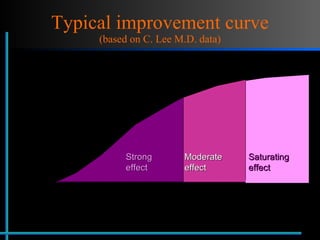
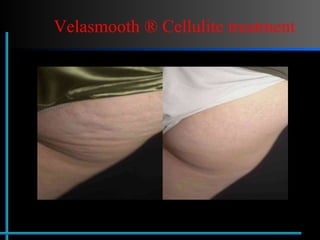
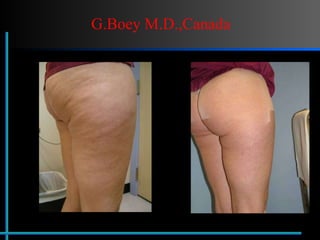
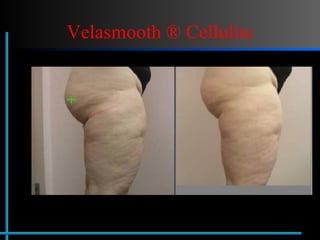
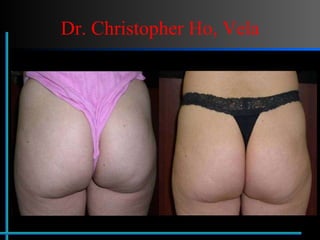
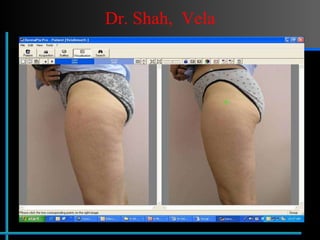
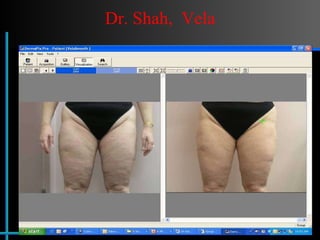
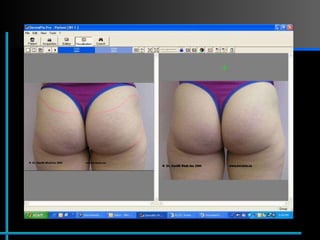
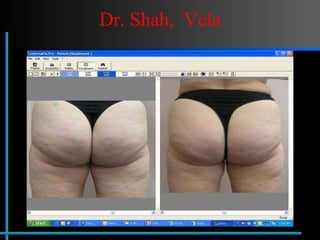
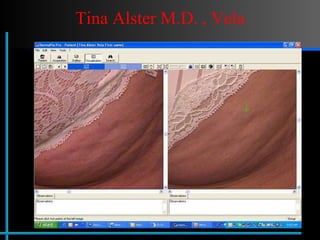
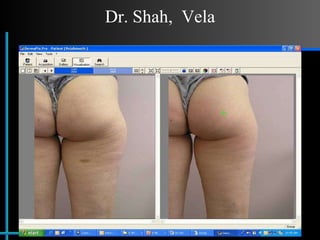
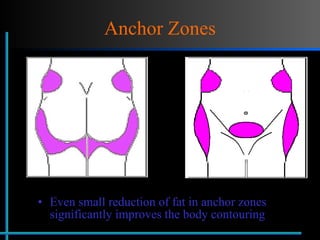
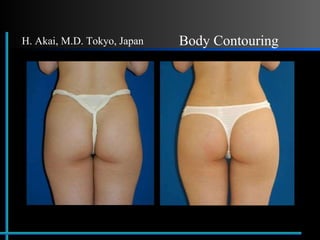
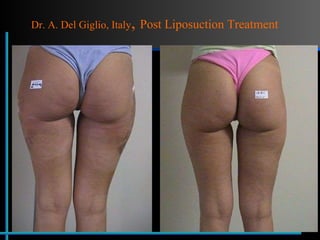
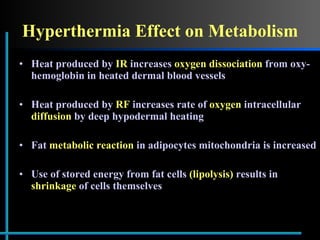
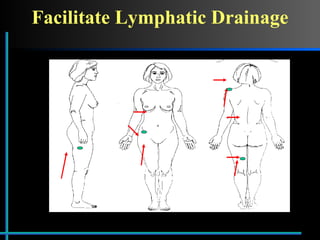
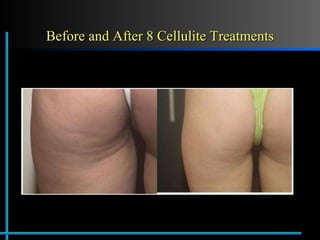
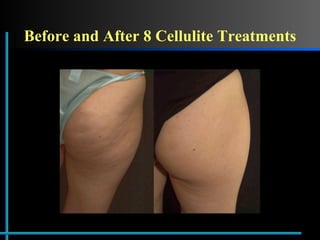
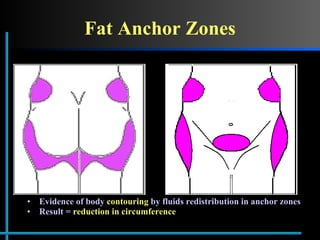
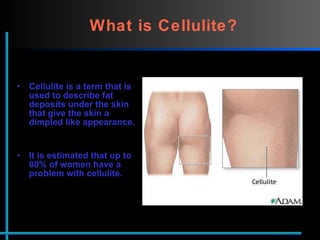
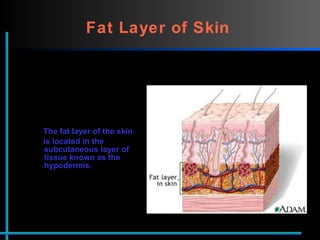
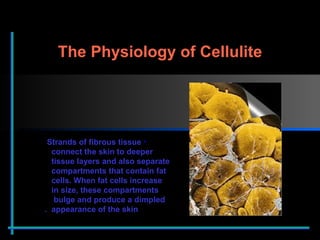
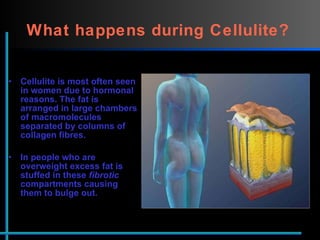
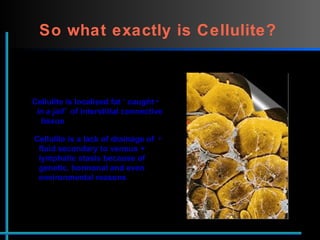
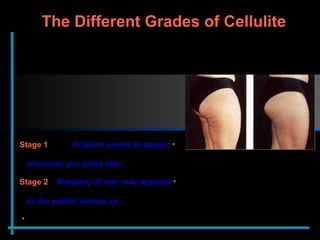
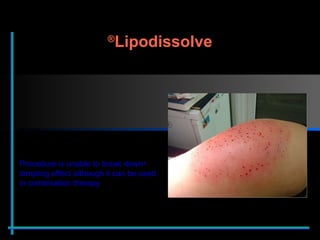
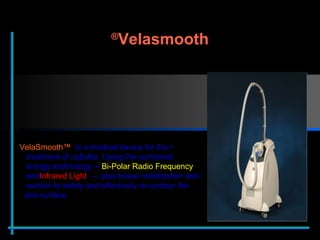
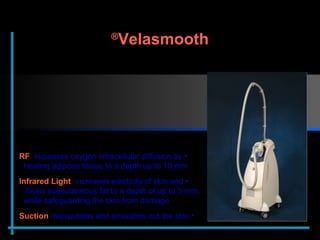
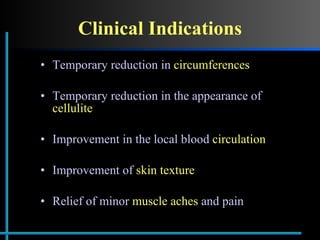
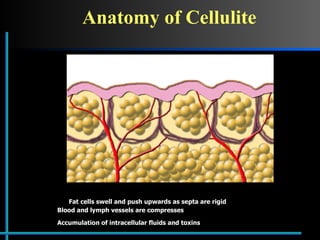
