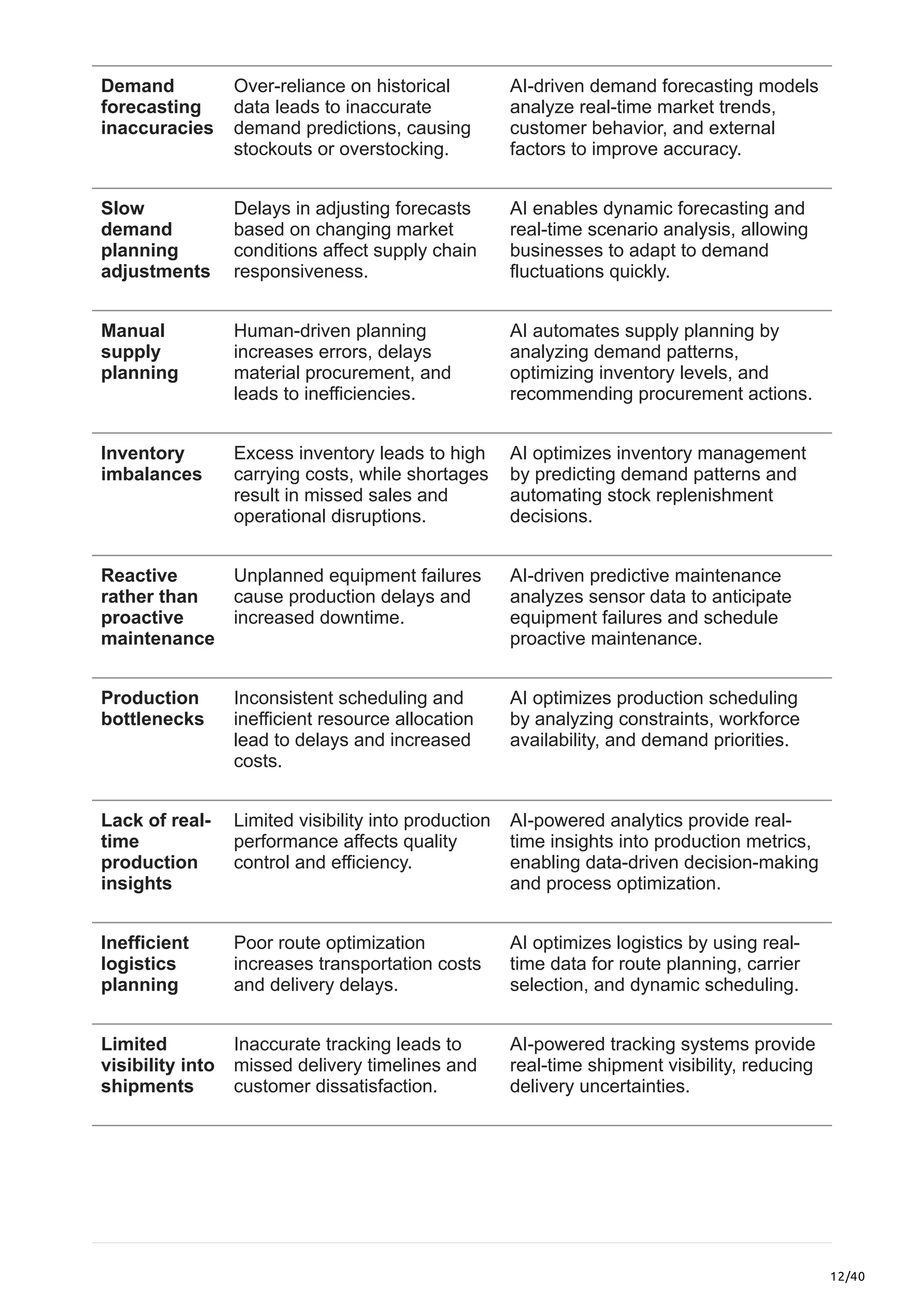
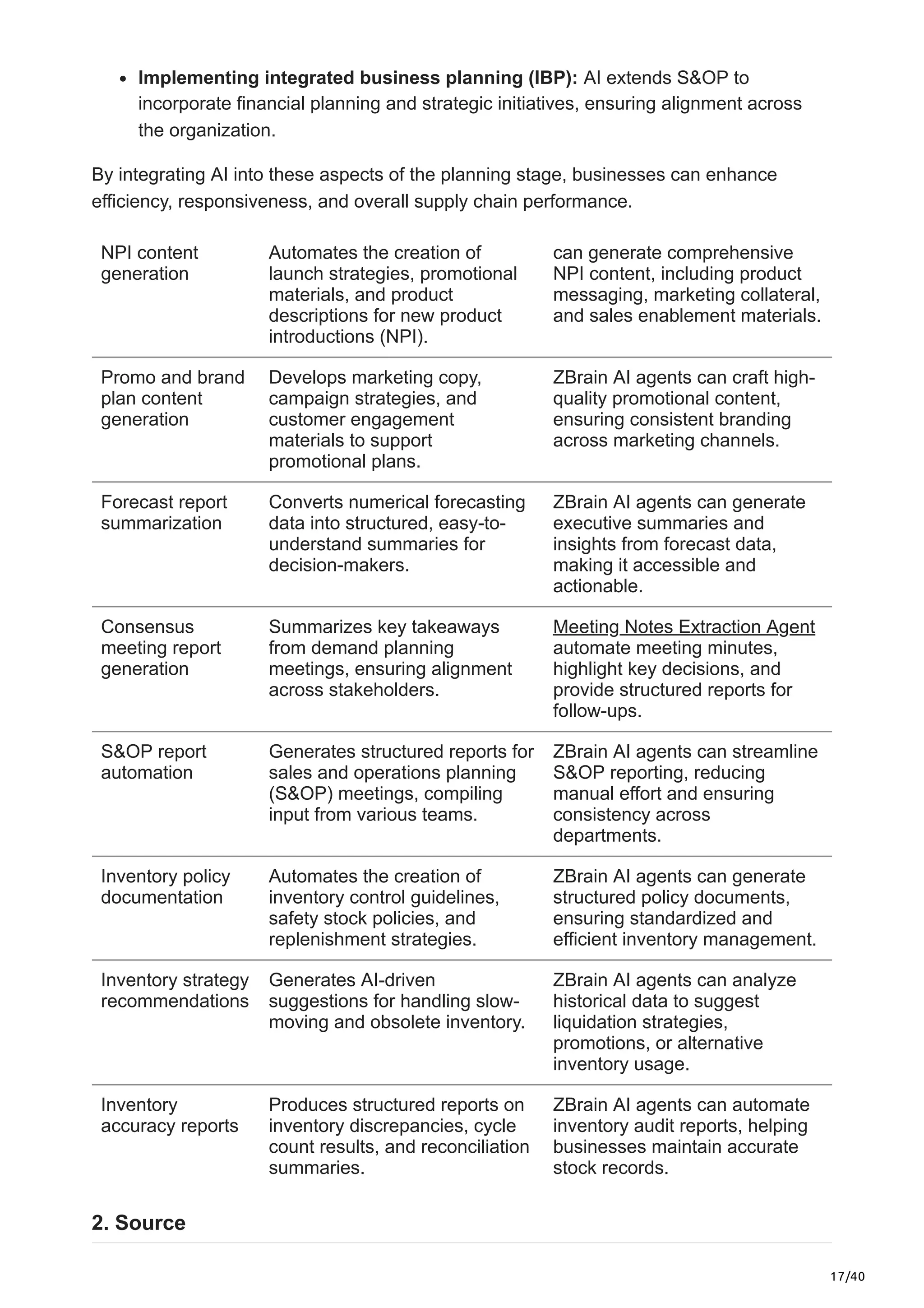
