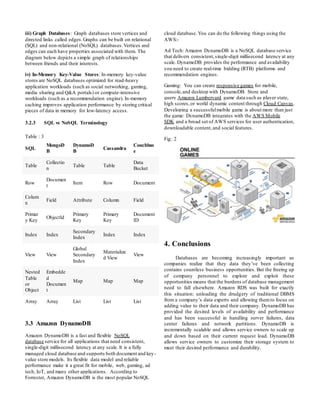
Amazon Web Services provides several fully managed database services, including Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for relational databases, Amazon DynamoDB for NoSQL databases, Amazon Redshift for data warehousing, and Amazon ElastiCache for caching. RDS supports databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. It provides tools for creating and managing database instances, backups, security groups and more. Users pay based on factors like the database type, storage size and throughput used.
![Amazon Web Services [Database]
A. Nishant Bhardwaj
Computer Science and Mathematics, Arkansas State University, Jonesboro, Arkansas, U.S.A
Abstract - Amazon Web Services provides fully managed
relational and NoSQL database services, as well as fully
managed in-memory caching as a service and a fully managed
data-warehouse service. In this report we will put a glance on
the the services AWS database provides to its
clients/customers. These database services are fully managed
and can be launched in minutes with just a few clicks. AWS
database services include Amazon Relational Database
Service (Amazon RDS), with support for six commonly used
database engines, Amazon Aurora, a MySQL-compatible
relational database with five times the performance, Amazon
DynamoDB, a fast and flexible NoSQL database service,
Amazon Redshift, a petabyte-scale data warehouse service,
and Amazon Elasticache, an in-memory cache service. AWS
also provides the AWS Database Migration Service, a service
which makes it easy and inexpensive to migrate your
databases to AWS cloud.
Keywords: Amazon RDS, Dynamo DB,
1 Introduction
In 2006, Amazon Web Services (AWS) began offering
IT infrastructure services to businesses in the form of web
services—now commonly known as cloud computing. One of
the key benefits of cloud computing is the opportunity to
replace up-front capital infrastructure expenses with low
variable costs that scale with your business. With the cloud,
businesses no longer need to plan for and procure servers and
other IT infrastructure weeks or months in advance. Instead,
they can instantly spin up hundreds orthousands of servers in
minutes and deliver results faster. Today, Amazon Web
Services provides a highly reliable, scalable, low-cost
infrastructure platform in the cloud that powers hundreds of
thousands of businesses in 190 countries around the world.
This white paper is an introduction to the AWS cloud
computing platform. It discusses the advantages of cloud
computing and the fundamentals of AWS. It provides an
overview of the AWS services that comprise the platform.
2 Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute
power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources
through a cloud services platformvia the internet with pay-as-
you-go pricing. Whether you are running applications that
share photos to millions of mobile users or you’re supporting
the critical operations of your business, a cloud services
platform provides rapid access to flexible and low cost IT
resources. With cloud computing, you can provision exactly
the right type and size of computing resources you need to
power your newest bright idea or operate your IT department.
You can access as many resources as you need, almost
instantly, and only pay for what you use.
2.1 The Differences that Distinguish AWS
AWS is readily distinguished from other vendors in the
traditional IT computing landscape because it is:
1.Flexible. AWS enables organizations to use the
programming models, operating systems, databases, and
architectures with which they are already familiar. In
addition, this flexibility helps organizations mix and match
architectures in order to serve their diverse business needs.
2.Cost-effective. With AWS, organizations pay only for what
they use, without up-front or long-term commitments.
3.Scalable and elastic. Organizations can quickly add and
subtract AWS resources to their applications in order to meet
customer demand and manage costs.
4.Secure. In order to provide end-to-end security and end-to-
end privacy, AWS builds services in accordance with security
best practices, provides the appropriate security features in
those services, and documents how to use those features.
5.Experienced. When using AWS, organizations can
leverage Amazon’s more than fifteen years of experience
delivering large-scale, global infrastructure in a reliable,
secure fashion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazonwebservices-180425225845/75/Amazon-web-services-1-2048.jpg)



![4 References
[1] https://aws.amazon.com/relational-database/
[2] https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s
&source=web&cd=6&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjxpY
W6iq_SAhVDxCYKHarcDpYQFgg2MAU&url=http%3A%2
F%2Flosnuevosguerreros.org%2Fpluginfile.php%2F16%2Fm
od_glossary%2Fattachment%2F461%2FWP_AWS_IntroToA
mazonRDS.pdf&usg=AFQjCNGZ7g07rtKflawkQe3MLVYN
9u-xMg&bvm=bv.148073327,d.eWE
[3] http://www.datastax.com/dbas-guide-to-nosq
[4] https://aws.amazon.com/products/databases/
[5] http://searchsqlserver.techtarget.com/definition/relationa
l-database
[6] https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/aws-rdbms-oracle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazonwebservices-180425225845/85/Amazon-web-services-7-320.jpg)