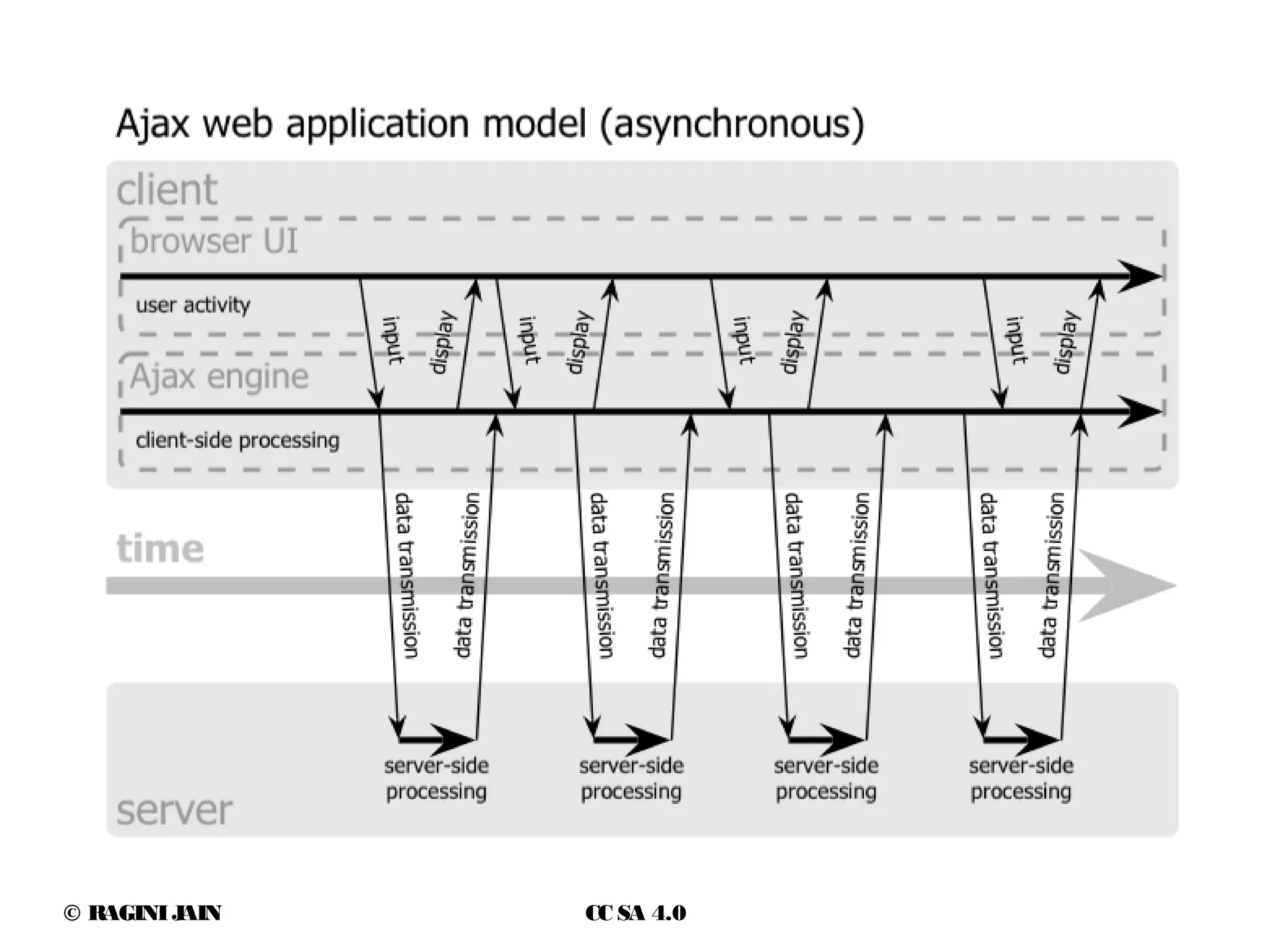
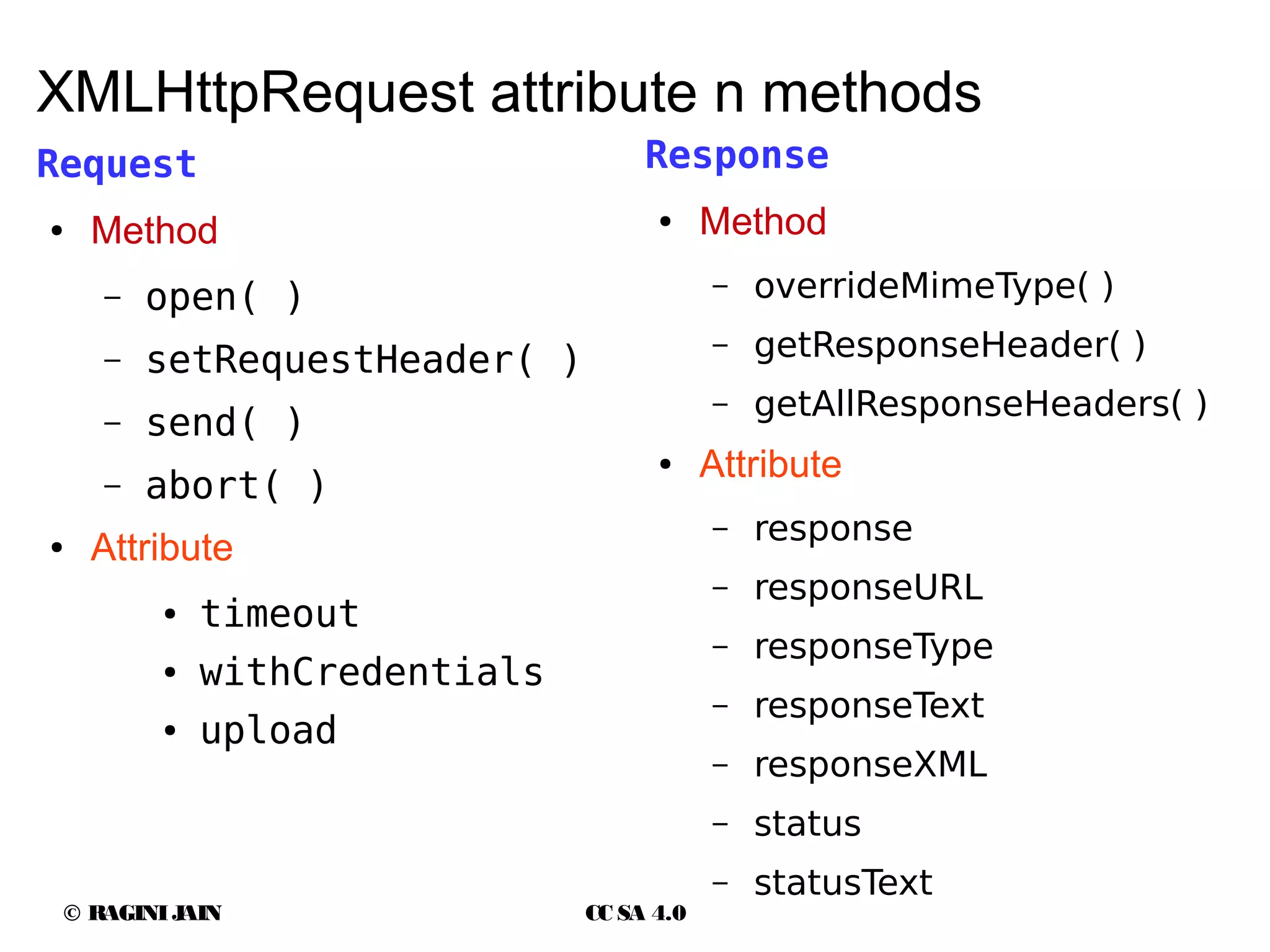
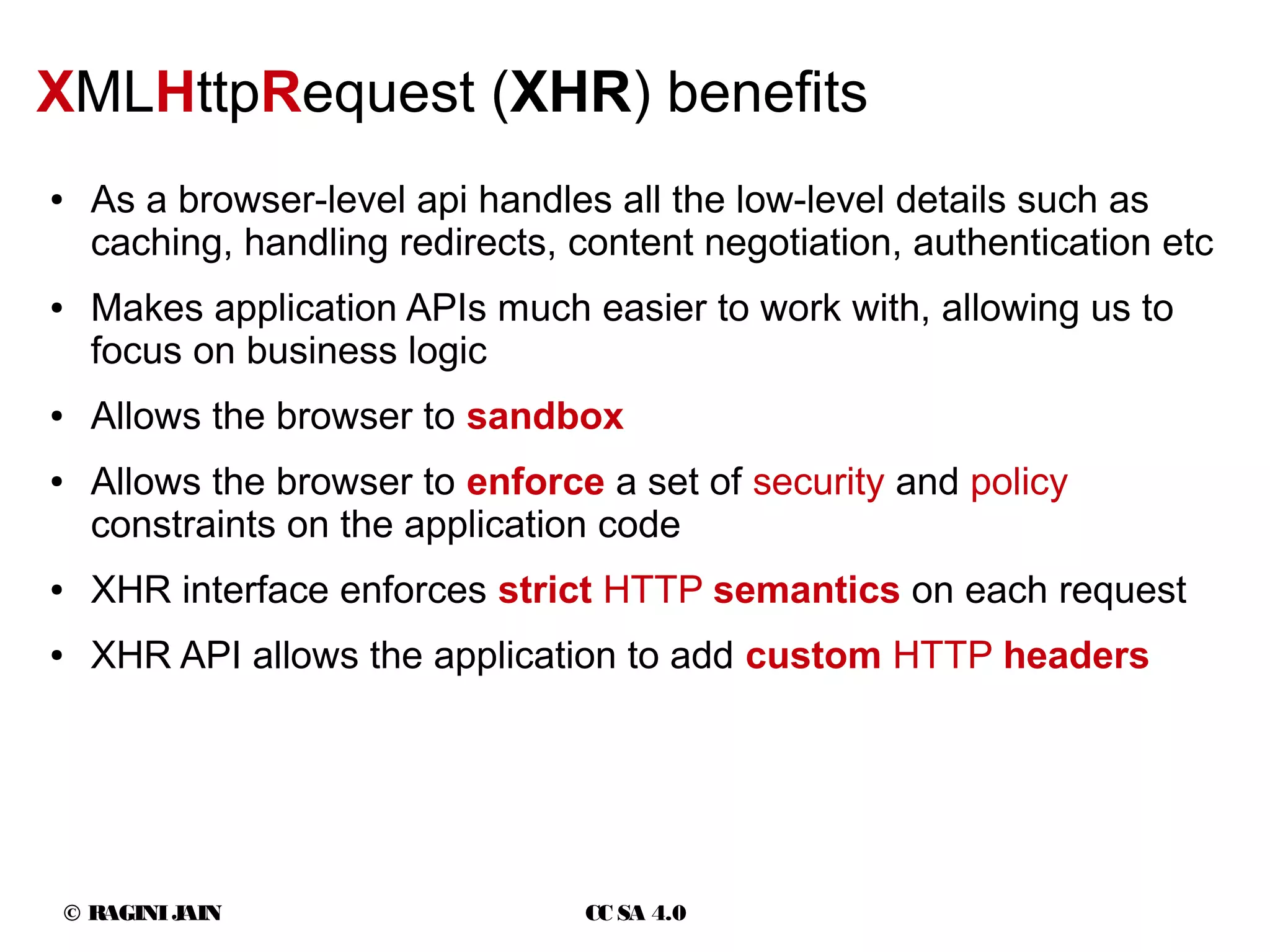
The document discusses Ajax and its usage in web applications. It provides an overview of Ajax including the XMLHttpRequest object, asynchronous requests, response types and events. It outlines best practices for using Ajax such as partial page updates, validation and status messages while avoiding overuse that could impact search engine optimization. Security considerations like cross-site scripting are also covered.


