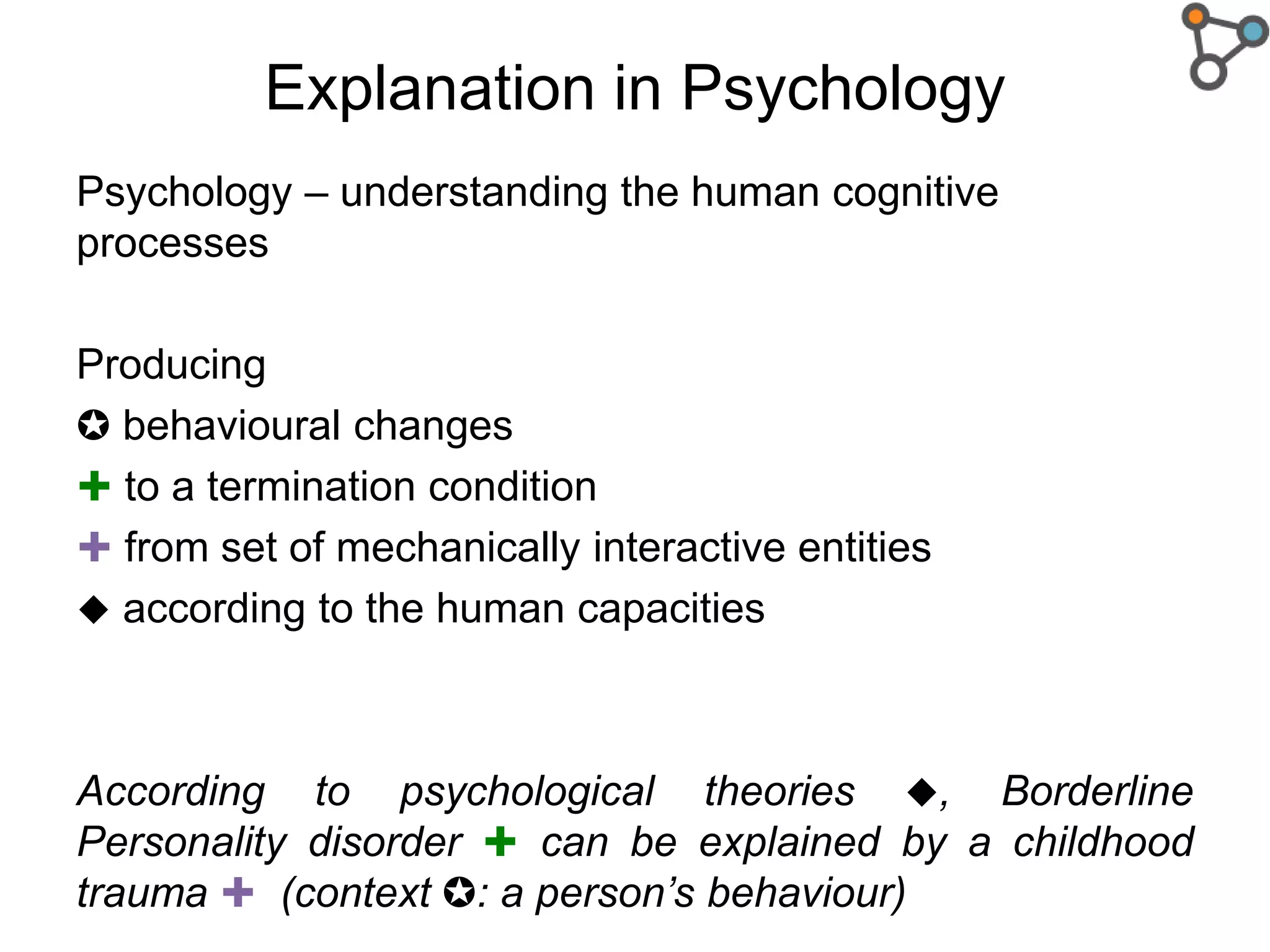
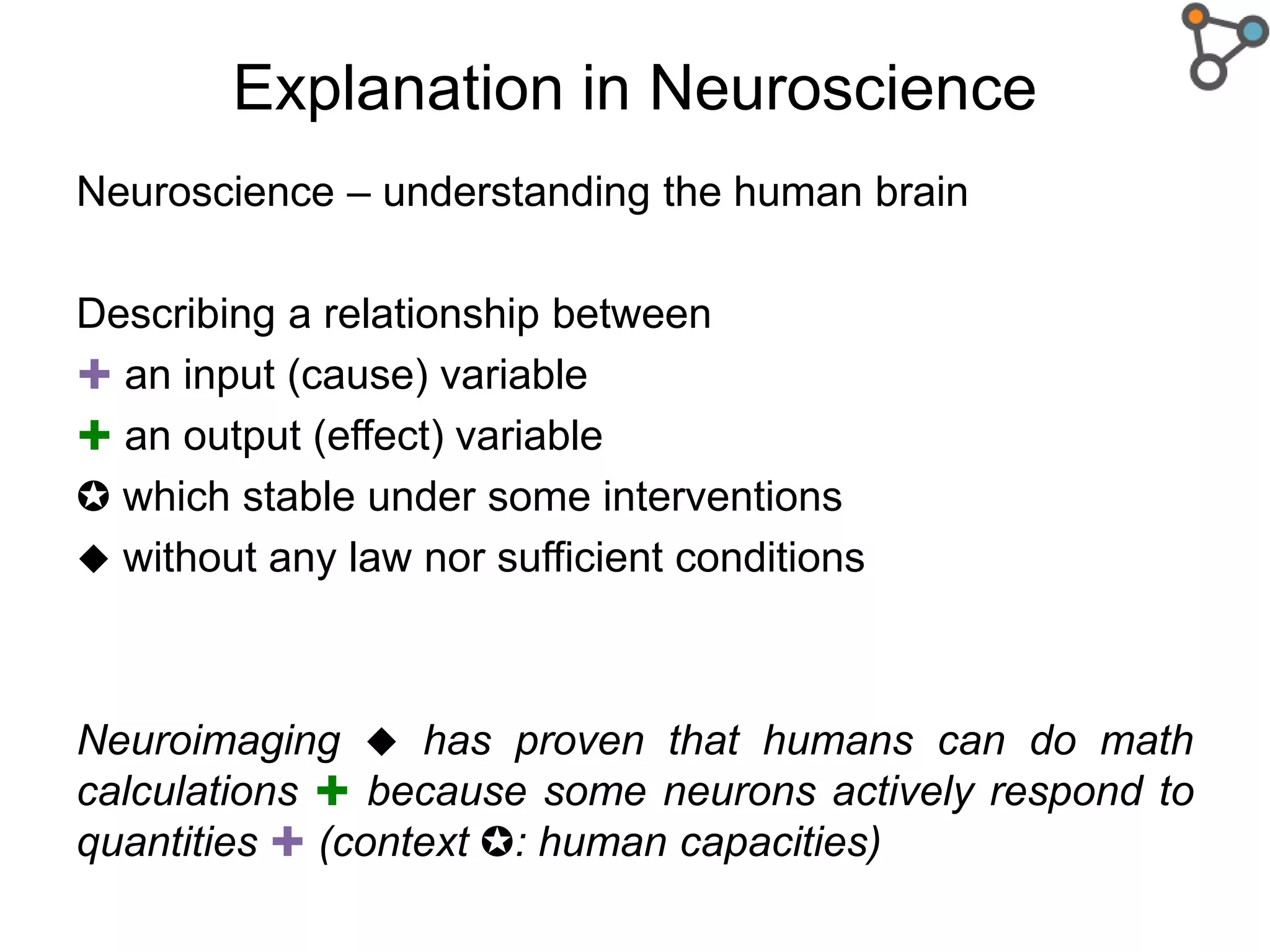
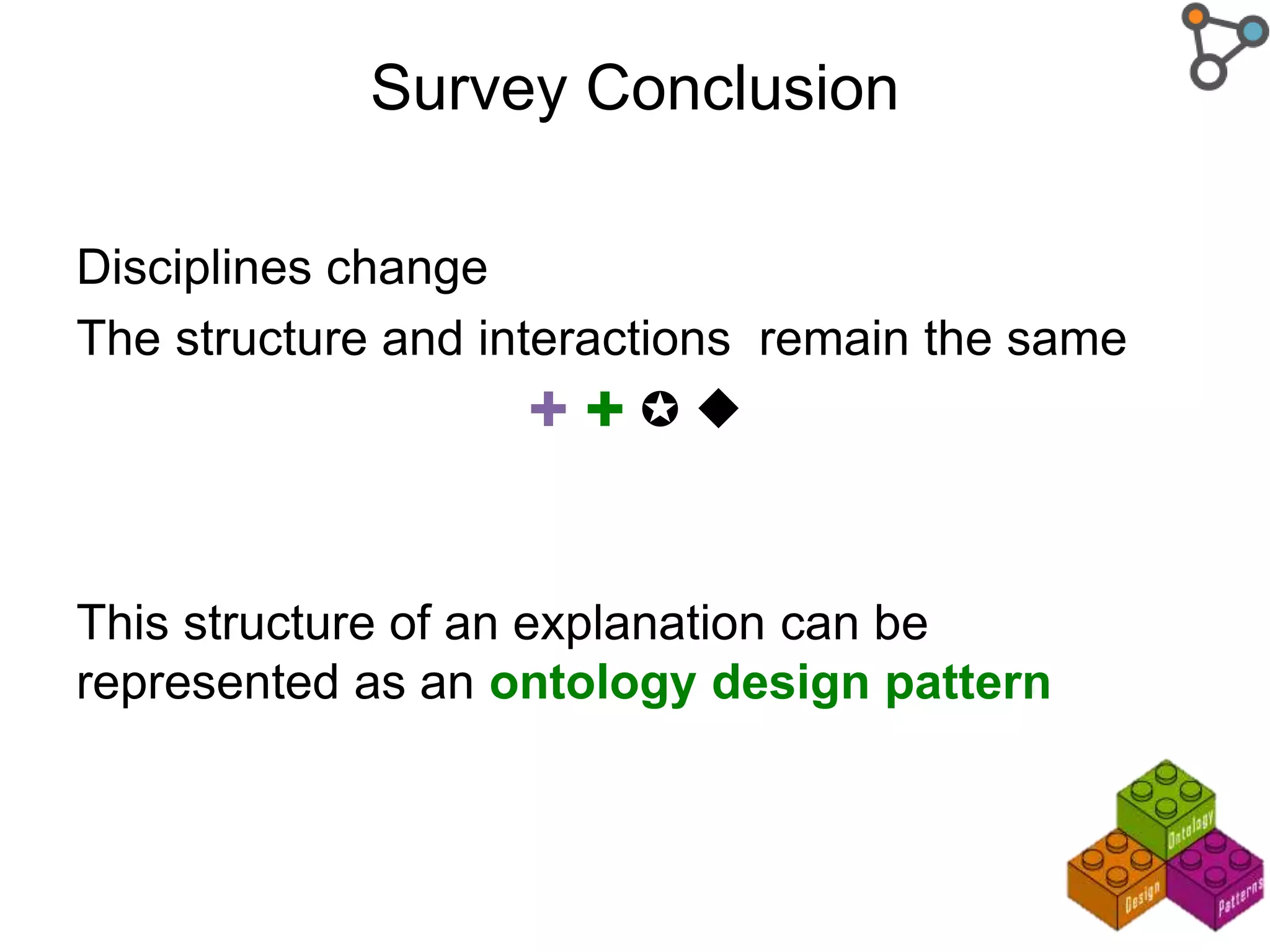
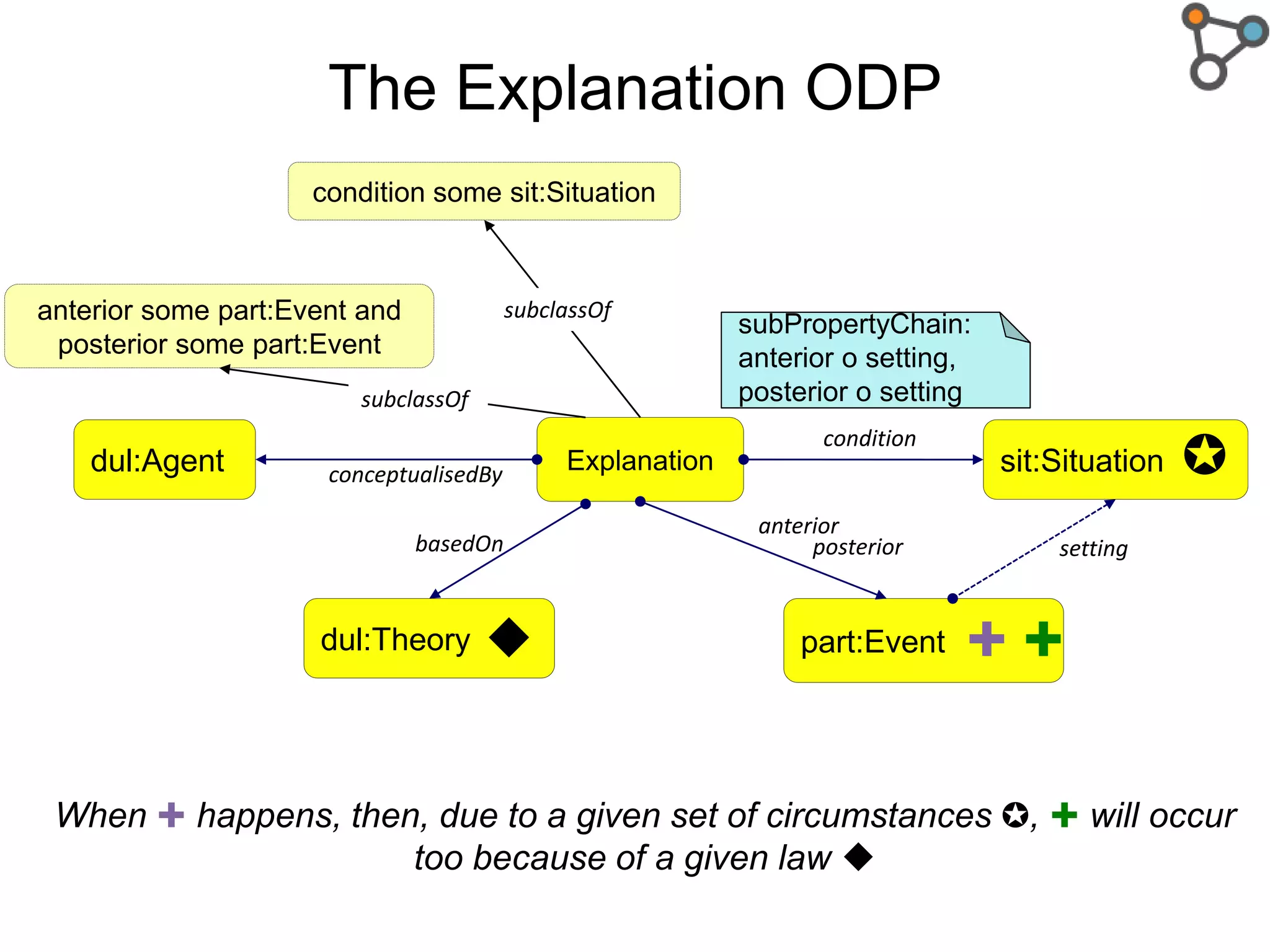
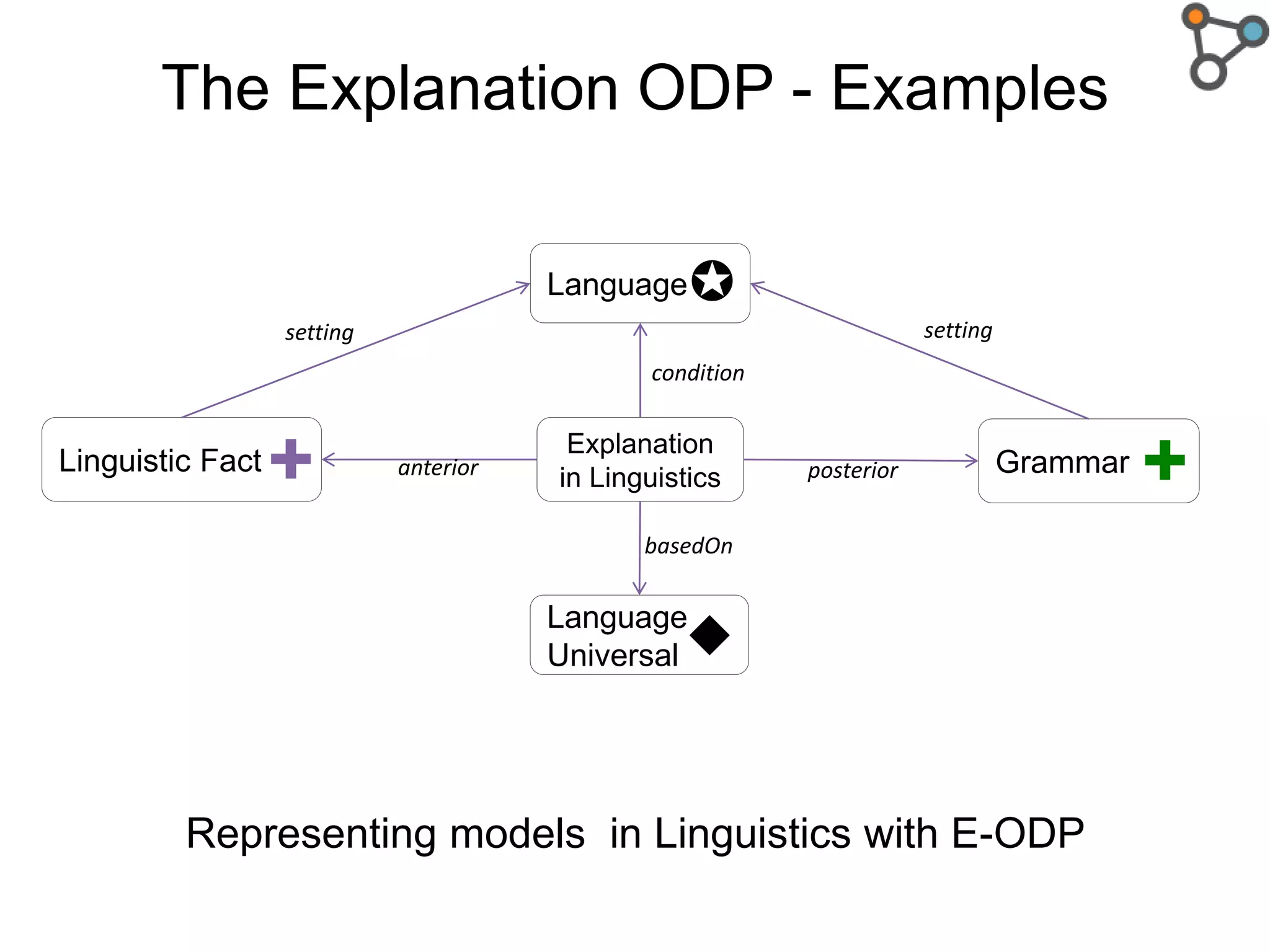
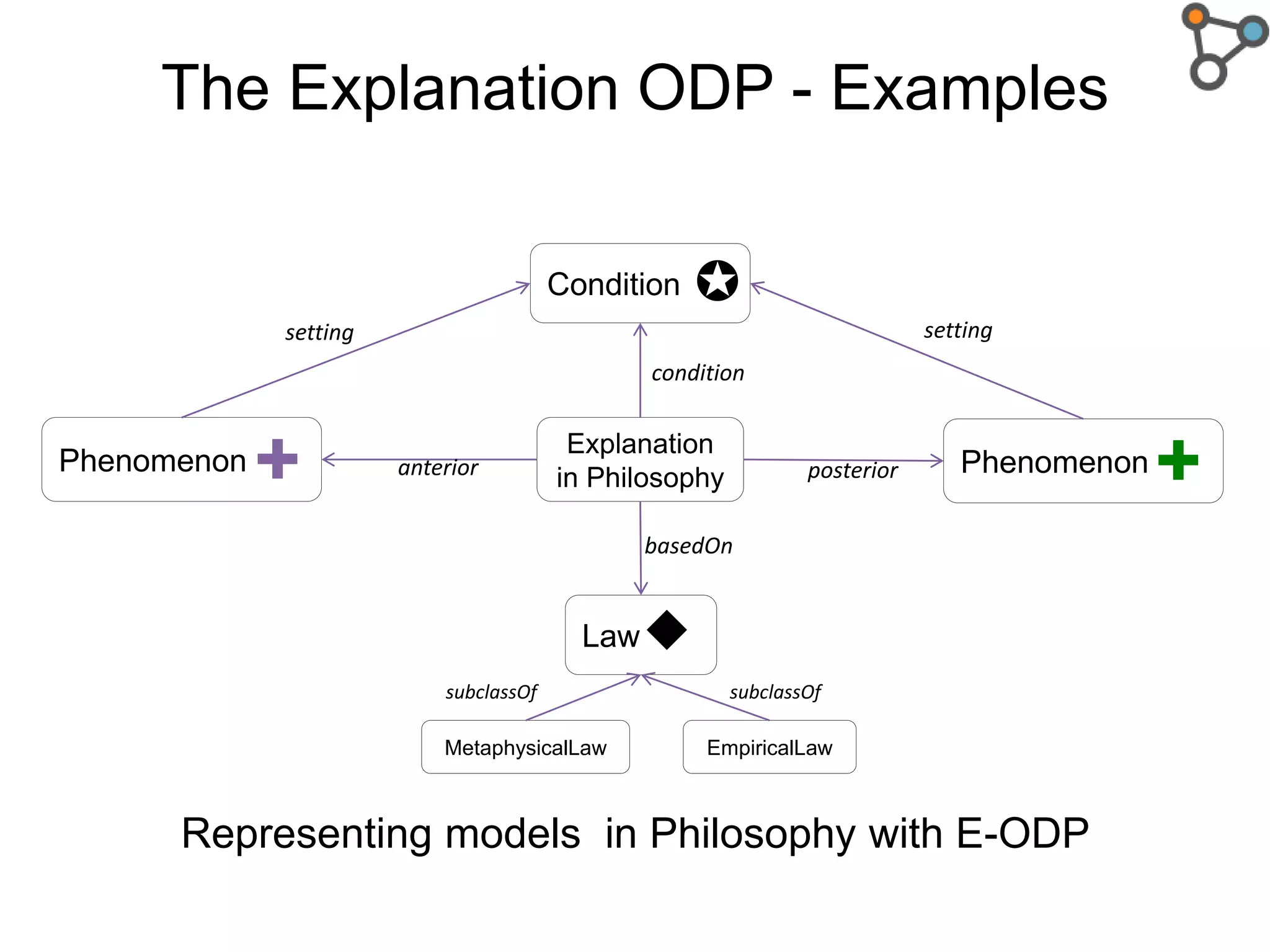
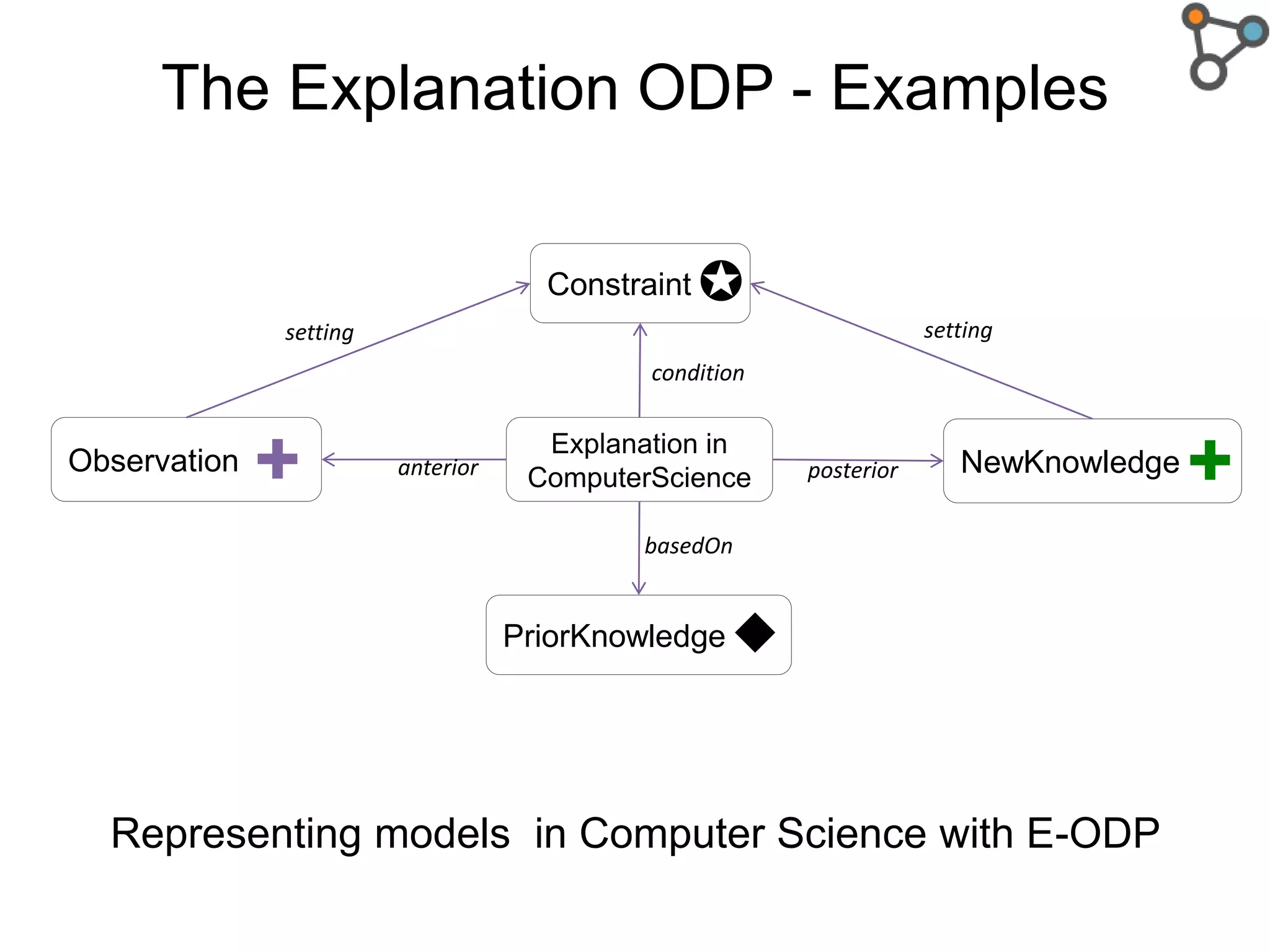
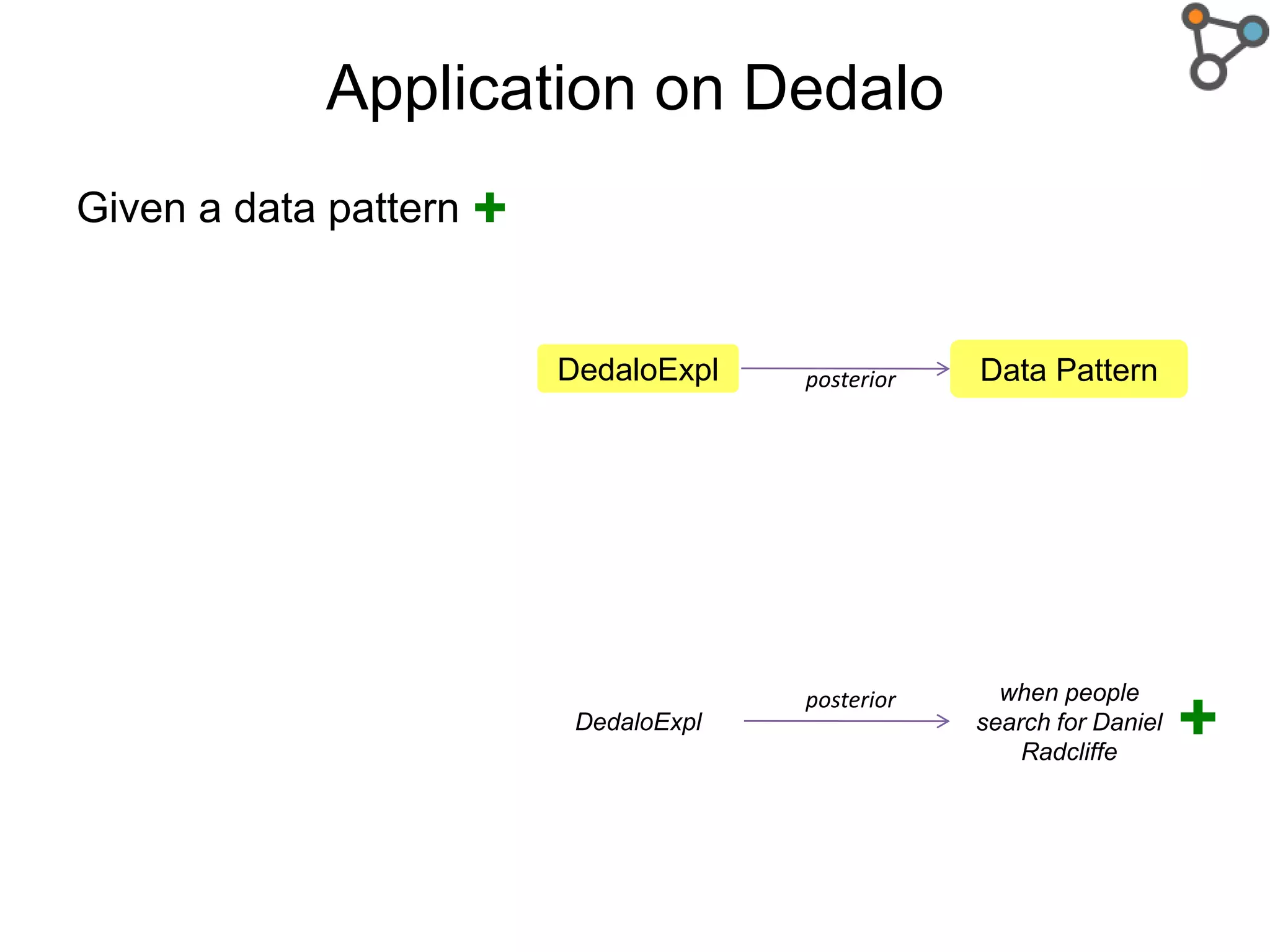
