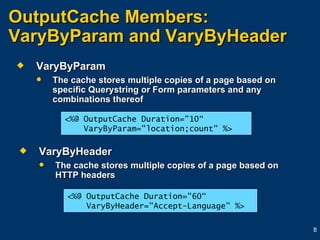
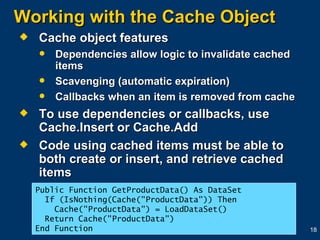
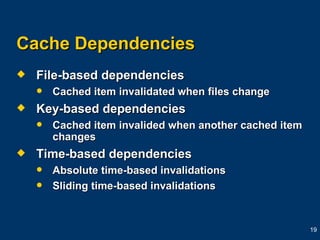
The document provides an overview of caching in ASP.NET, including output caching to cache entire pages, fragment caching to cache parts of pages, and data caching to cache application data in memory for faster access. It discusses using the @OutputCache directive and Cache object to control caching along with settings like duration, location, and varying caches based on parameters or headers. Caching can improve performance and scalability by reducing server response times and CPU loads when pre-rendering pages and storing frequently accessed data.





![@ OutputCache Directive and the Cache Object @ OutputCache declaratively controls caching behavior For .aspx, .asmx, or .ascx The cache object programmatically controls caching behavior <%@ OutputCache Duration="600“ Location="Any“ VaryByParm=“none” %> Is equivalent to: [C#] Response.Cache.SetExpires(DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(600)); Response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.Public);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wc080102-110602031306-phpapp02/85/aergserga-6-320.jpg)




![Fragment Caching a User Control [*.ascx] <%@ Language="C#" %> <%@ OutputCache Duration="10“ VaryByControl="State;Country" VaryByParam="*"%> <script runat=server> public String State { get { return state.Value; } set { state.Value = State; } } public String Country { get { return country.Value; } set { country.Value = Country; } } </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wc080102-110602031306-phpapp02/85/aergserga-12-320.jpg)









![Thank you for joining today’s Microsoft Support WebCast. For information about all upcoming Support WebCasts, and access to the archived content (streaming media files, PowerPoint ® slides, and transcripts), please visit: http:// support.microsoft.com/webcasts / Your feedback is sincerely appreciated. Please send any comments or suggestions about the Support WebCasts to [email_address] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wc080102-110602031306-phpapp02/85/aergserga-24-320.jpg)