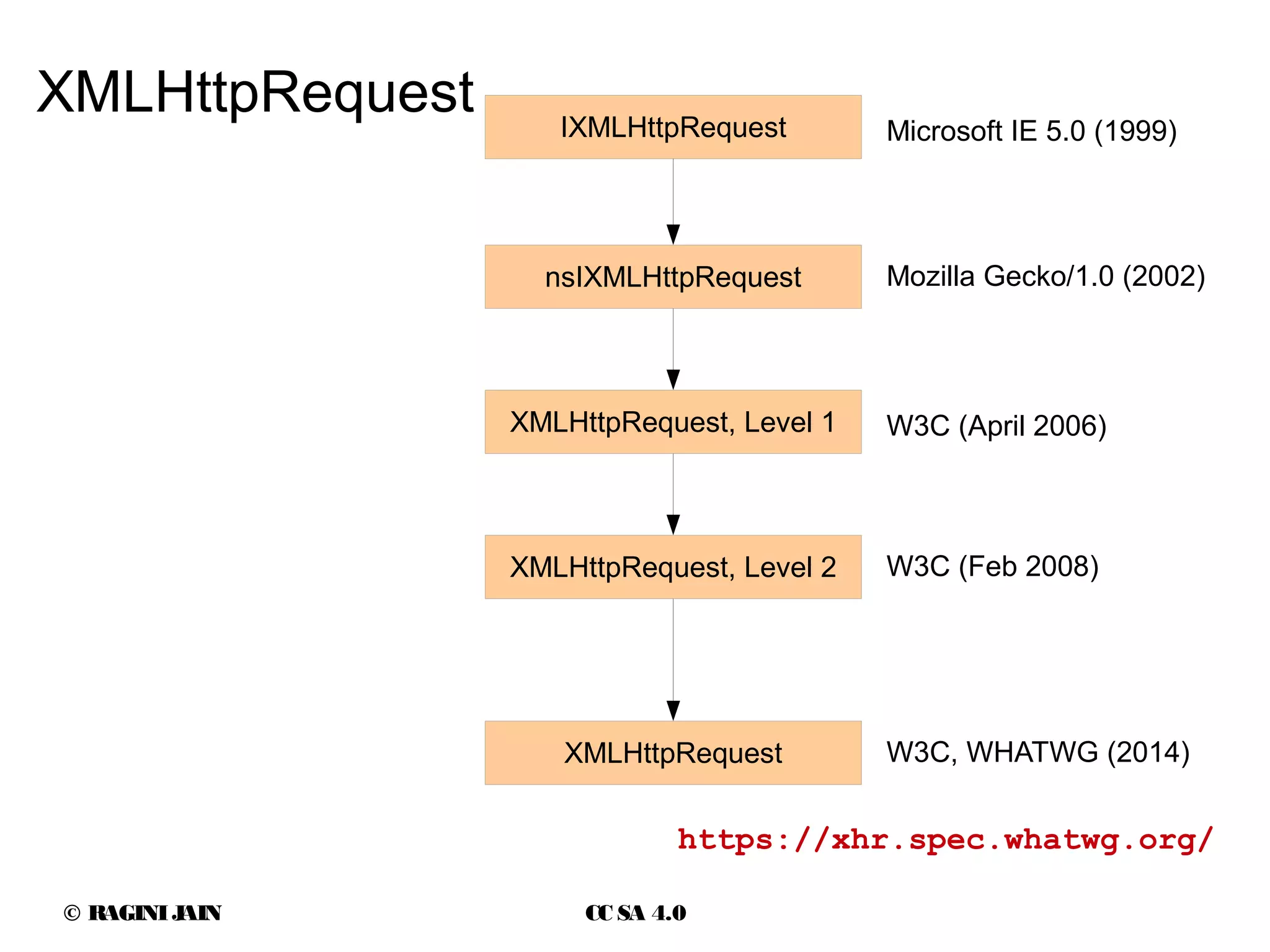
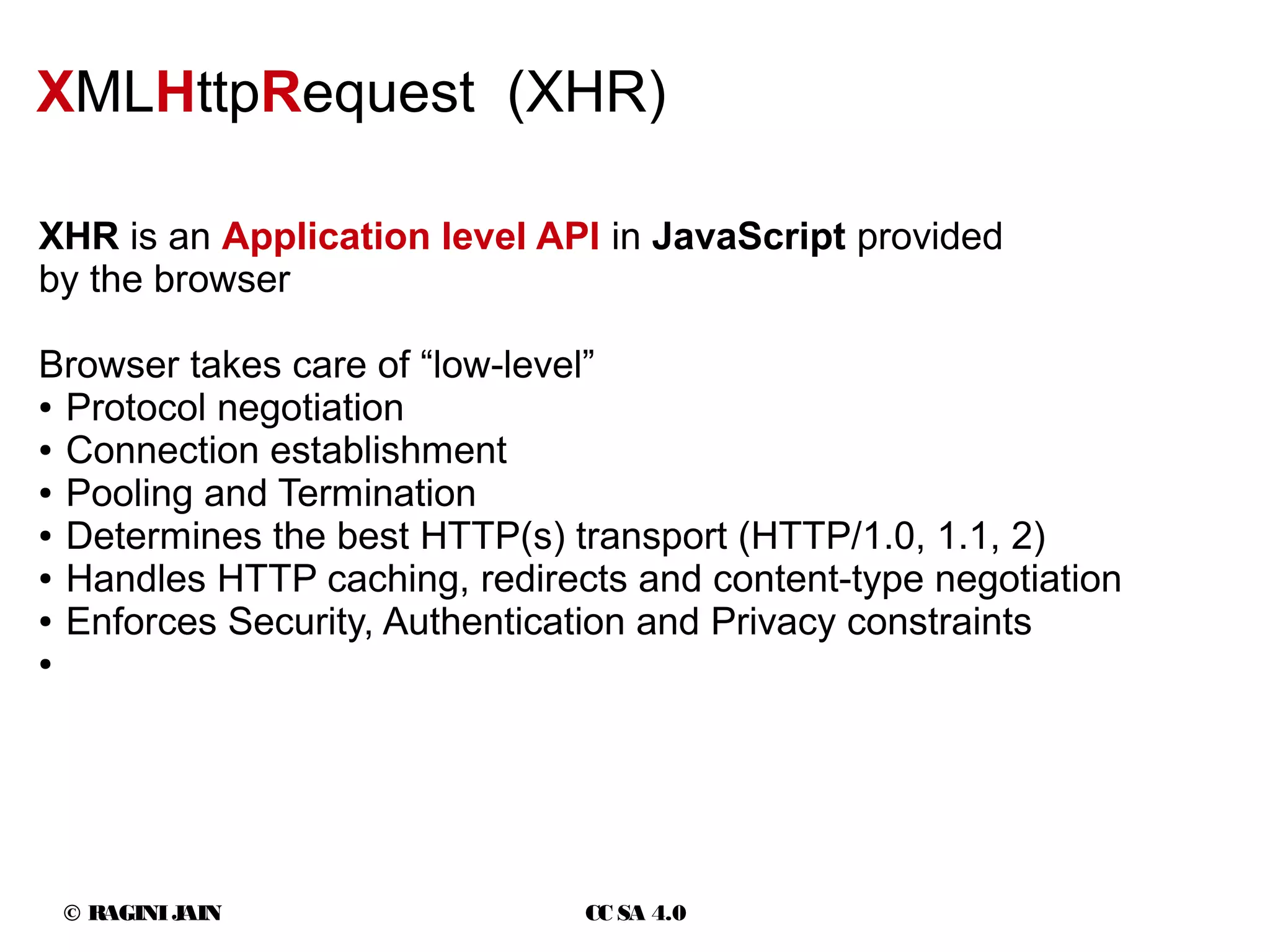



![© RAGINIJAIN CC SA 4.0
Asynchronous in Ajax
open(method, url [, async = true [, username = null [, password = null]]])
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
var method = "GET";
var url = "http://github.com/mexem";
var isAsync = true;
request.open(method, url, isAsync);
if (200 == request.status) {
console.log(request.responseText);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajax-160125111814/75/Ajax-10-2048.jpg)