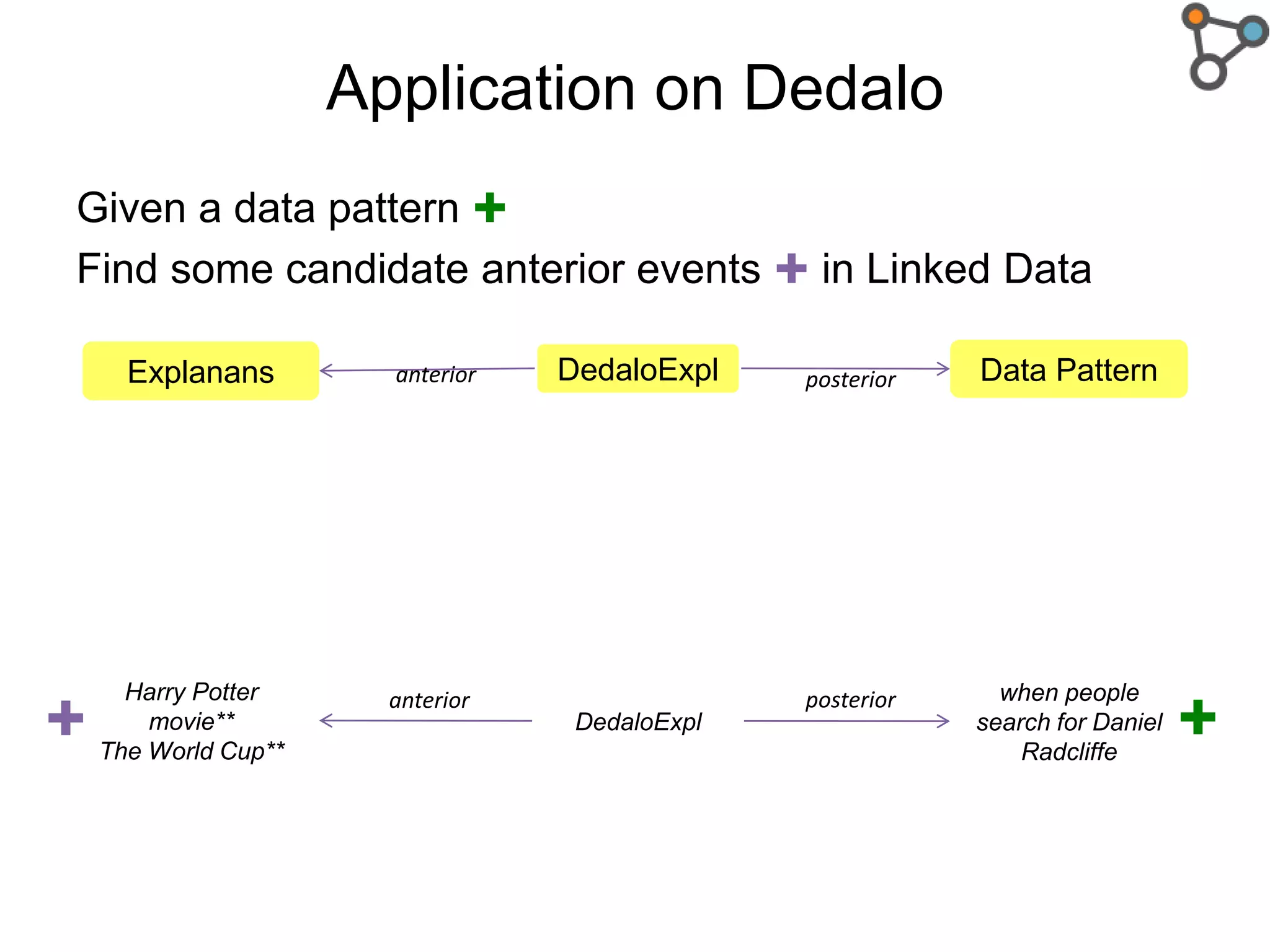
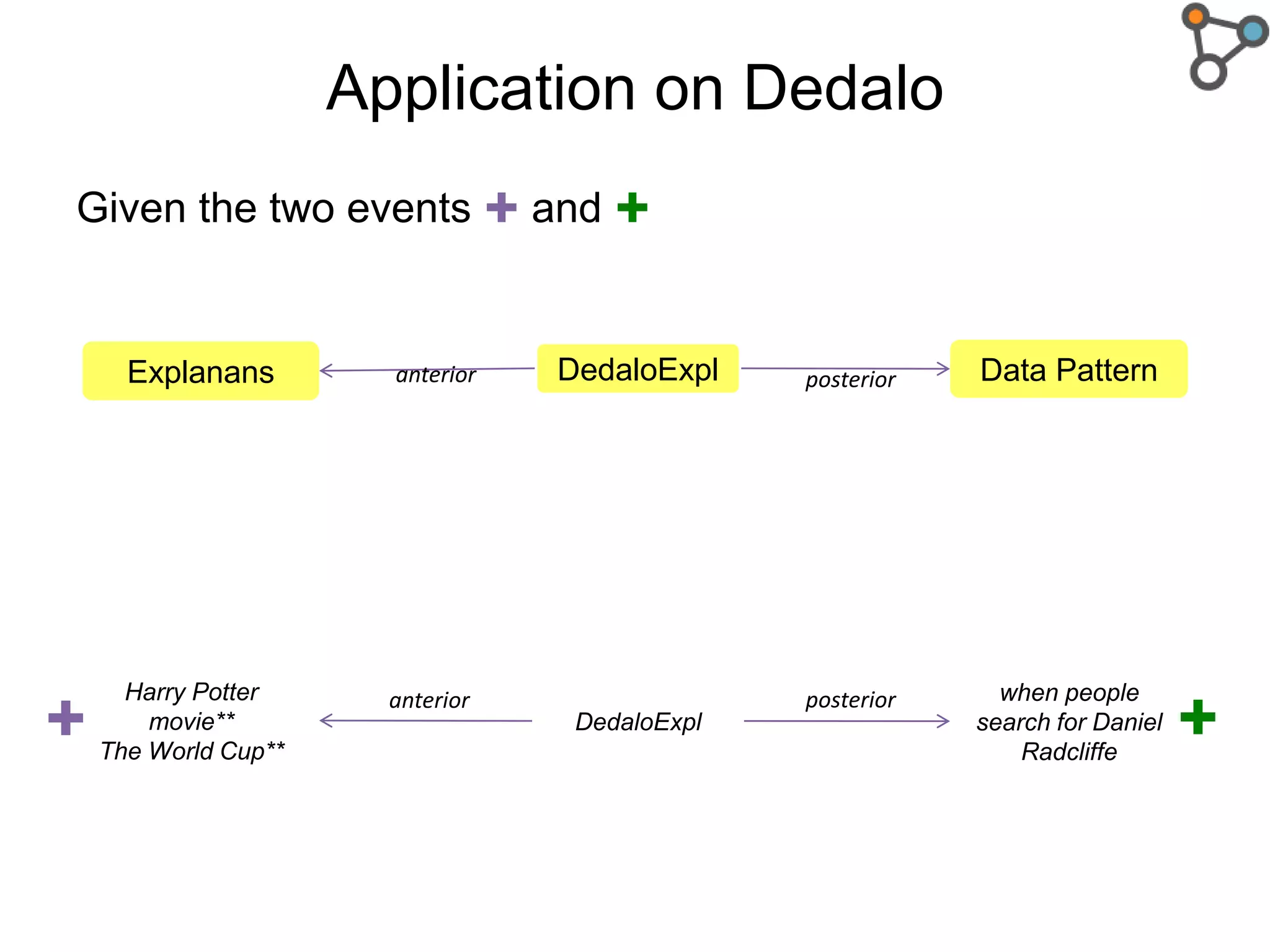
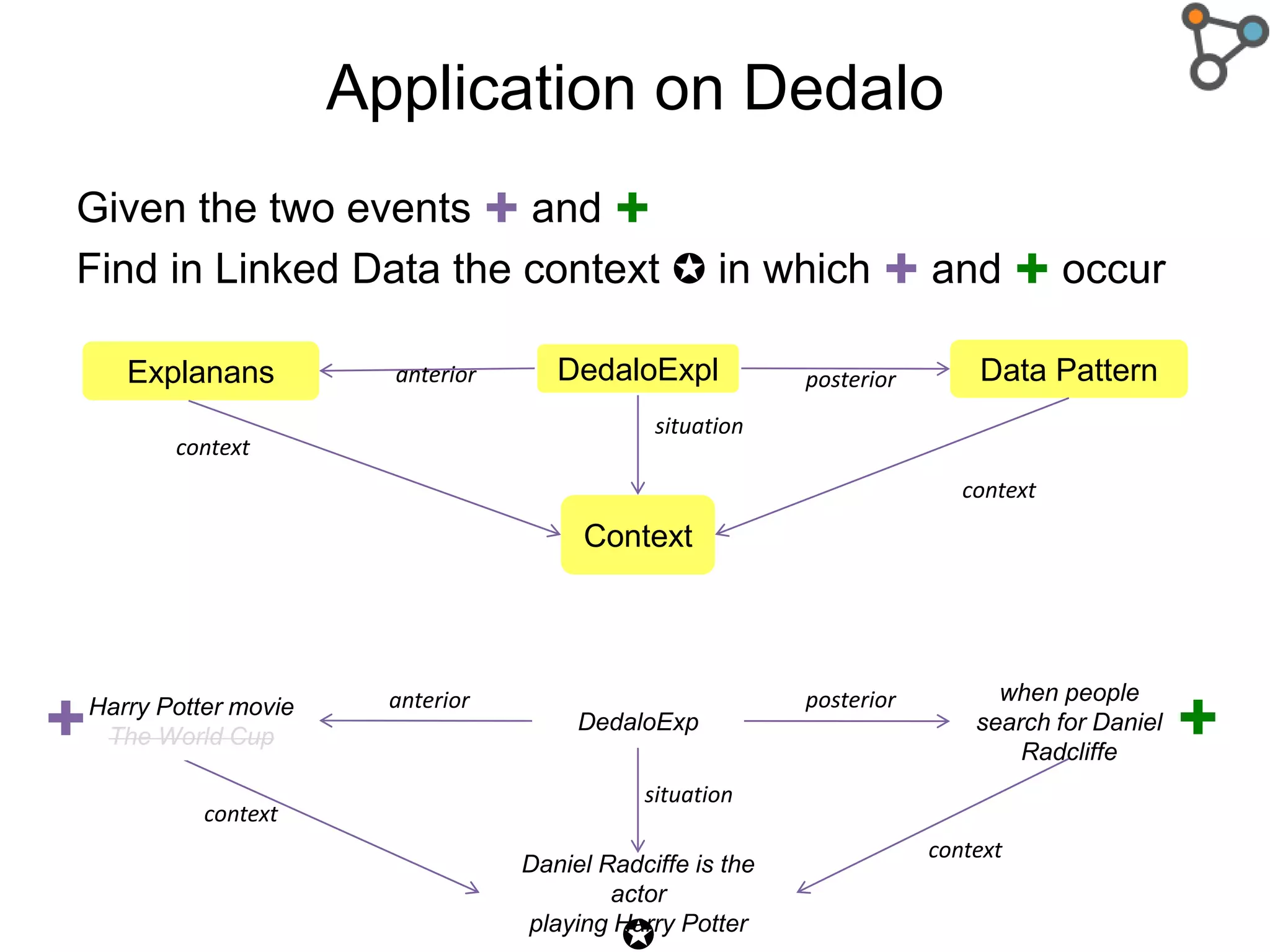
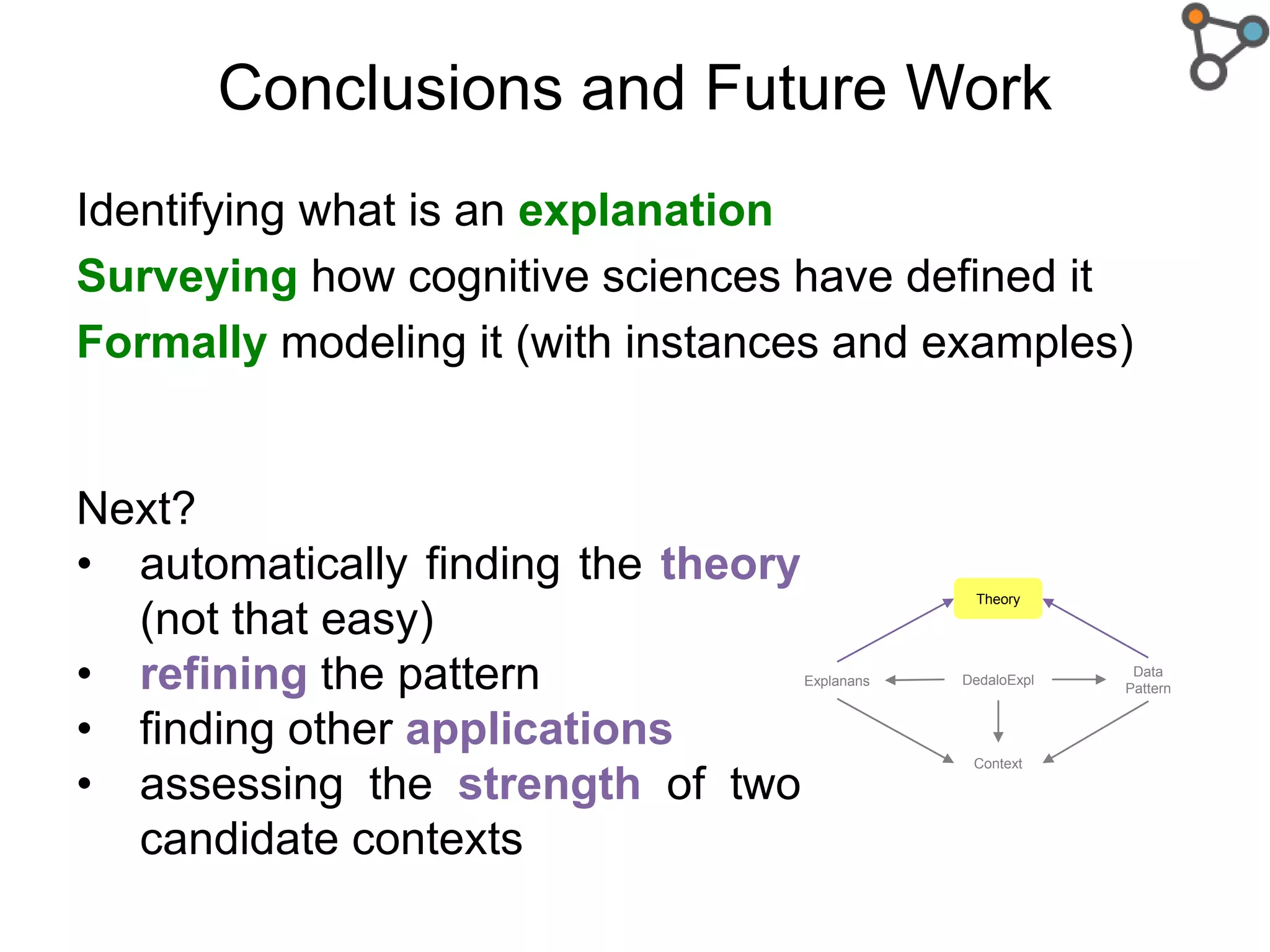
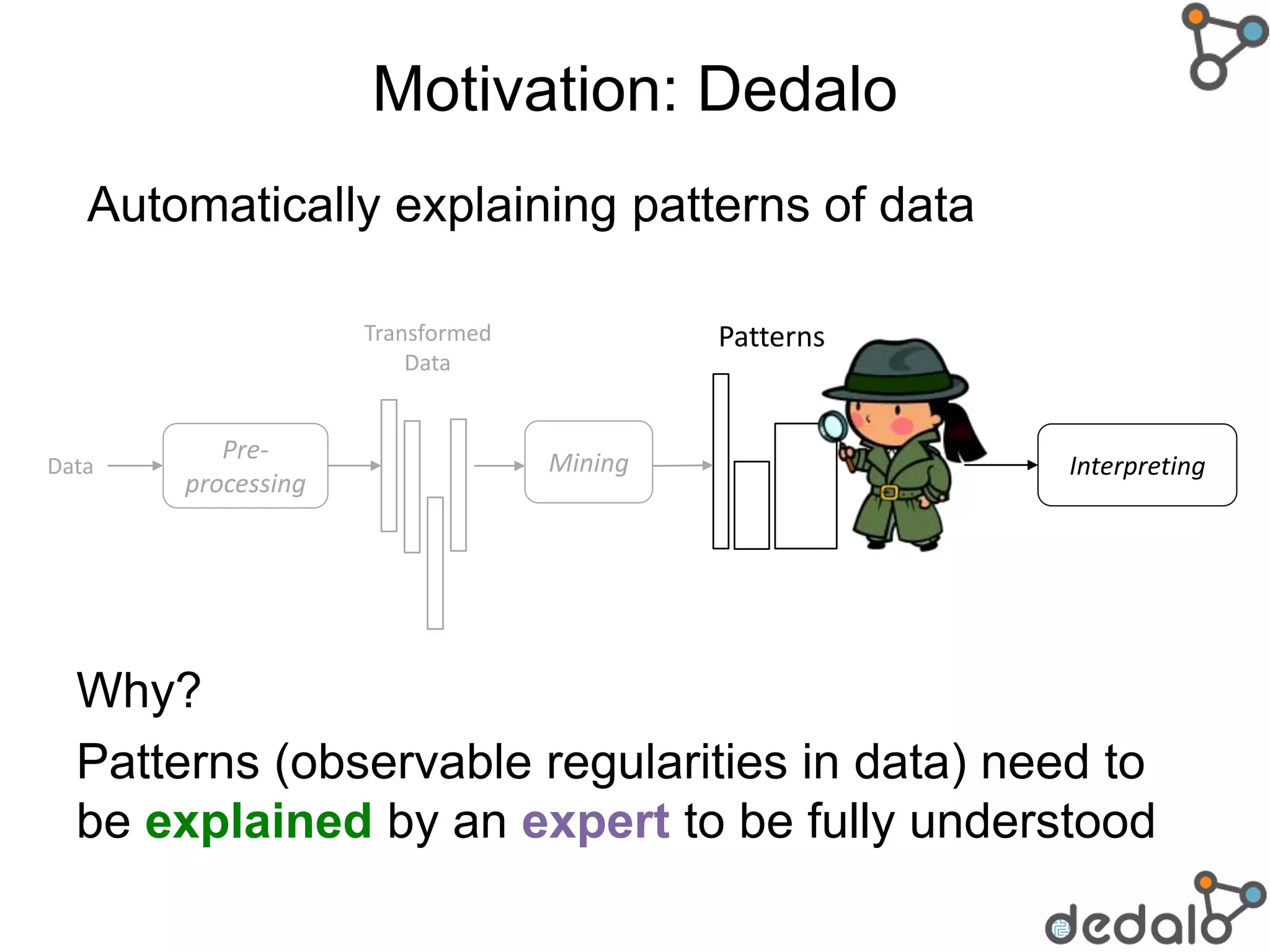
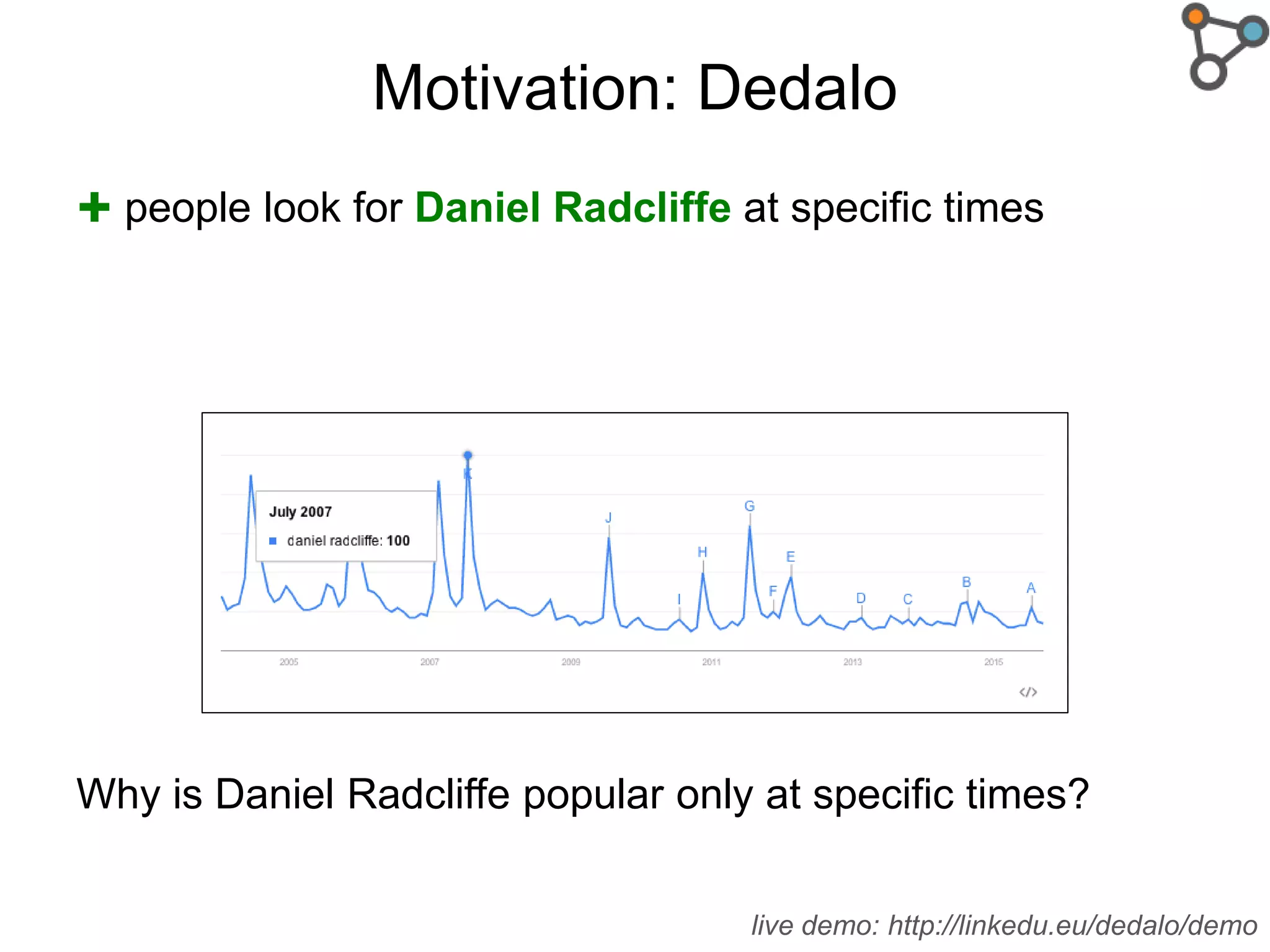
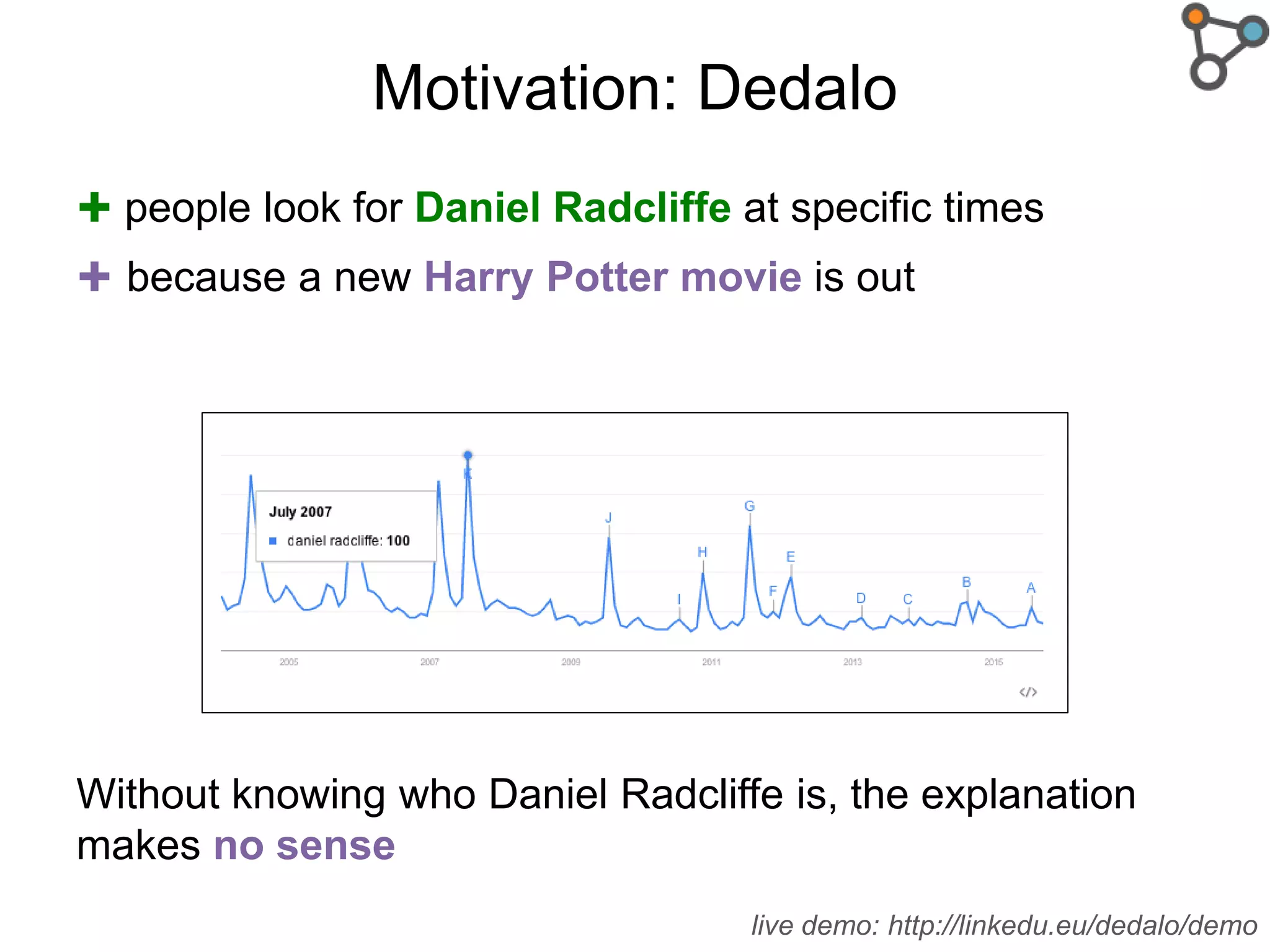
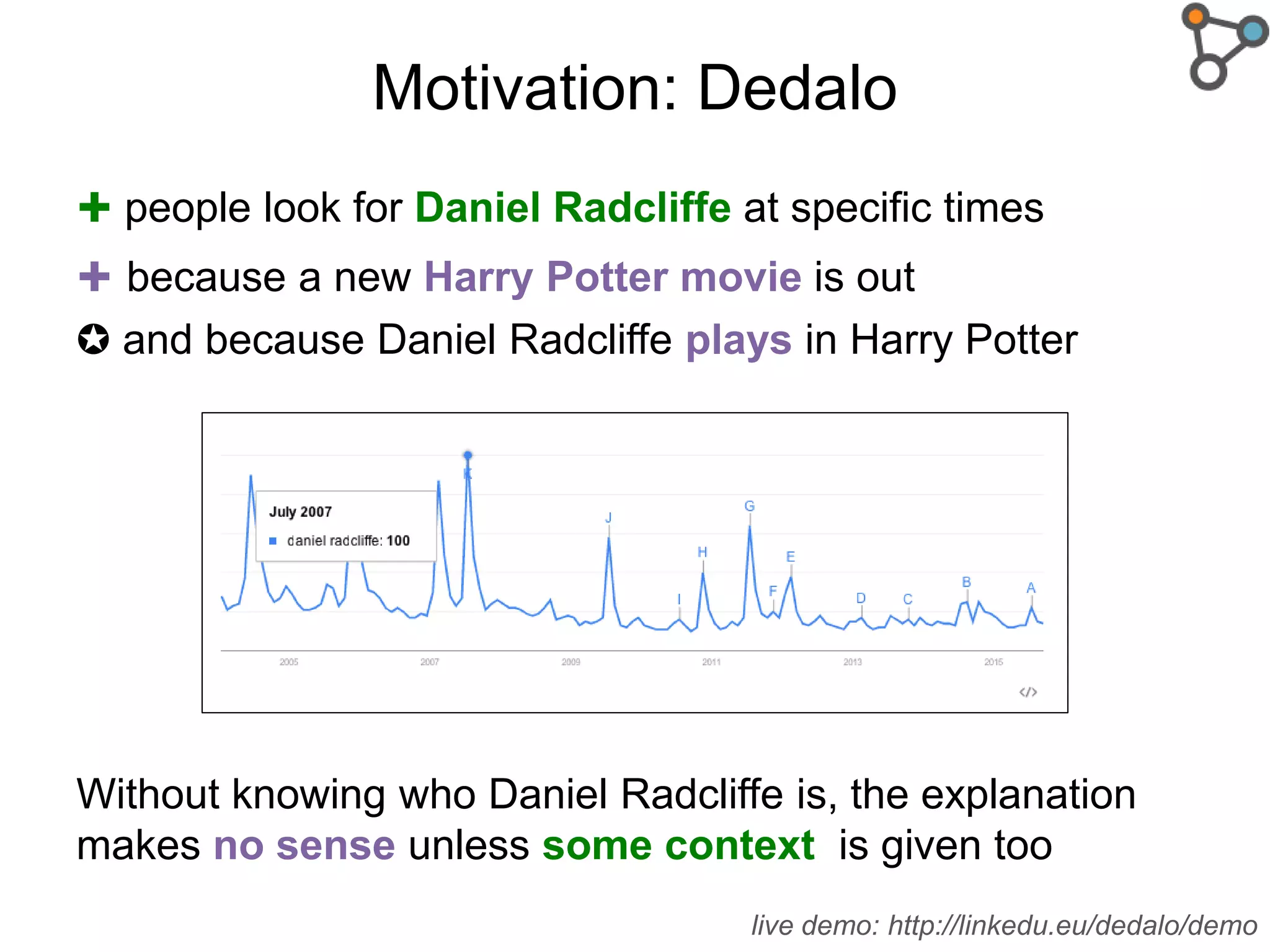
