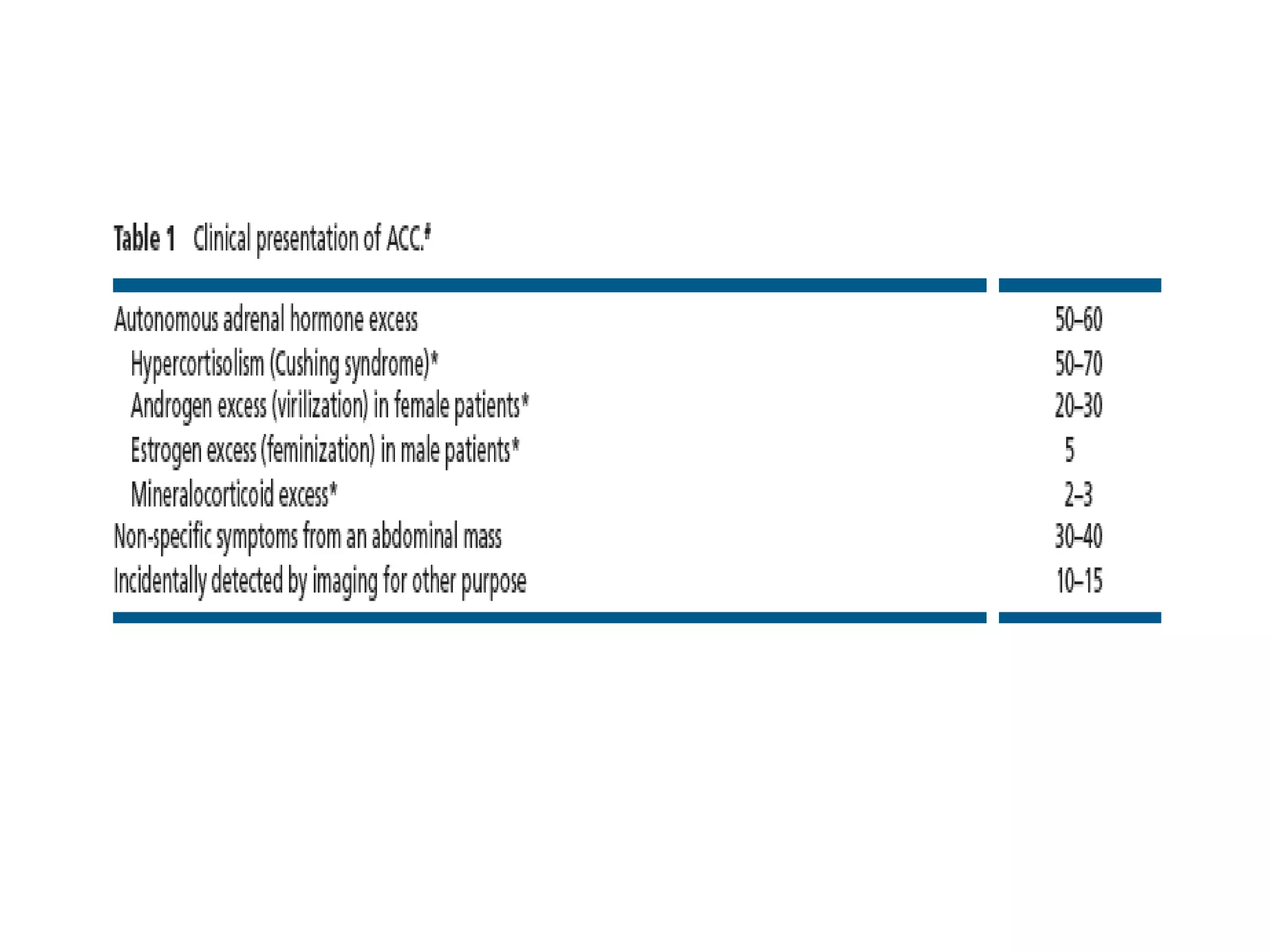
This document summarizes information about adreno-cortical carcinoma (ACC), including:
- ACC has an incidence rate of 0.7 to 2 per million people per year, unusually high in southern Brazil. Risk factors include genetic conditions and large tumor size.