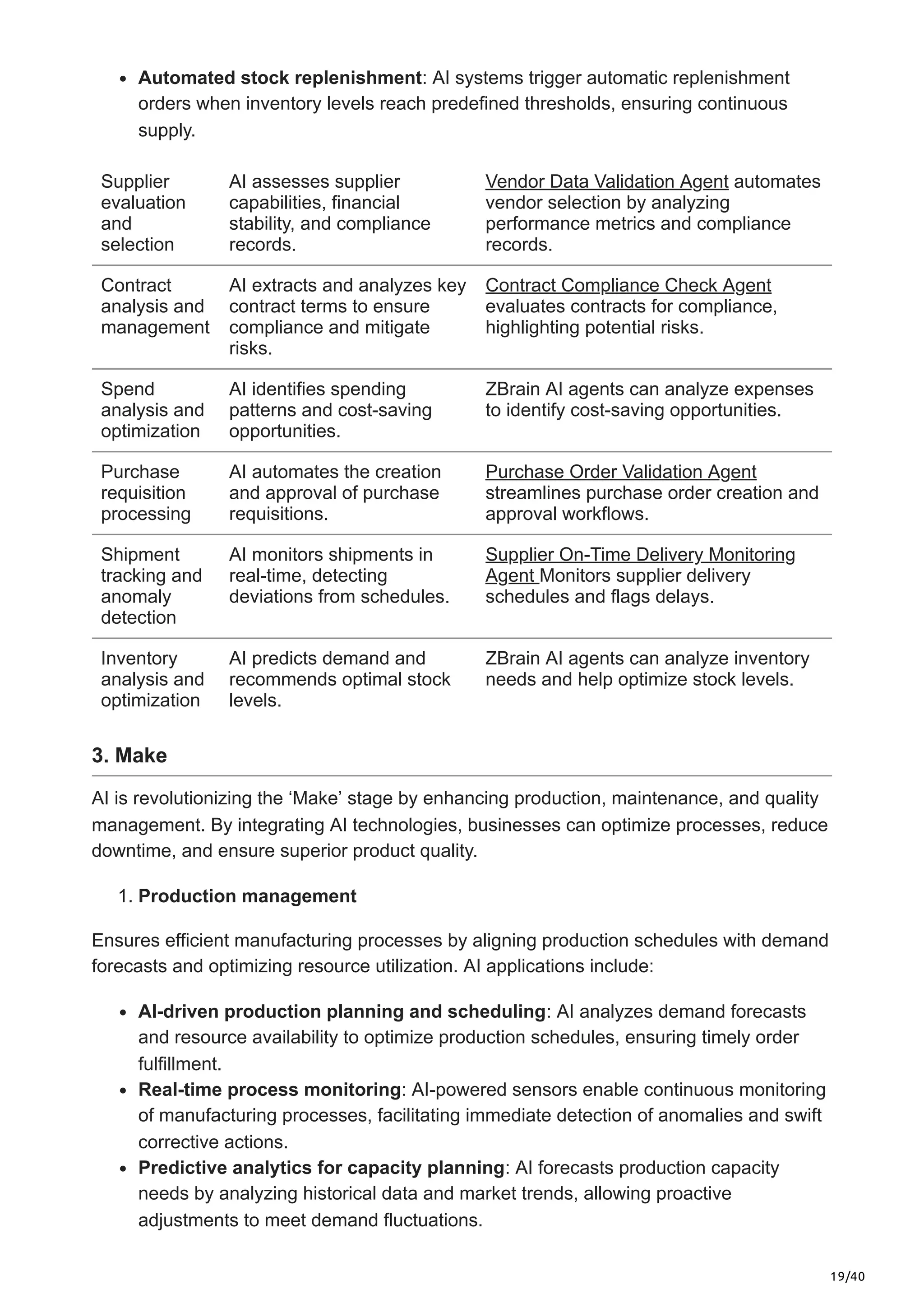
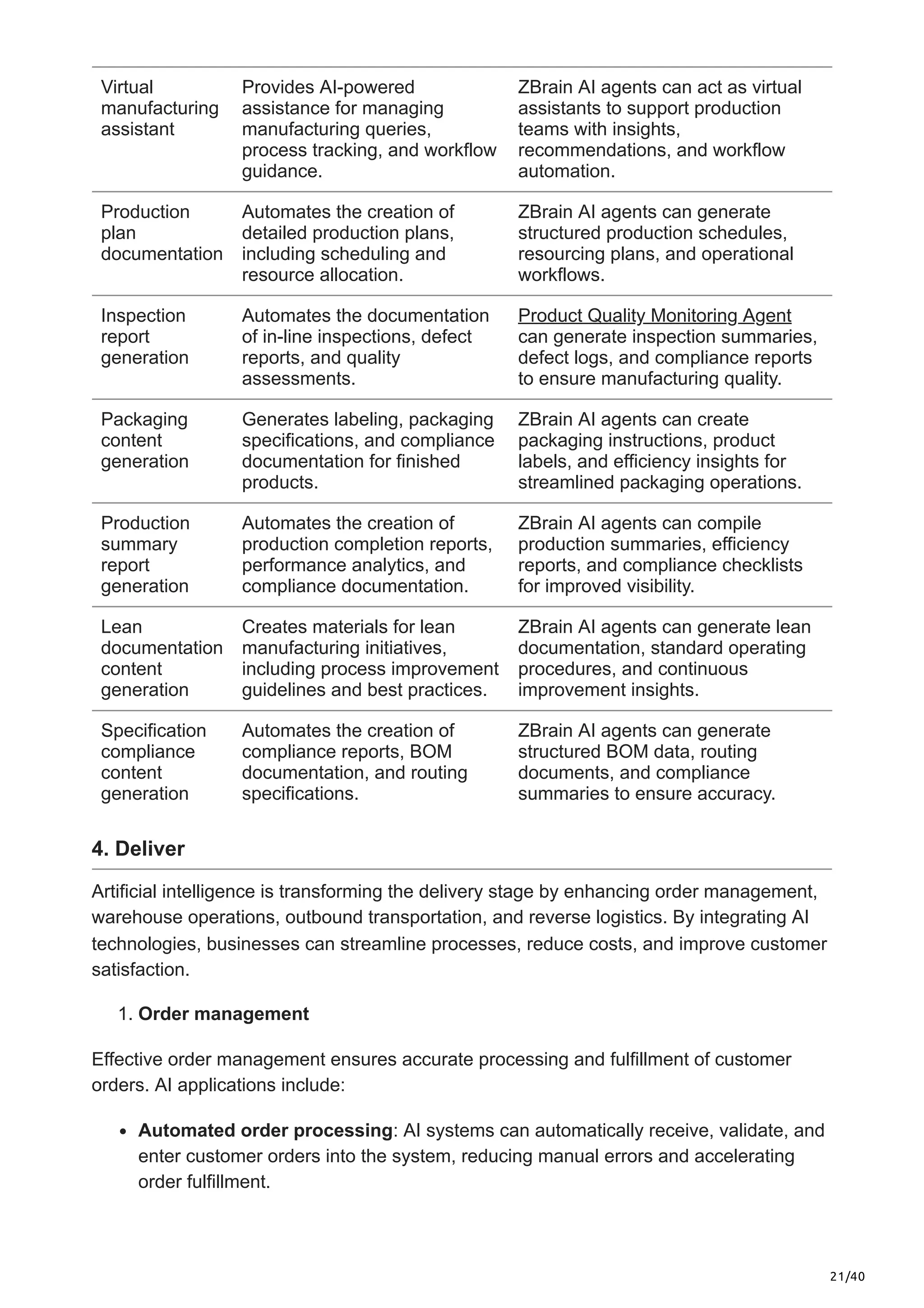
