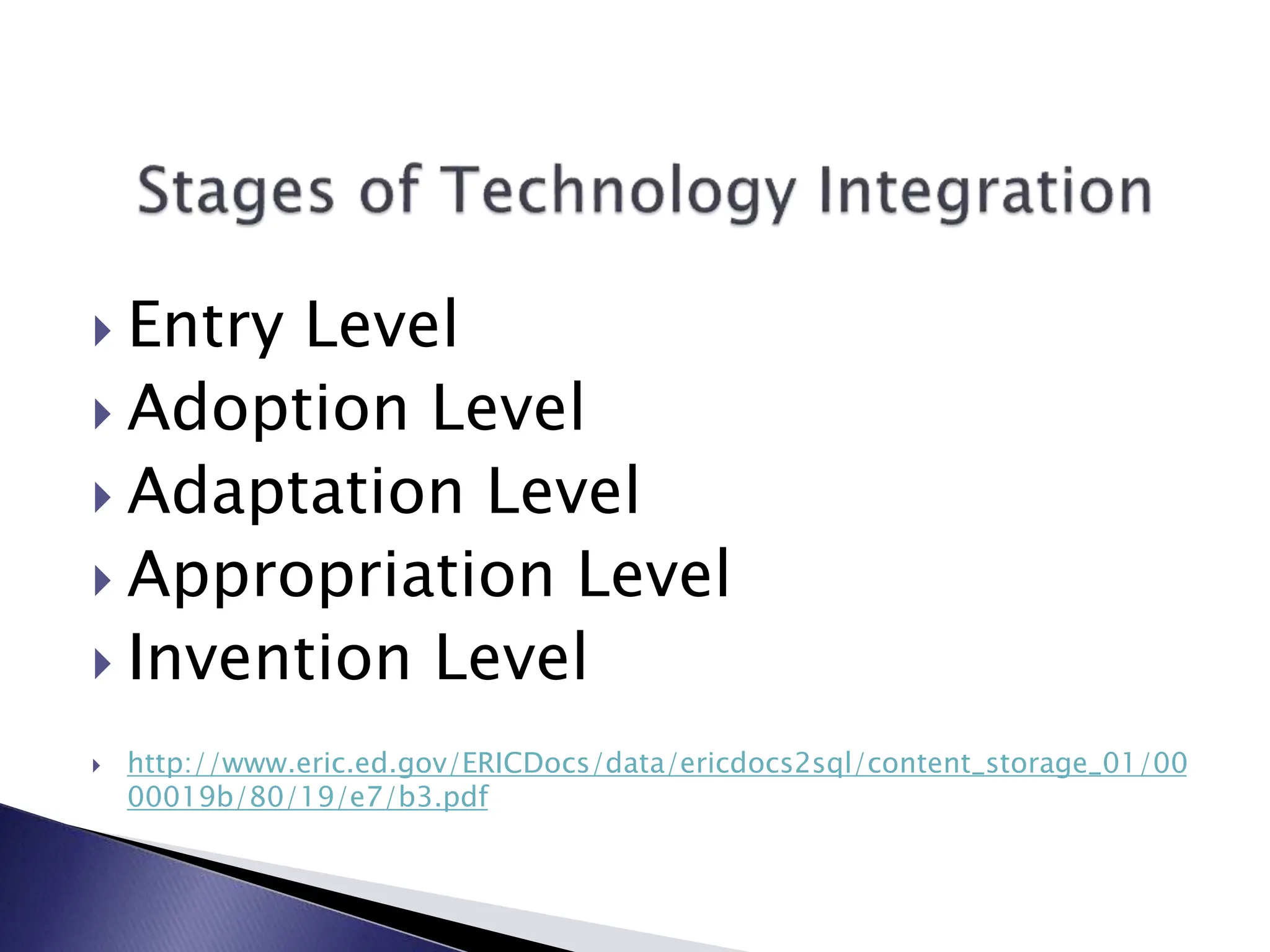
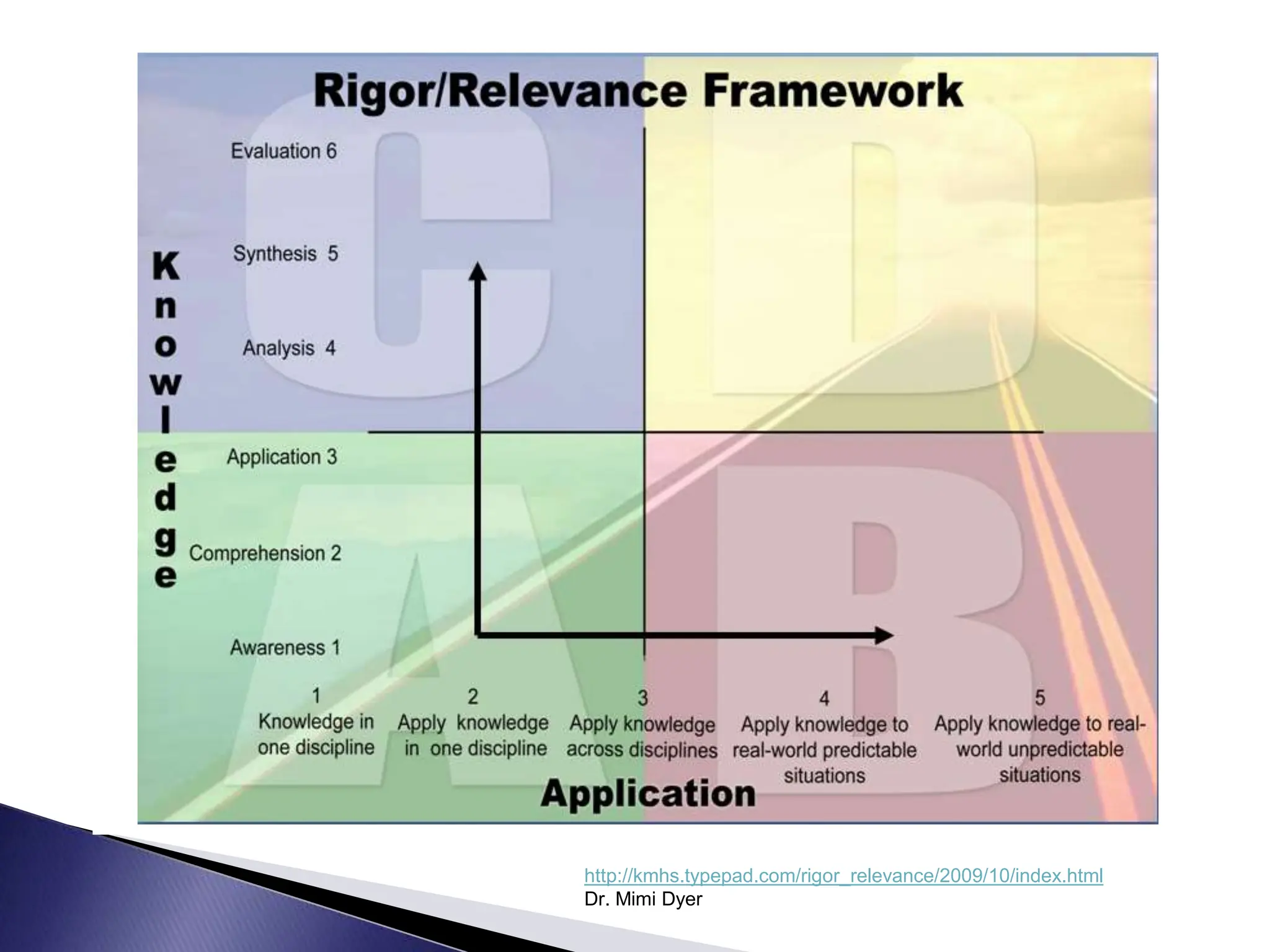
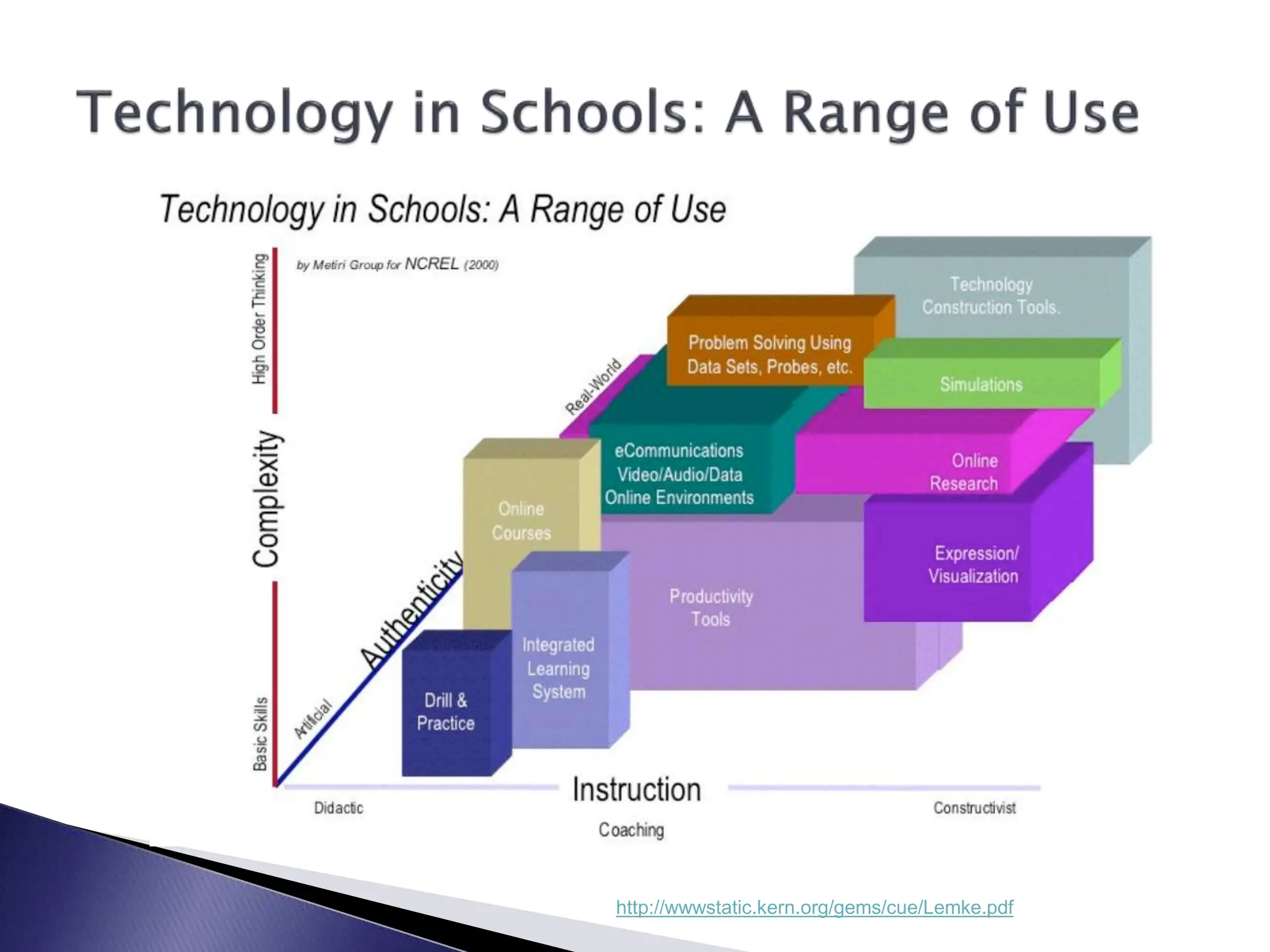
The LCSC Technology Conference details a program initiated three years ago for high school teachers, aiming to enhance teaching through technology with training and resource support. The program has expanded to 44 teachers and focuses on developing crucial skills in creativity, critical thinking, and digital citizenship. Feedback from participating teachers highlights improvements in student engagement and the effectiveness of integrating technology into learning.

























![“[What I like best is] my ability to
reflect and rethink my practice in
the classroom. My lessons have
been richer by integrating online
digital content.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alexandriaclassroomsofthefuture-240501142837-ed8bca67/75/Alexandria_Classrooms_of_the_Futureb-ppt-29-2048.jpg)


