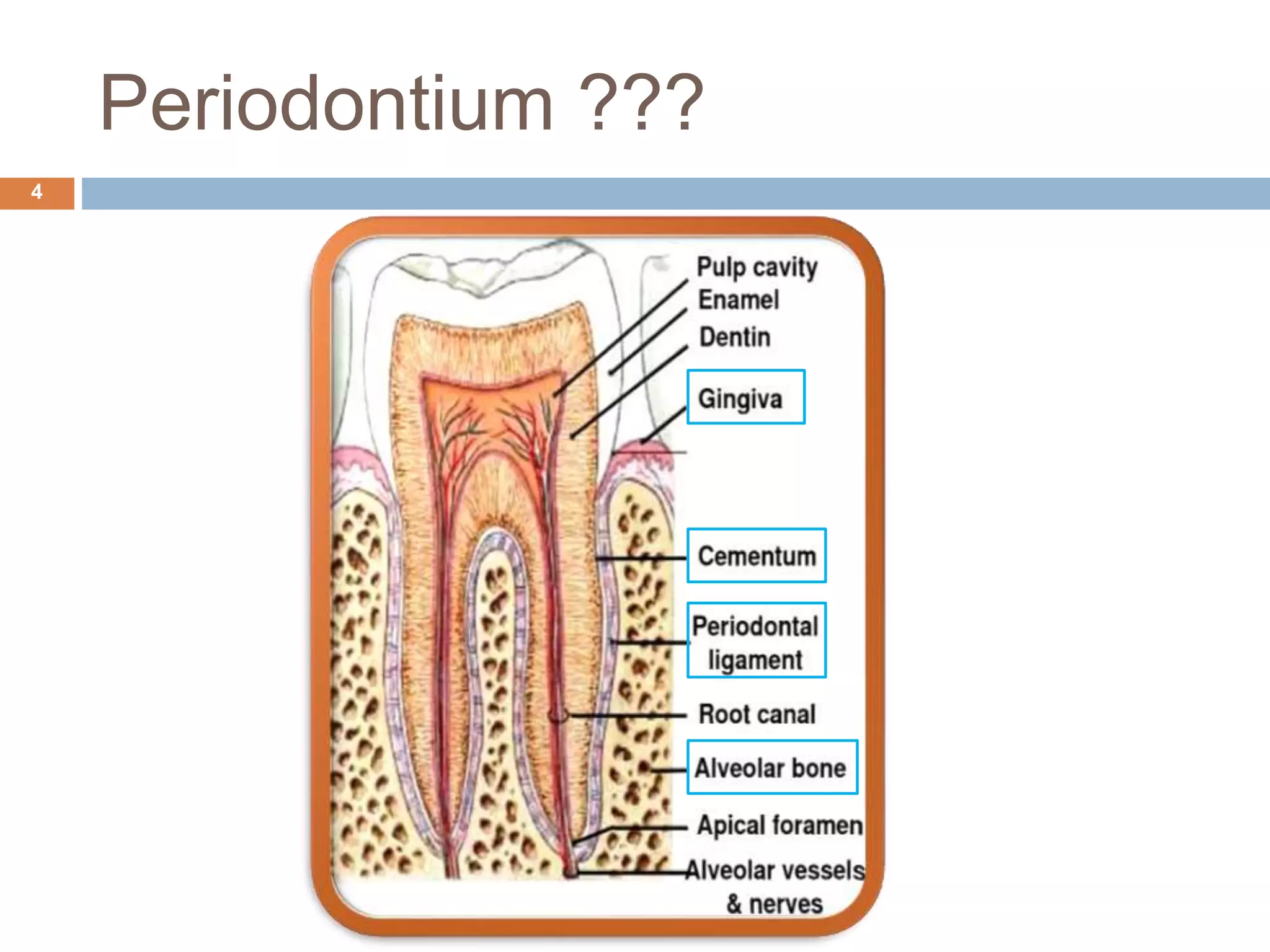
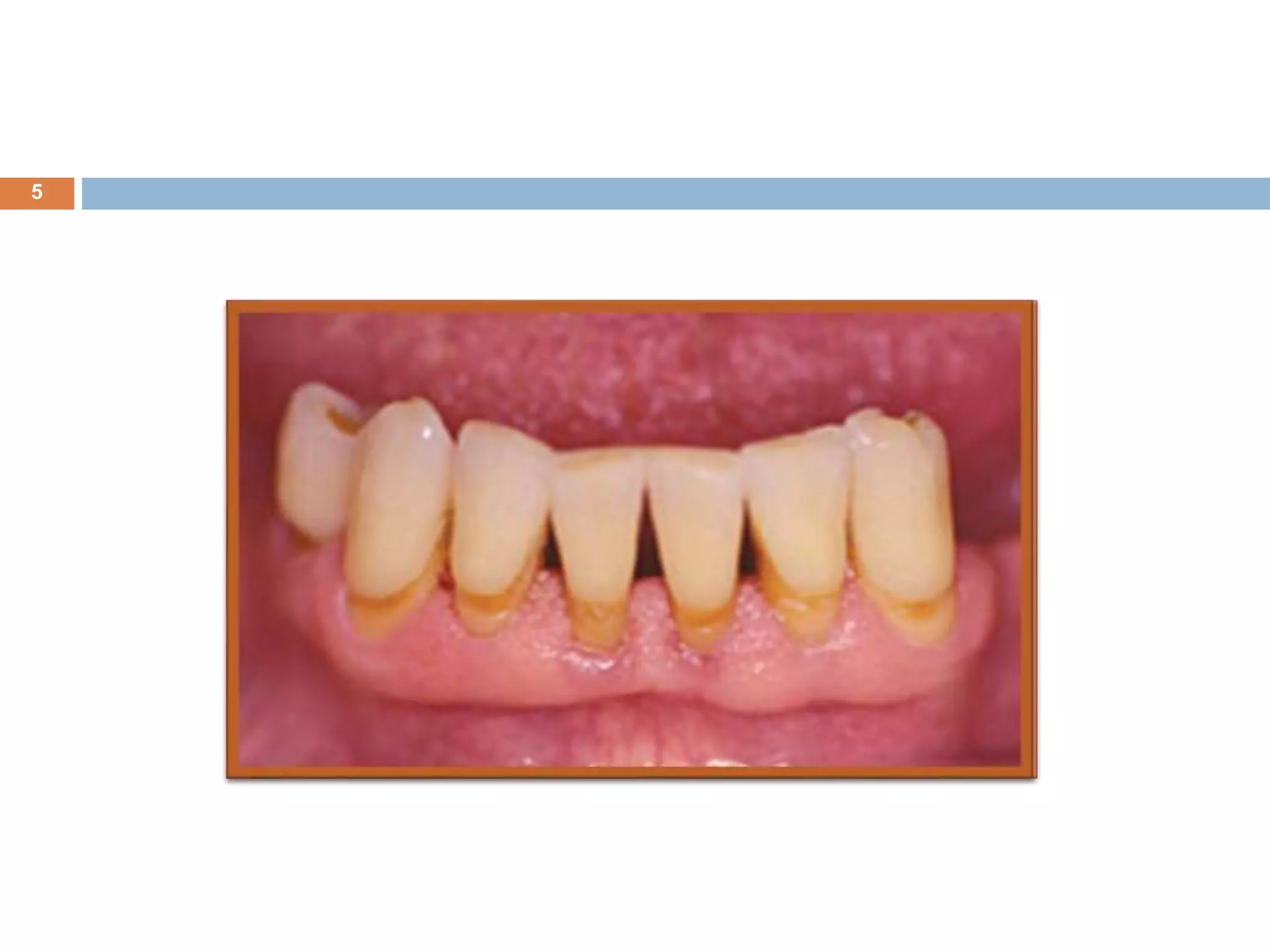
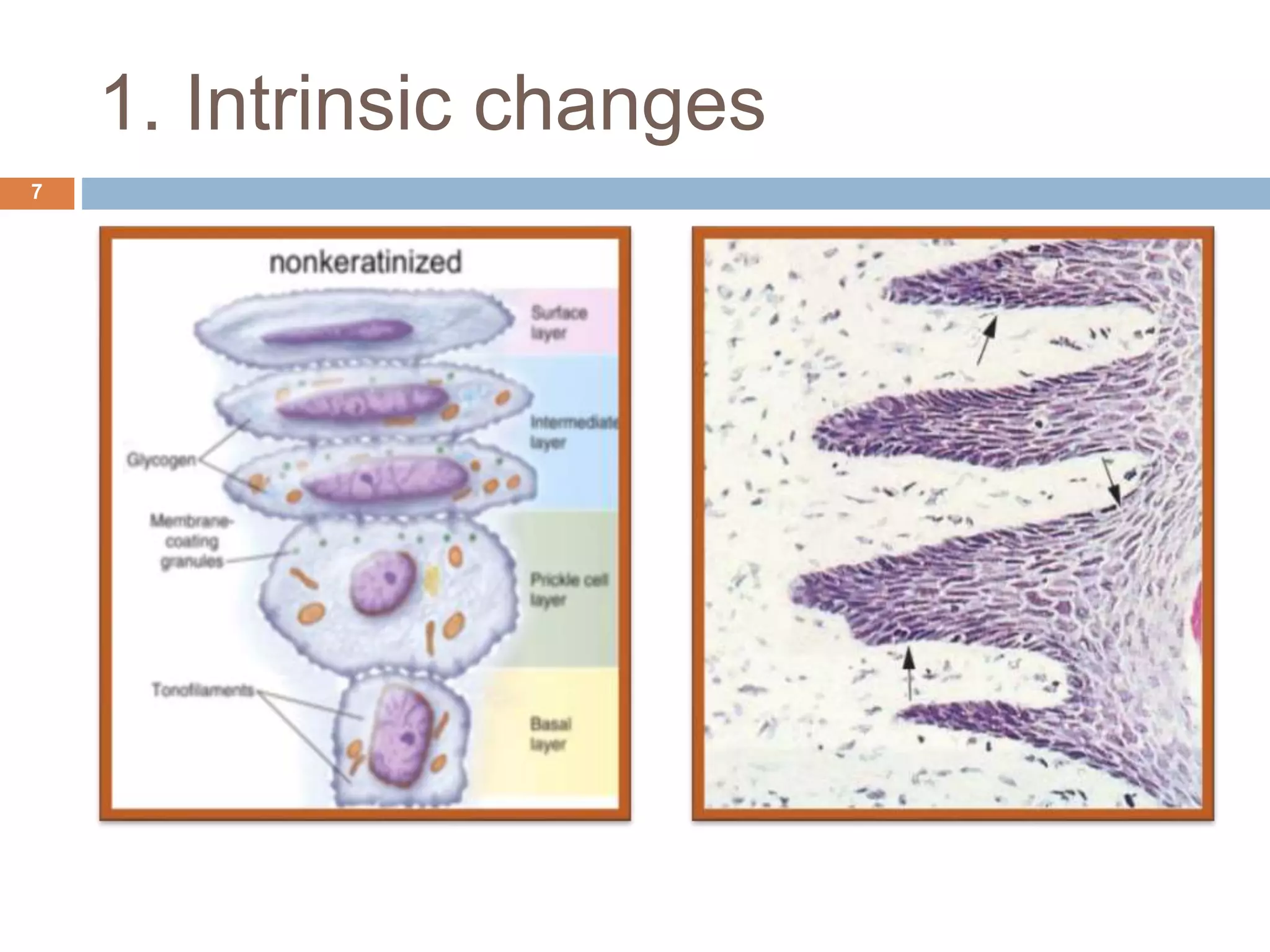
