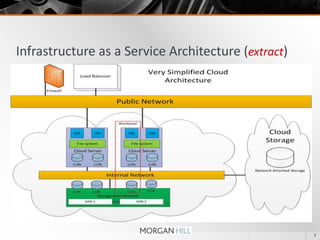
The document outlines a quick start course for enterprise architects focusing on Amazon AWS, covering cloud concepts, key AWS components, and best practices for architecting applications in the cloud. It includes hands-on practical exercises for deploying applications and managing resources, as well as discussions on security and hybrid cloud strategies. The course also details the infrastructure as a service architecture and various scaling strategies within AWS.