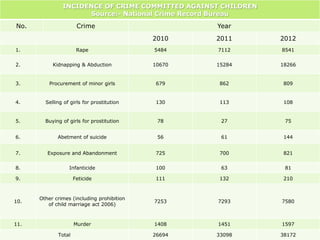
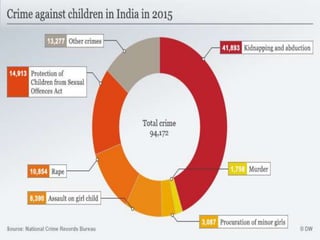
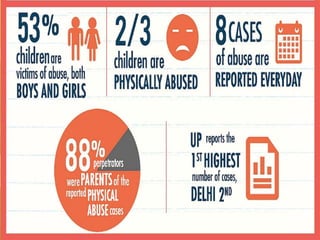
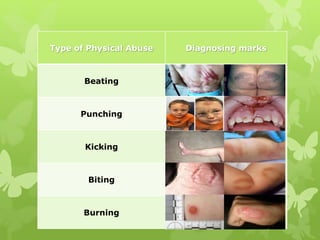
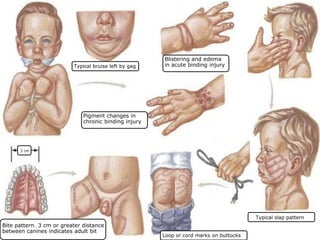
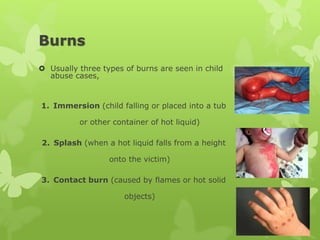
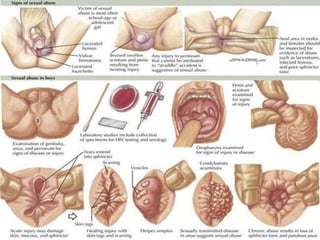
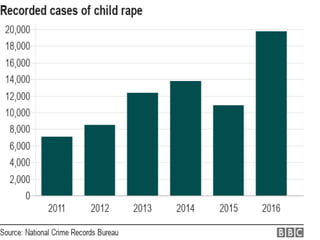
The document provides an overview of child abuse in India, highlighting the alarming prevalence and various forms including physical, sexual, emotional abuse, and neglect. It cites statistics showing a significant number of children suffering from abuse, with many cases going unreported due to societal misconceptions and lack of awareness. It also discusses existing laws and shortcomings in legal protections for children against abuse.