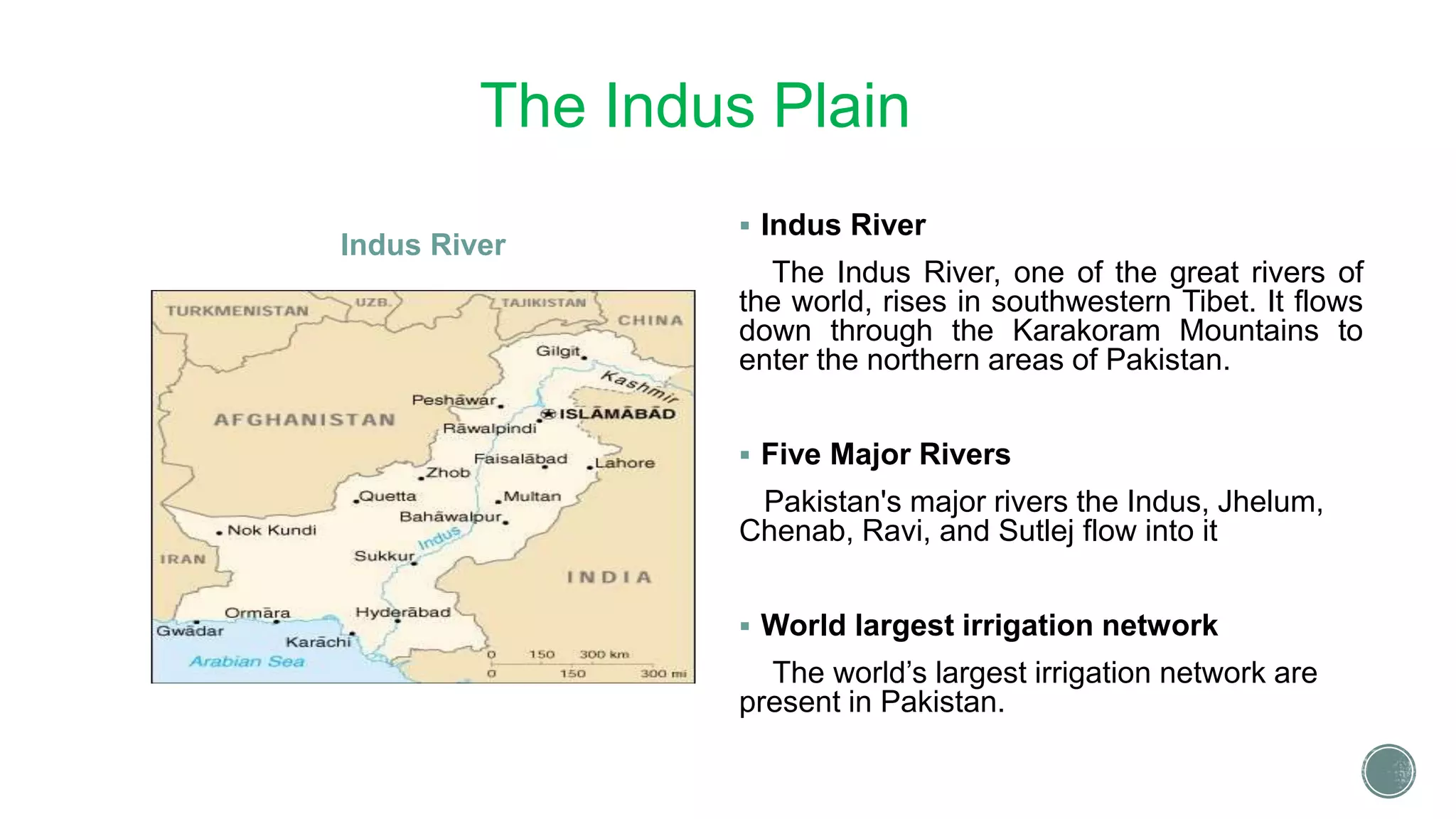
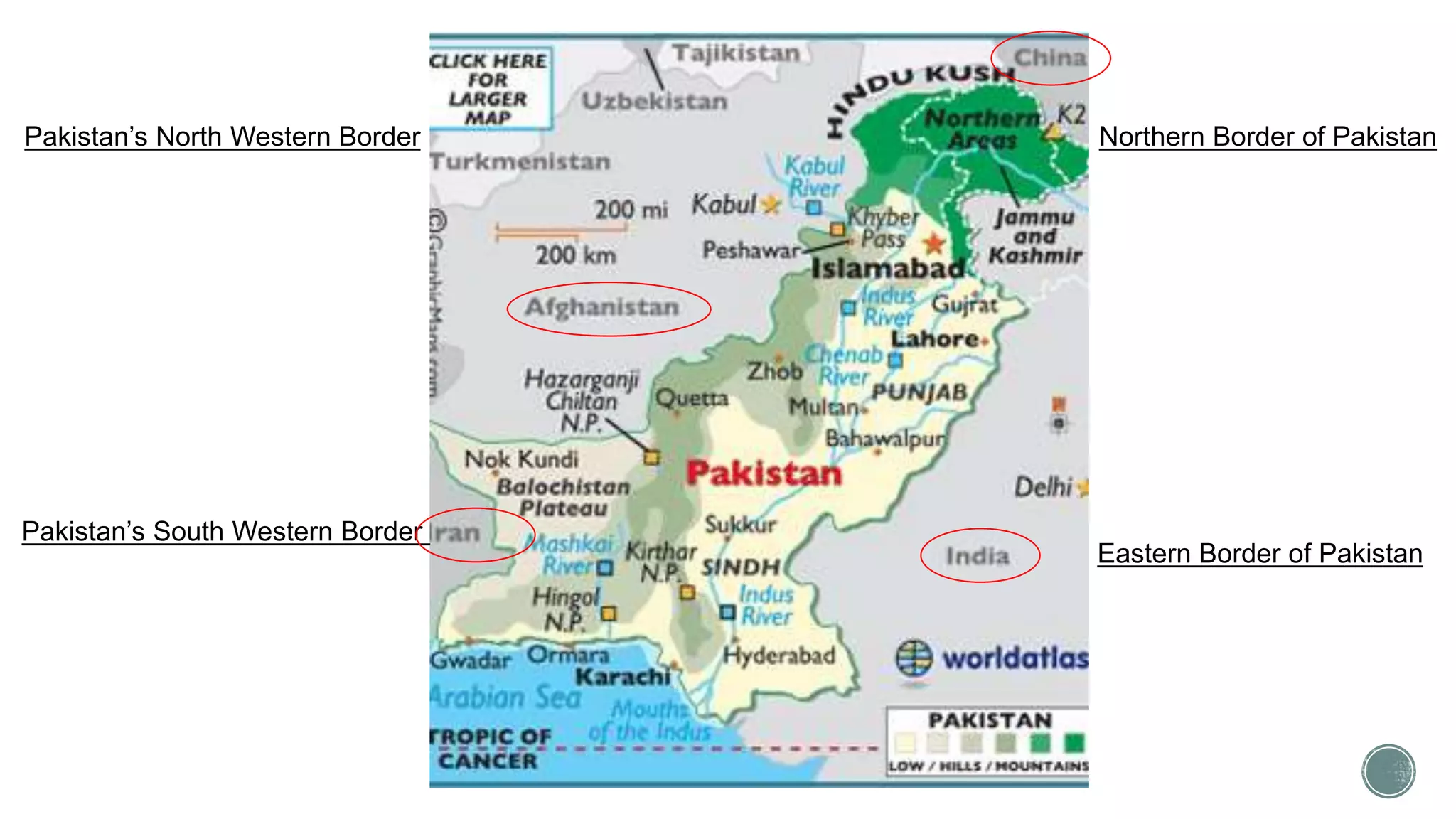
This document provides an overview of Pakistan, including its geography, climate, agriculture, and cultural relationships with China. It notes that Pakistan has diverse terrain including northern highlands, the Indus plain, and deserts. The country's geography has both traditional and modern geopolitical importance. Agriculture, especially wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane, is a key part of Pakistan's economy. The document also discusses Pakistan gaining independence in 1947 and establishing diplomatic relations with China in 1950 and 1951.