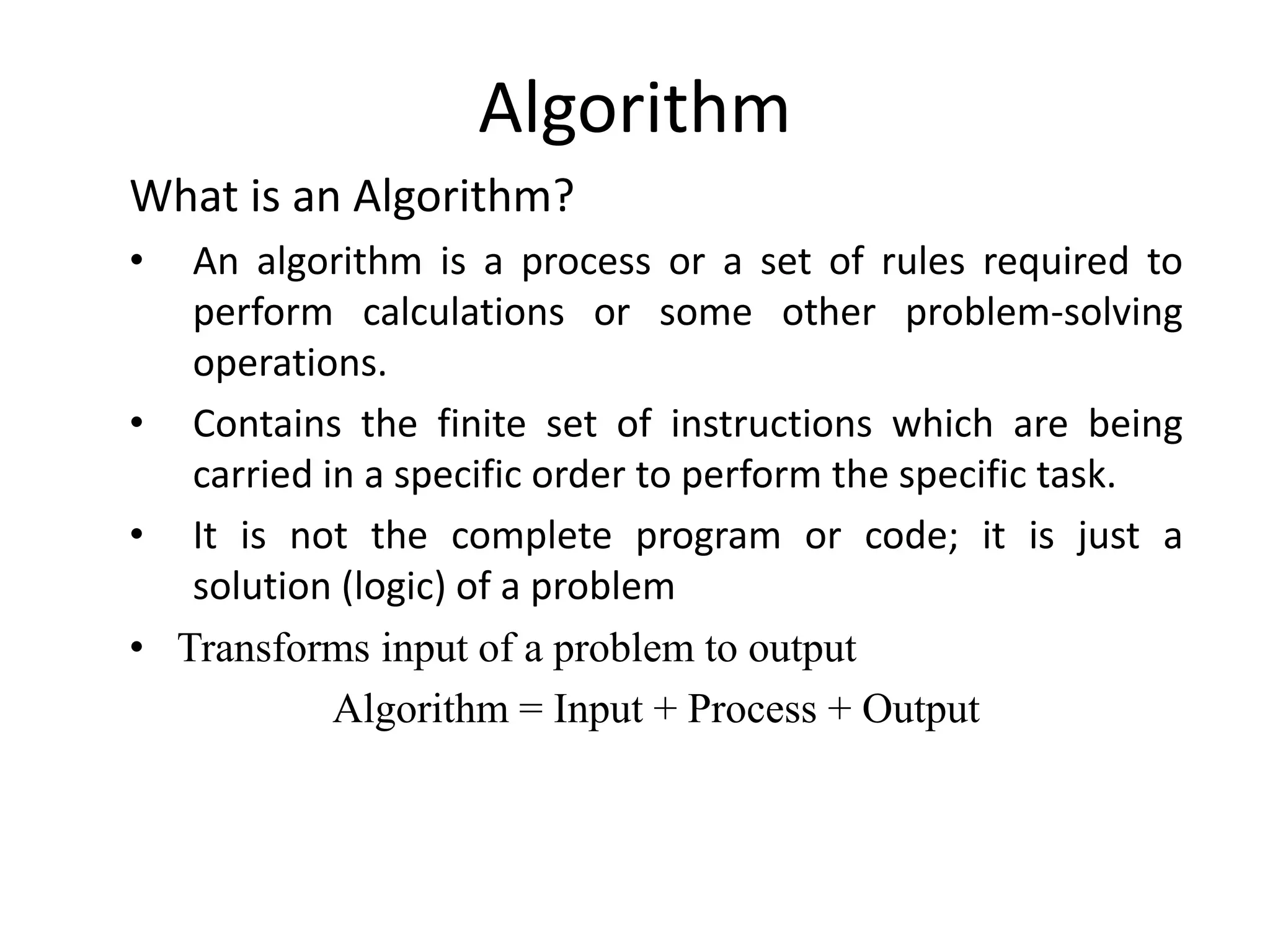
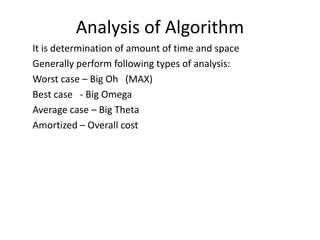
An algorithm is a defined set of rules or instructions used to solve problems or perform calculations, transforming input into output. Key characteristics include input, output, finiteness, and effectiveness, while factors to consider during design involve modularity and maintainability. Efficiency is analyzed both theoretically and practically using asymptotic notations such as big-O, omega, and theta to evaluate time and space requirements.