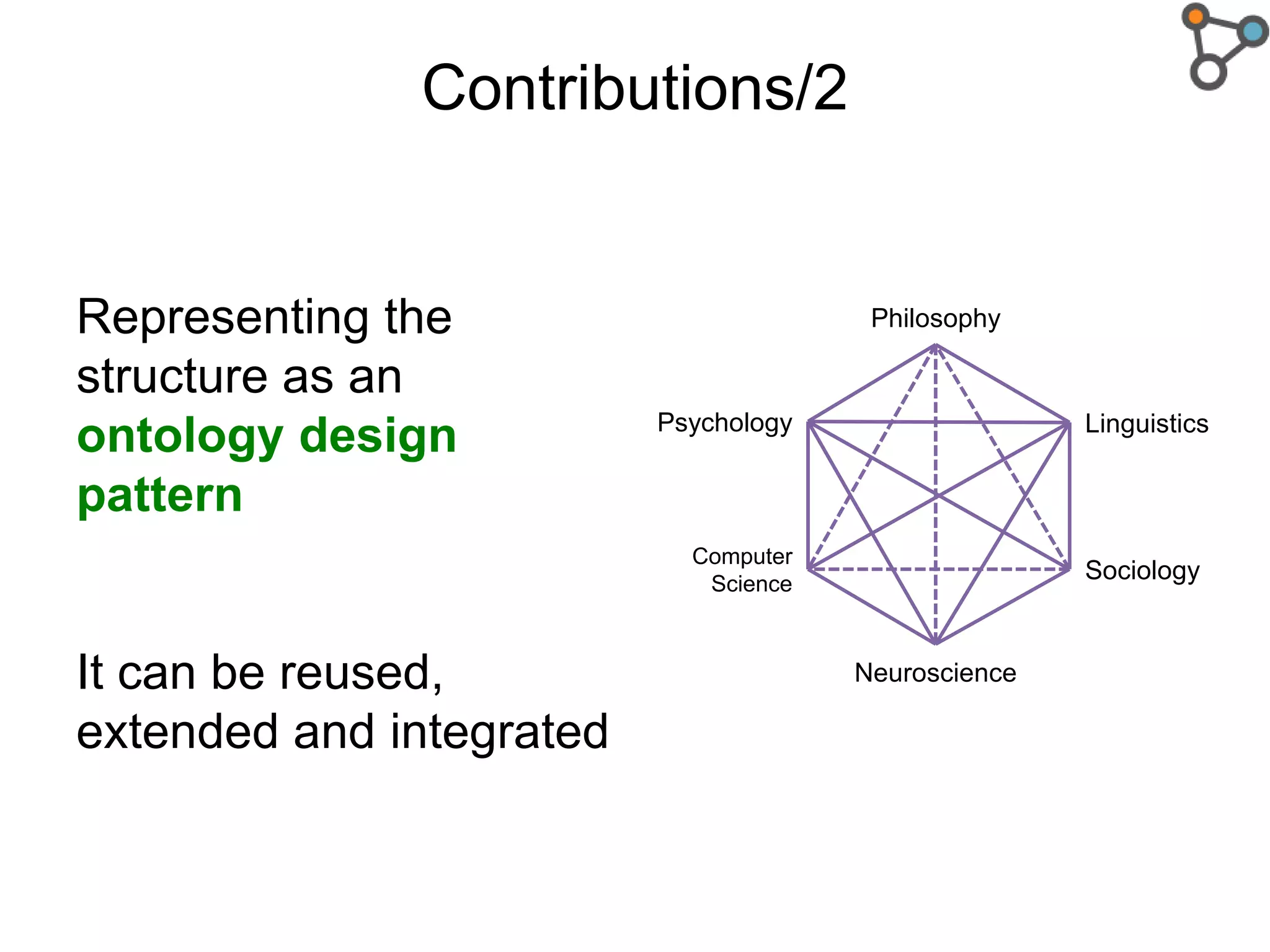
The document discusses the need for a formal definition of 'explanation' in various fields, including philosophy, neuroscience, linguistics, psychology, and computer science, to enhance understanding of data patterns. It presents an ontology design pattern (ODP) that