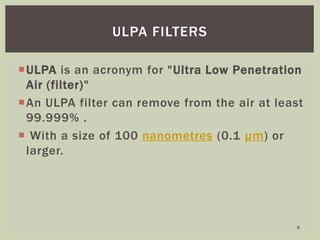
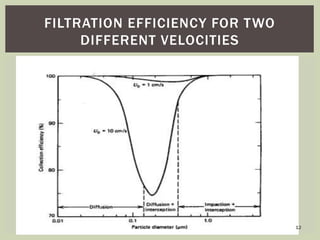
The document discusses different types of air filters, including coarse filters, fine filters, HEPA filters, ULPA filters, carbon air filters, and UV light air filters. It explains that air filters are composed of fibrous materials that remove particles from the air to maintain good indoor air quality. The effectiveness of a filter depends on factors like air velocity, particle size, dust loading, and filter material properties. Common applications of air filters include hospital operating rooms, medical clean rooms, toxic environments, and air conditioning systems.