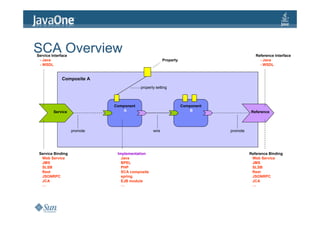
This document discusses building asynchronous services with Service Component Architecture (SCA). It begins with an overview of SCA and why asynchronous services are important. It then covers facilities that support asynchronous services like concurrency classes, JAX-WS, JMS, and BPEL. The document explains how SCA supports asynchronous service interactions through callbacks and bidirectional interfaces. It provides an example of an asynchronous service, client, and composite. Finally, it compares asynchronous services to using events and provides a demo scenario of an asynchronous travel search application built with SCA.
























![Bidirectional Interface
• Forward Interface
@Remotable
@Callback(SearchCallback.class)
public interface Search {
TripItem[] searchSynch(TripLeg tripLeg);
@OneWay
void searchAsynch(TripLeg tripLeg);
}
• Callback Interface
@Remotable
public interface SearchCallback {
void searchResults(TripItem[] items);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ts-4846-buildingasynchronousserviceswithsca-100112124231-phpapp02/85/Building-Asynchronous-Services-With-Sca-26-320.jpg)


![Catalog client application
import org.osoa.sca.annotations.*;
public class TravelCatalogImpl implements TravelCatalogSearch, SearchCallback{
@Reference
protected Search flightSearch;
……
public TripItem[] search(TripLeg tripLeg) {
flightSearch.searchAsynch(tripLeg);
……
}
public void searchResults(TripItem[] items){
if (items != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < items.length; i++ ){
searchResults.add(items[i]);
}
}
……
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ts-4846-buildingasynchronousserviceswithsca-100112124231-phpapp02/85/Building-Asynchronous-Services-With-Sca-29-320.jpg)











