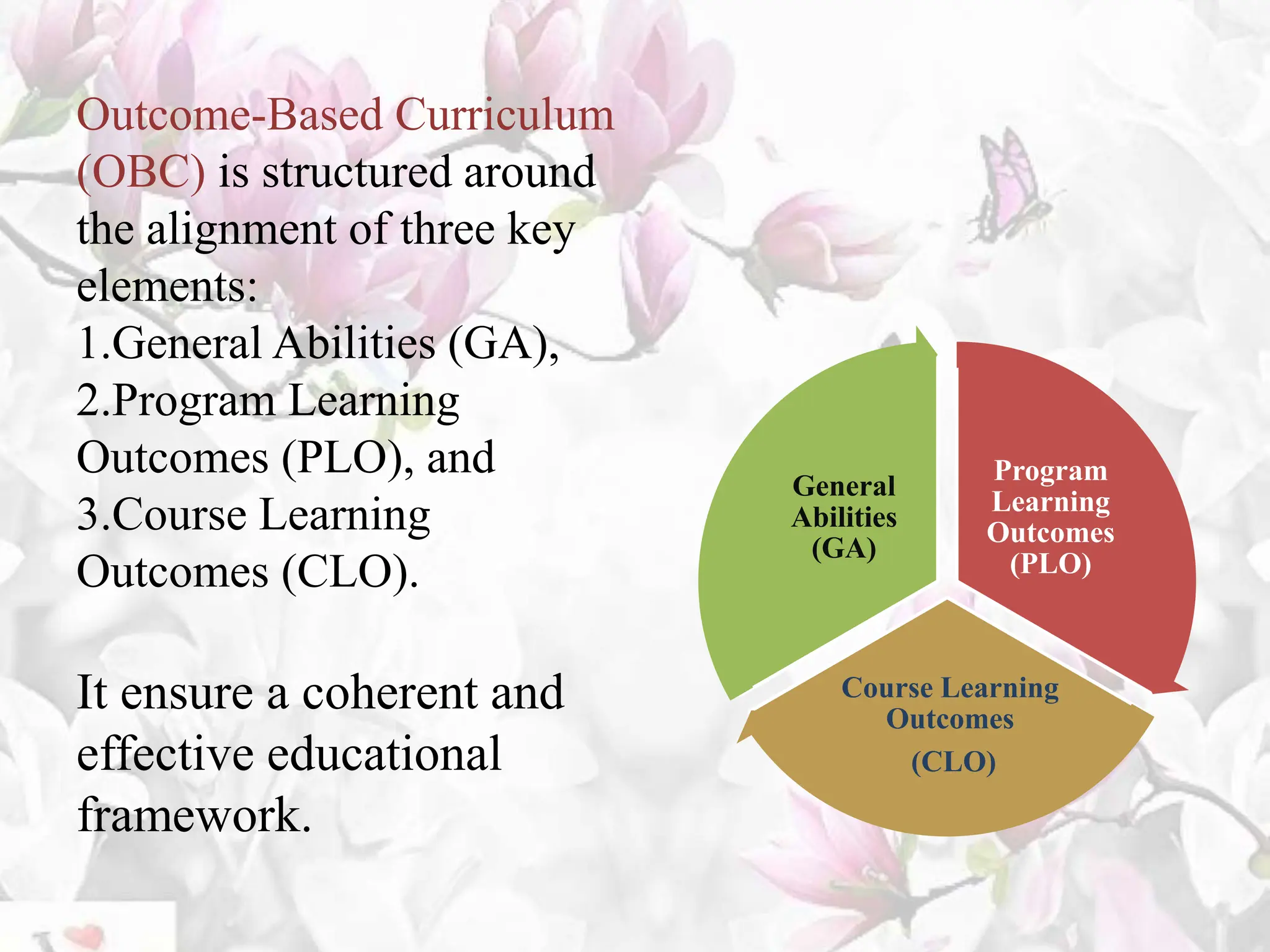
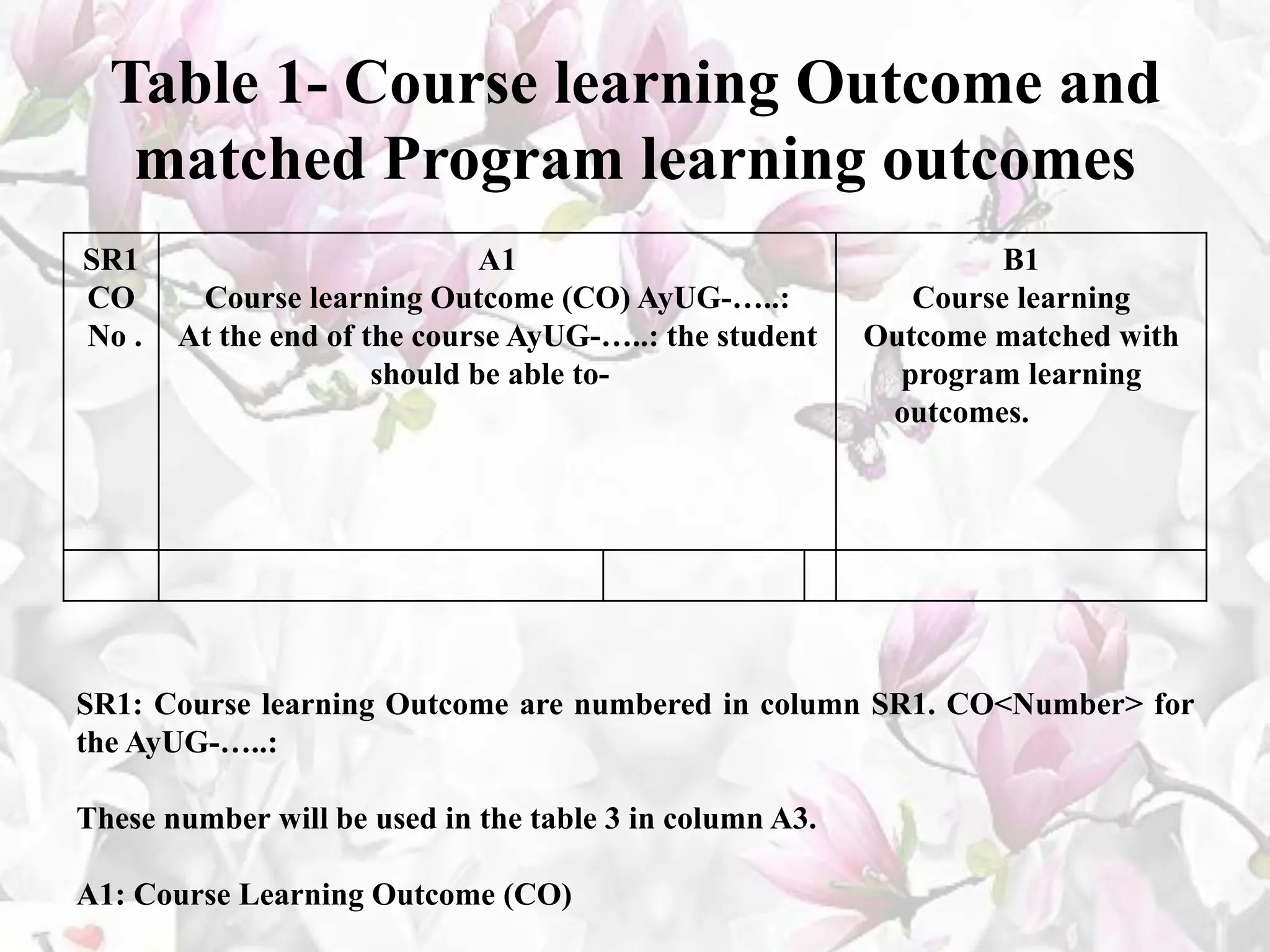
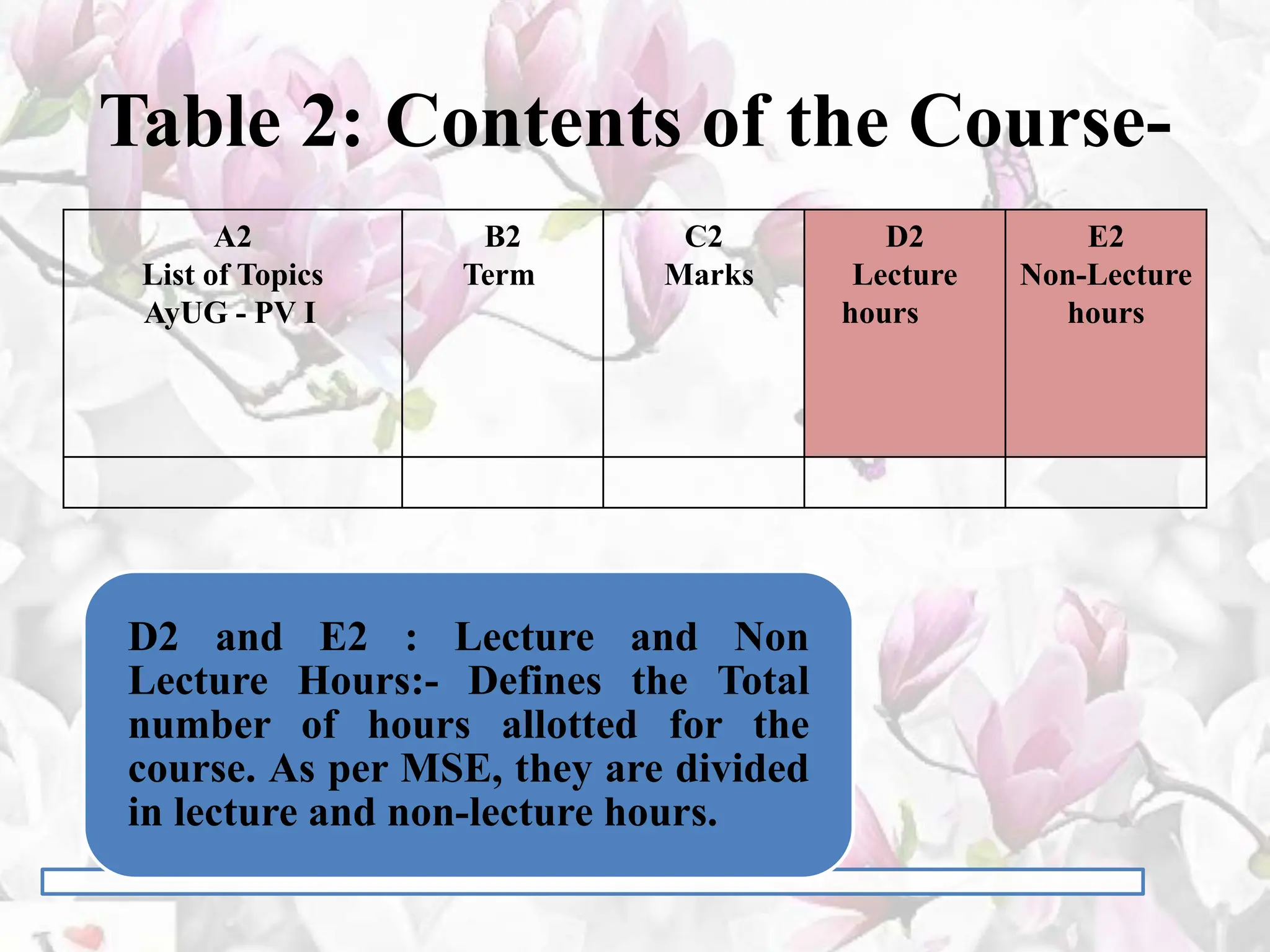
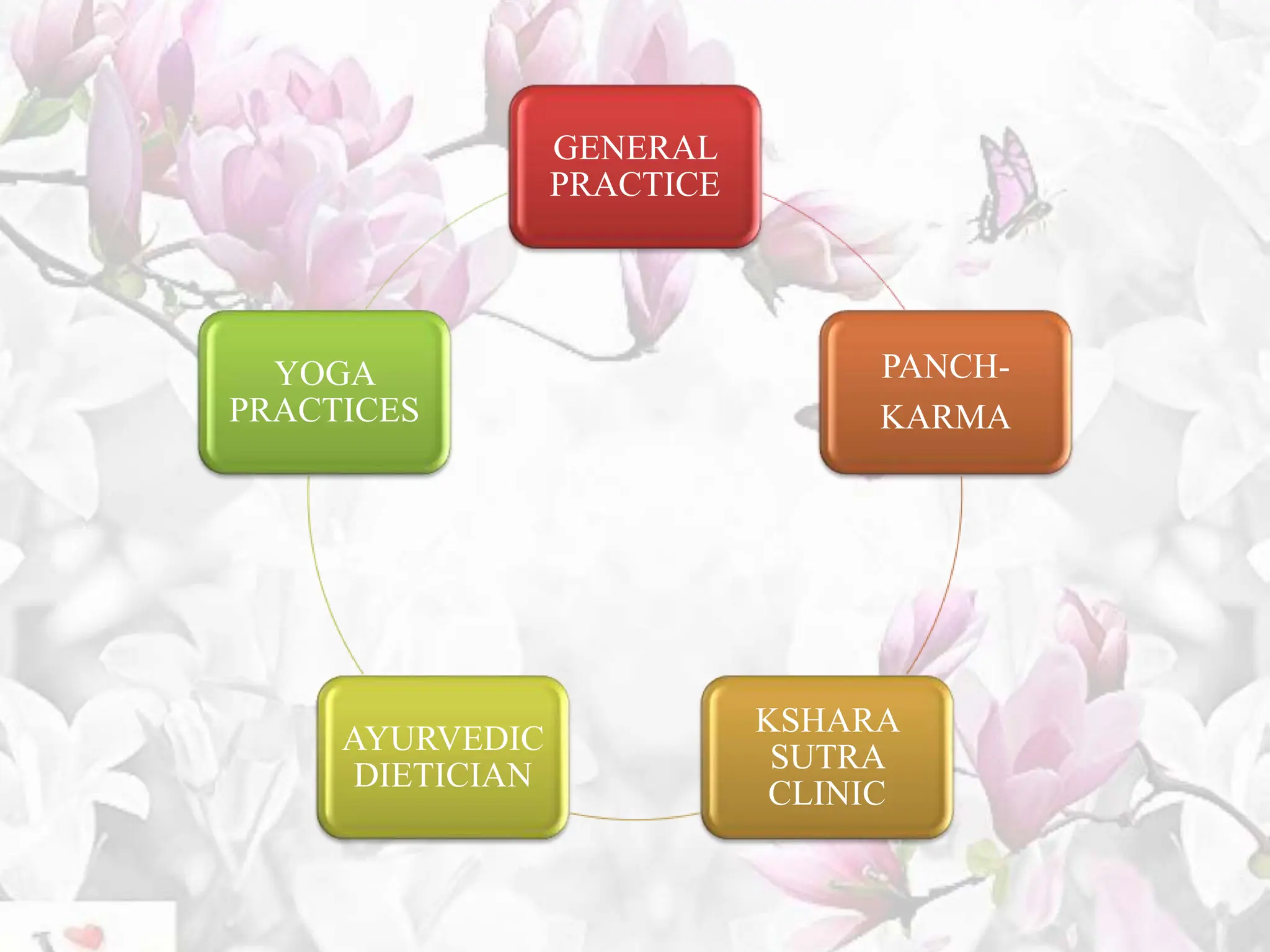
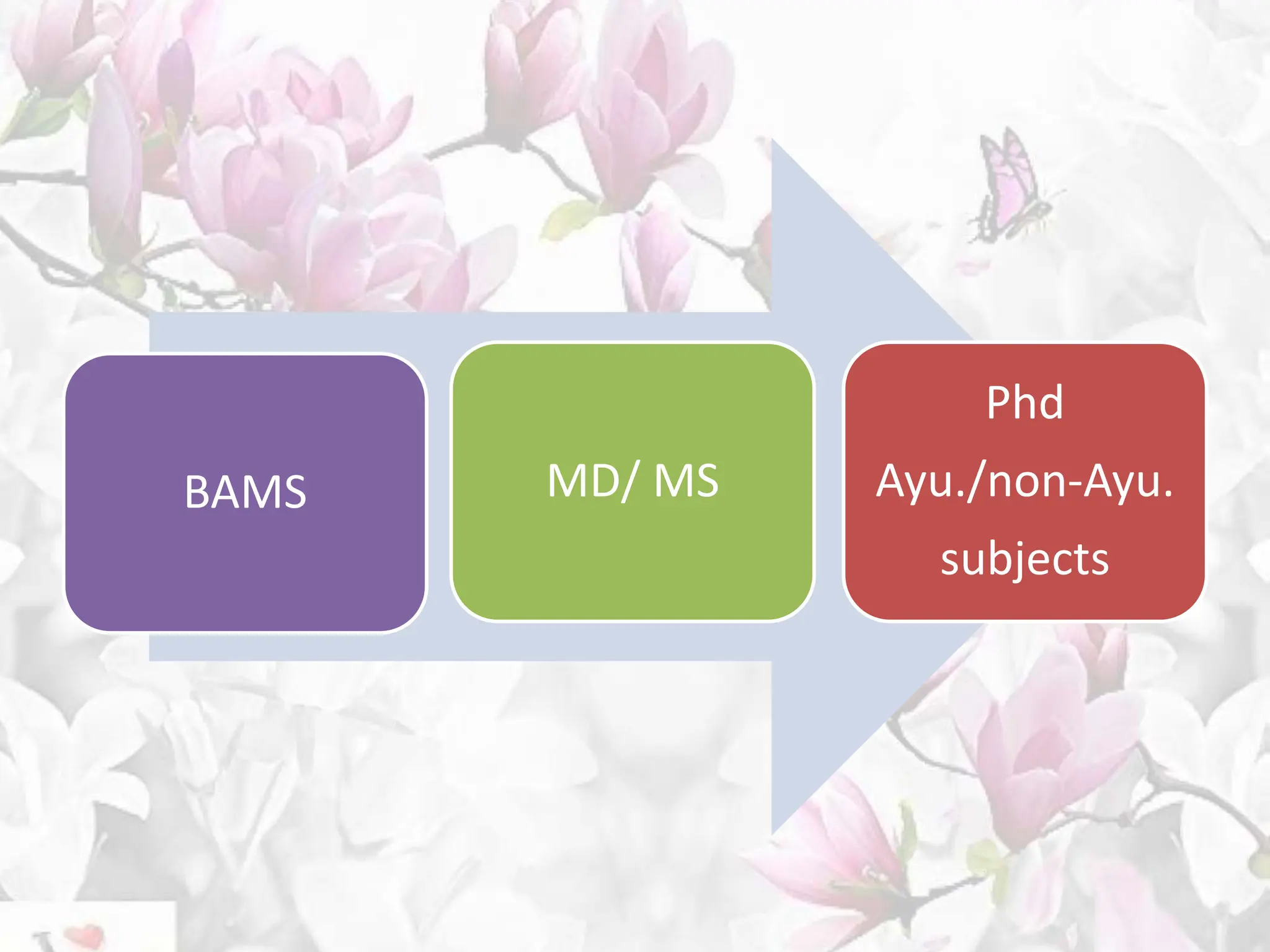
The document provides an overview of the BAMS curriculum and syllabus including highlights of the Minimum Standards of Education 2021. It discusses the origins and aims of Ayurveda, outlines the BAMS degree program and subjects covered in each professional year. It also introduces key aspects of the new outcome-based curriculum approach including general abilities, program learning outcomes, and course learning outcomes. Finally, it discusses various job opportunities available after completing BAMS including clinical practice, academics, research, and opportunities in allied industries.






































![This program is only for interested Bachelor of
Ayurvedic Medicine and Surgery (BAMS)
students [1st year to 4th year (before appearing
in 4th year final exams)] studying in Ayurvedic
college recognized by NCISM, before they
appear in their final exams and therefore,
interns/ PG students are not eligible to apply.
The value of the studentship will be
Rs.25,000/- per month for two months duration
is meant to be a stipend for the student.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bamscurriculum-240109072834-60e937cf/75/An-overview-of-BAMS-Curriculum-or-Syllabus-including-highlights-of-Minimum-Standards-of-Education-2021-51-2048.jpg)

