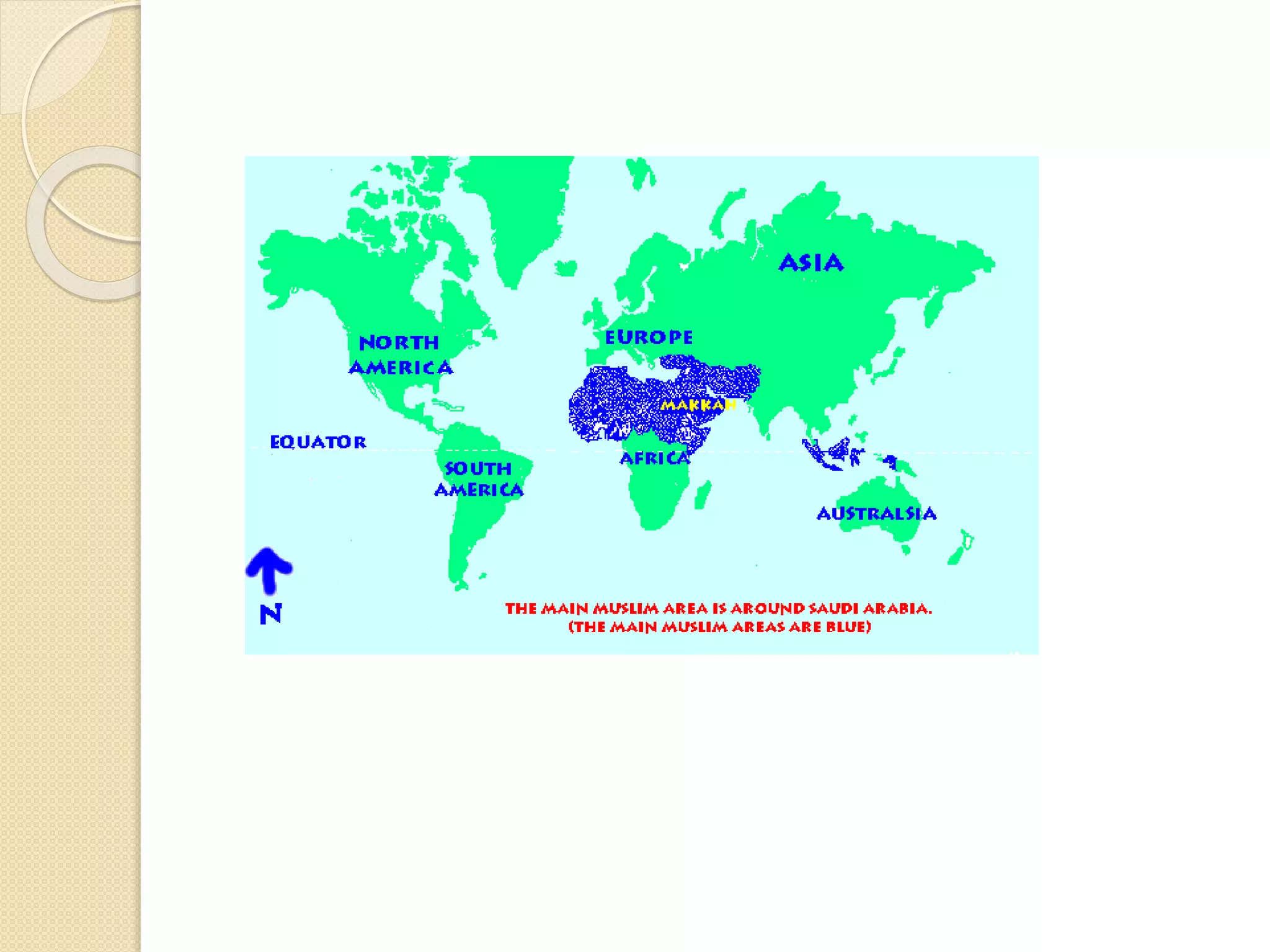
The document provides information about the religion of Islam. It states that Islam is the world's second largest religion with over 1 billion followers who are called Muslims. The core beliefs of Islam include the oneness of God whose name is Allah, and that Muhammad is God's final prophet. The document outlines some of the main aspects of the Islamic faith such as the Quran being the holy book, the 5 Pillars of Islam including prayer and fasting, festivals like Eid, rules around mosques and the importance of the pilgrimage to Mecca.