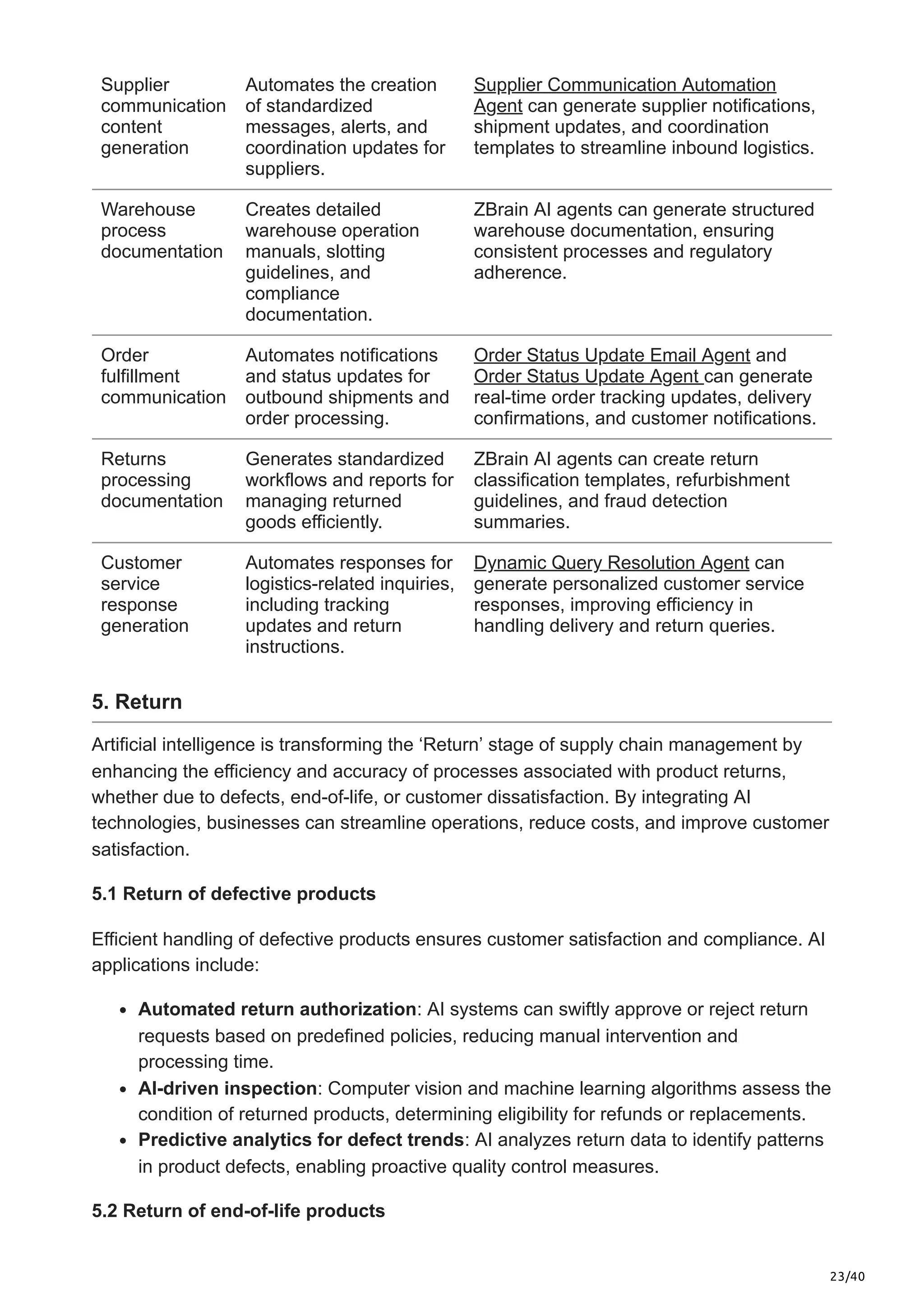
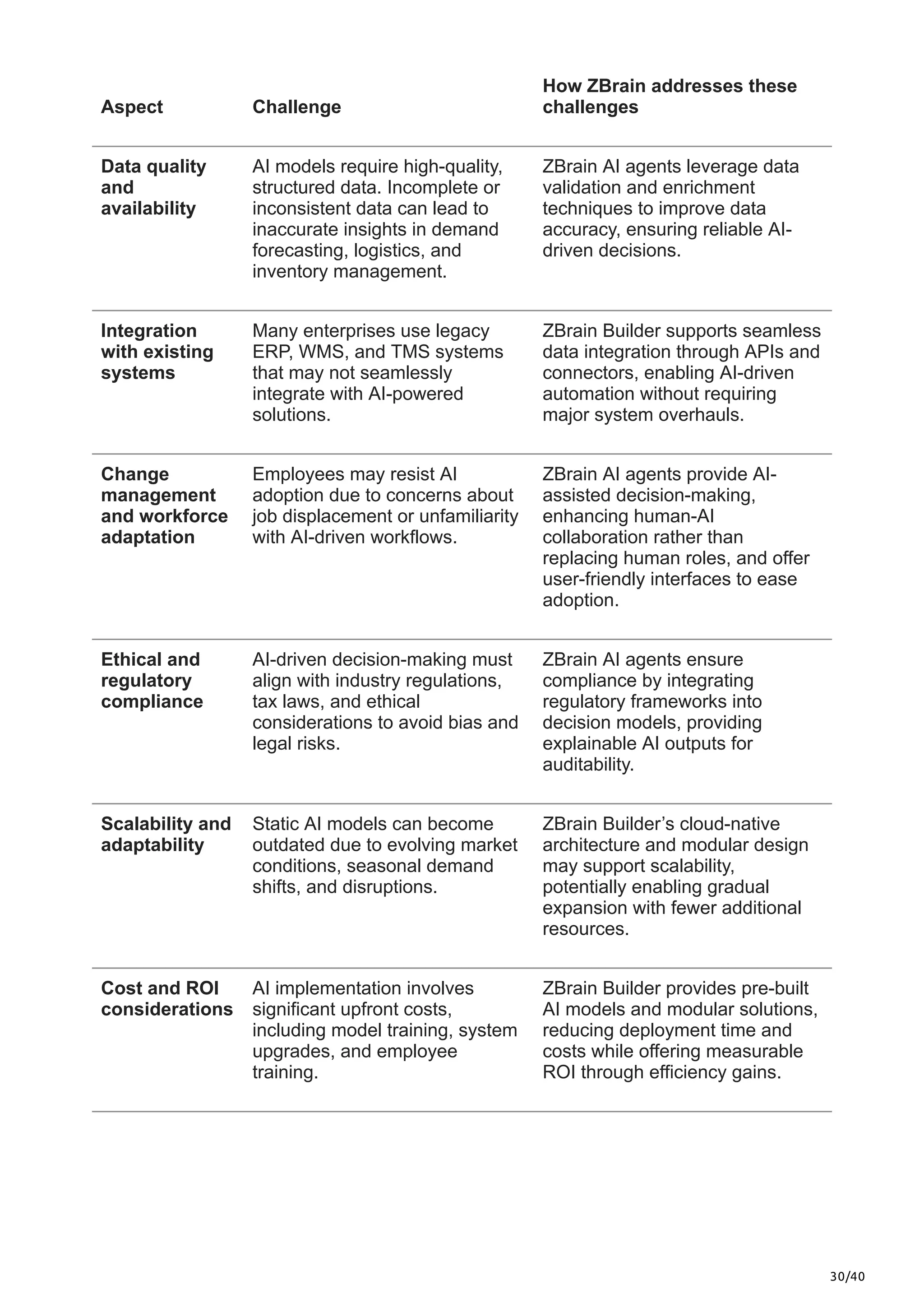
This article explores the limitations of traditional plan-to-deliver processes, the transformative impact of AI in supply chain optimization, and how ZBrain equips businesses with AI-driven capabilities to enhance agility, streamline operations, and future-proof their supply chain strategies.