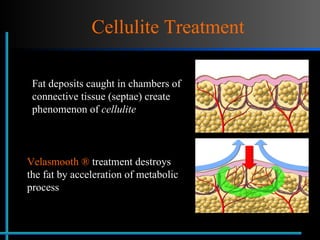
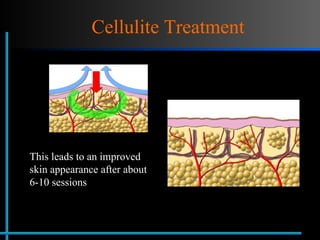
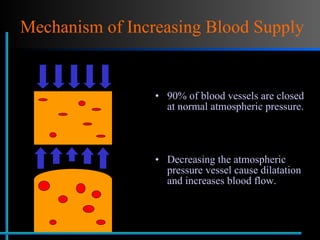
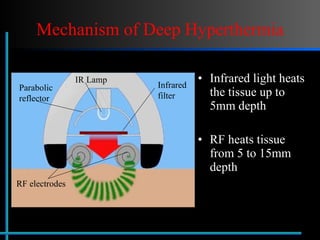
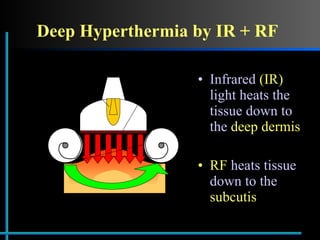
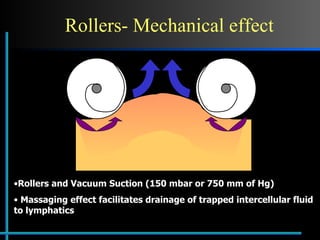
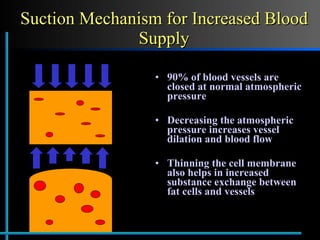
The document provides information about Velasmooth® treatment for cellulite. It defines cellulite and discusses its causes. It then describes the Velasmooth® treatment which uses radio frequency and infrared light to heat the skin and fat tissues. This promotes fat metabolism and lymphatic drainage to reduce the appearance of cellulite. The treatment schedule and parameters are outlined along with expected improvements seen after 6-10 sessions.






















![Oxygen Transport Coefficients in Water Hyperthermia increases diffusivity of oxygen and decreases skin viscosity delivering more oxygen from capillaries to mitochondrion 4.88x10 -5 0.467 60 3.99x10 -5 0.547 50 3.24x10 -5 0.653 40 1.97x10 -5 1.002 20 Diffusivity of O 2 [cm 2 /s] Viscosity of H 2 O [centipoises] Temperature O C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aestheticmedicine2006velasmooth-110922064936-phpapp02/85/Velasmooth-in-the-treatment-of-Cellulite-50-320.jpg)