structures the explanation process by illustrating the relationship between events, circumstances, and outcomes. The authors aim to refine this ODP and explore its applications, particularly in the Dedalo project for automatic data analysis and explanation.


![Approach
Philosophy
Neuroscience
Linguistics
Anthropology
Psychology
Artificial
Intelligence
How were “explanations” defined in Cognitive Science[1]?
H. Gardner (1985). The mind’s new science: A history of the cognitive revolution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kcap2015-151009174409-lva1-app6892/75/An-Ontology-Design-Pattern-to-Define-Explanations-8-2048.jpg)
![Contributions/1
Philosophy
Neuroscience
Linguistics
Sociology
Psychology
Computer
Science
Surveying “explanations”
in Cognitive Science
Structure : ✚ ✚ ✪
“When ✚ happens, then,
due to a given set of
circumstances ✪, ✚ will
occur too because of a
given law ”[2]
E. Maaløe (2007). Modes of Explanation: From Rules to Emergence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kcap2015-151009174409-lva1-app6892/75/An-Ontology-Design-Pattern-to-Define-Explanations-9-2048.jpg)
![Explanation in Philosophy
Philosophy – asking questions and checking answers
Putting in a relation
✚ an event
✪ some initial conditions
✚ with an output phenomenon
according to a set of (empirical or metaphysical) laws
Planets are near ✚; what is near does not twinkle
; therefore, planets do not twinkle ✚ (context ✪: planets)
[Aristotles]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kcap2015-151009174409-lva1-app6892/75/An-Ontology-Design-Pattern-to-Define-Explanations-11-2048.jpg)