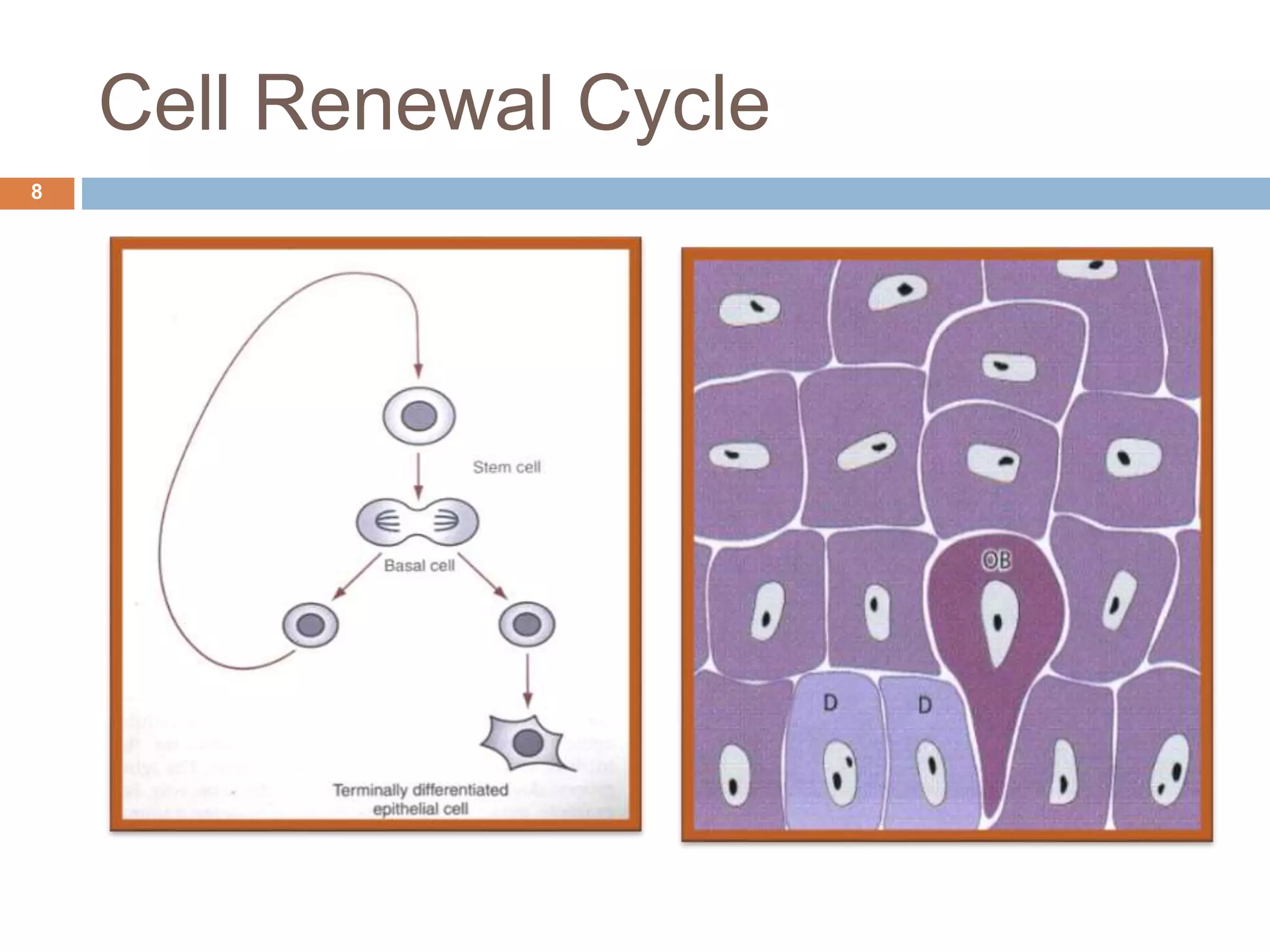
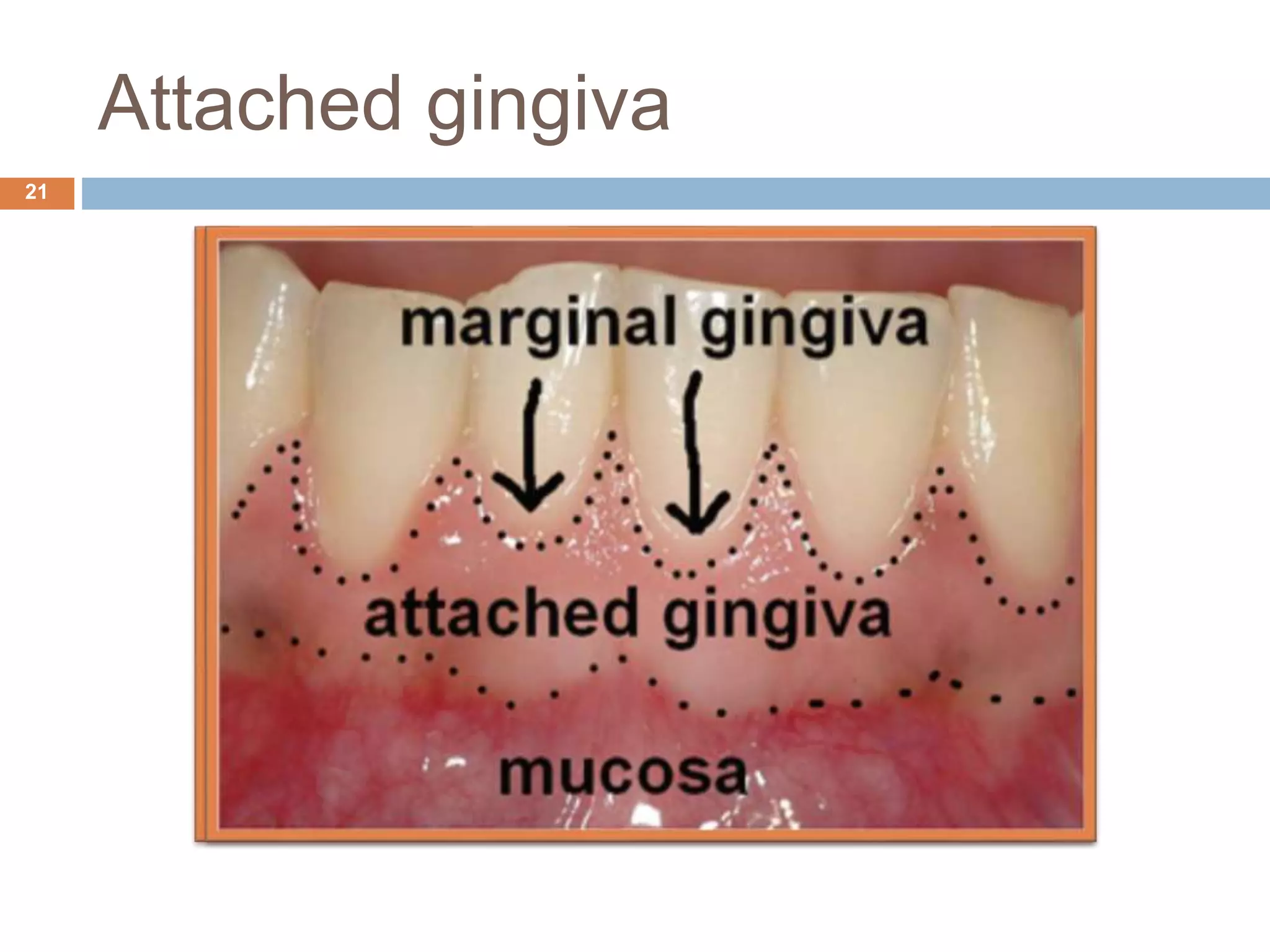
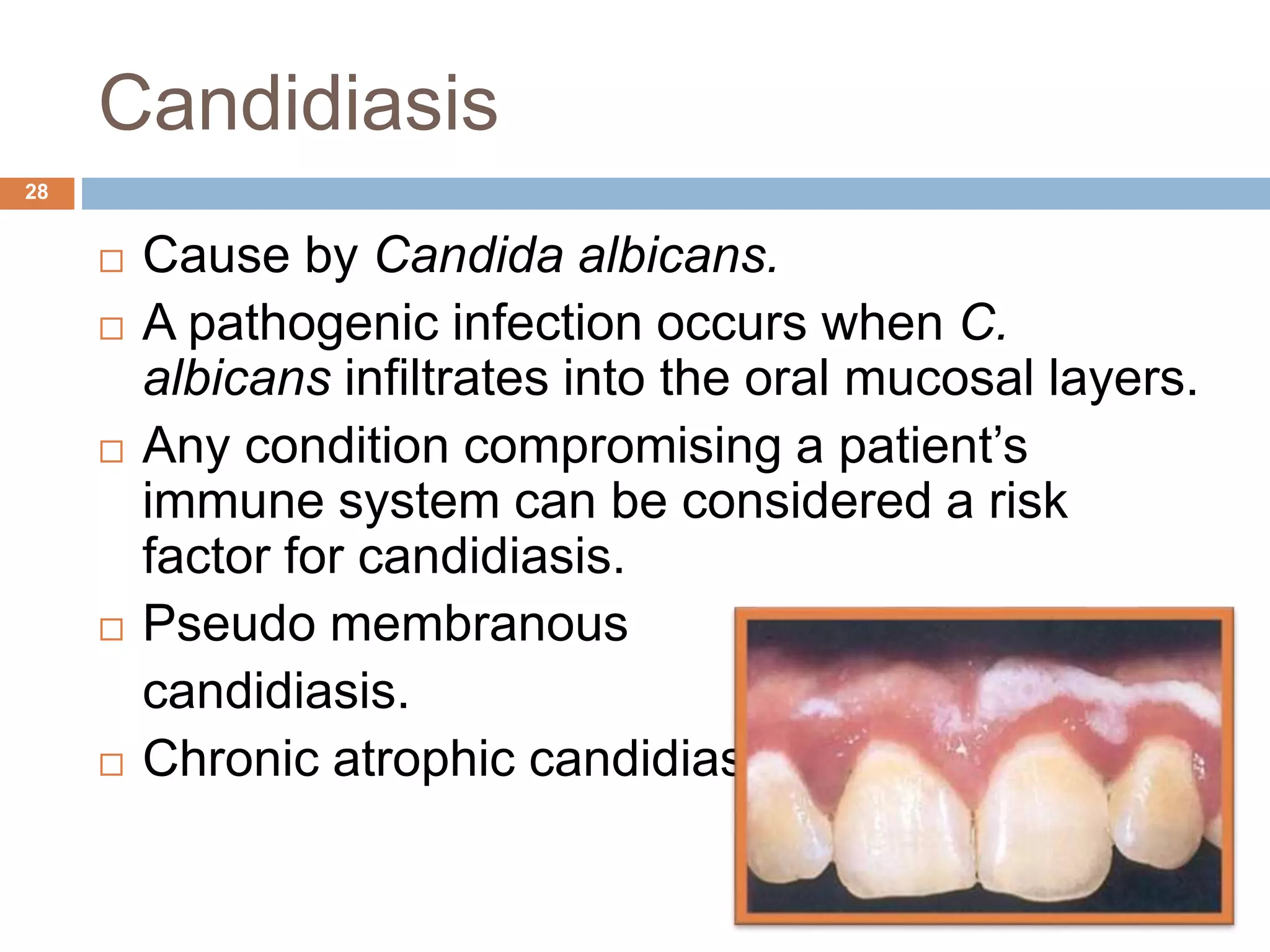
The document discusses aging and its impact on the periodontium, detailing intrinsic, stochastic, physiologic, functional, and clinical changes associated with aging and periodontal health. It highlights effects such as changes in cellular components, gingival epithelium, and connective tissue, while also addressing the implications of xerostomia and candidiasis in older adults. The text concludes with prevention strategies and maintenance tips for preserving periodontal health in aging populations.