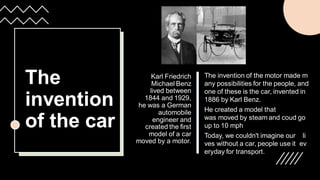
The industrialization period between 1850-1914 saw the introduction of many technologies that enabled mass production and new industries. This included improvements in steel production and a large increase in the number of companies. Major inventions like the car and light bulb emerged during this time, transforming society. The first modern car capable of 10 mph was created by Karl Benz in 1886.