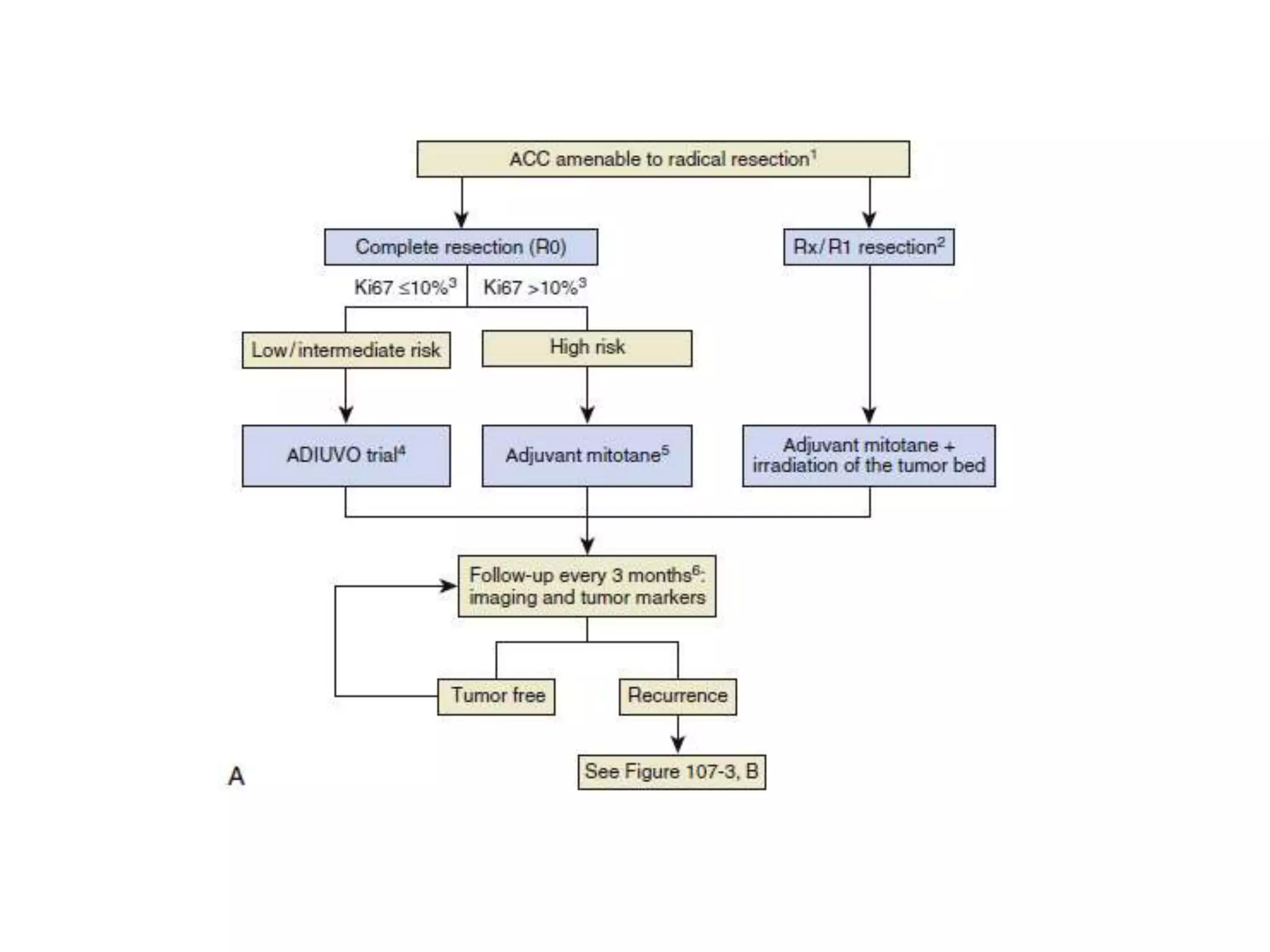
- Complete tumor removal through surgery is the most important treatment, with clear margins associated with better long-term prognosis.
- Radiation therapy alone has not shown survival benefits, but can help with pain from metastases.
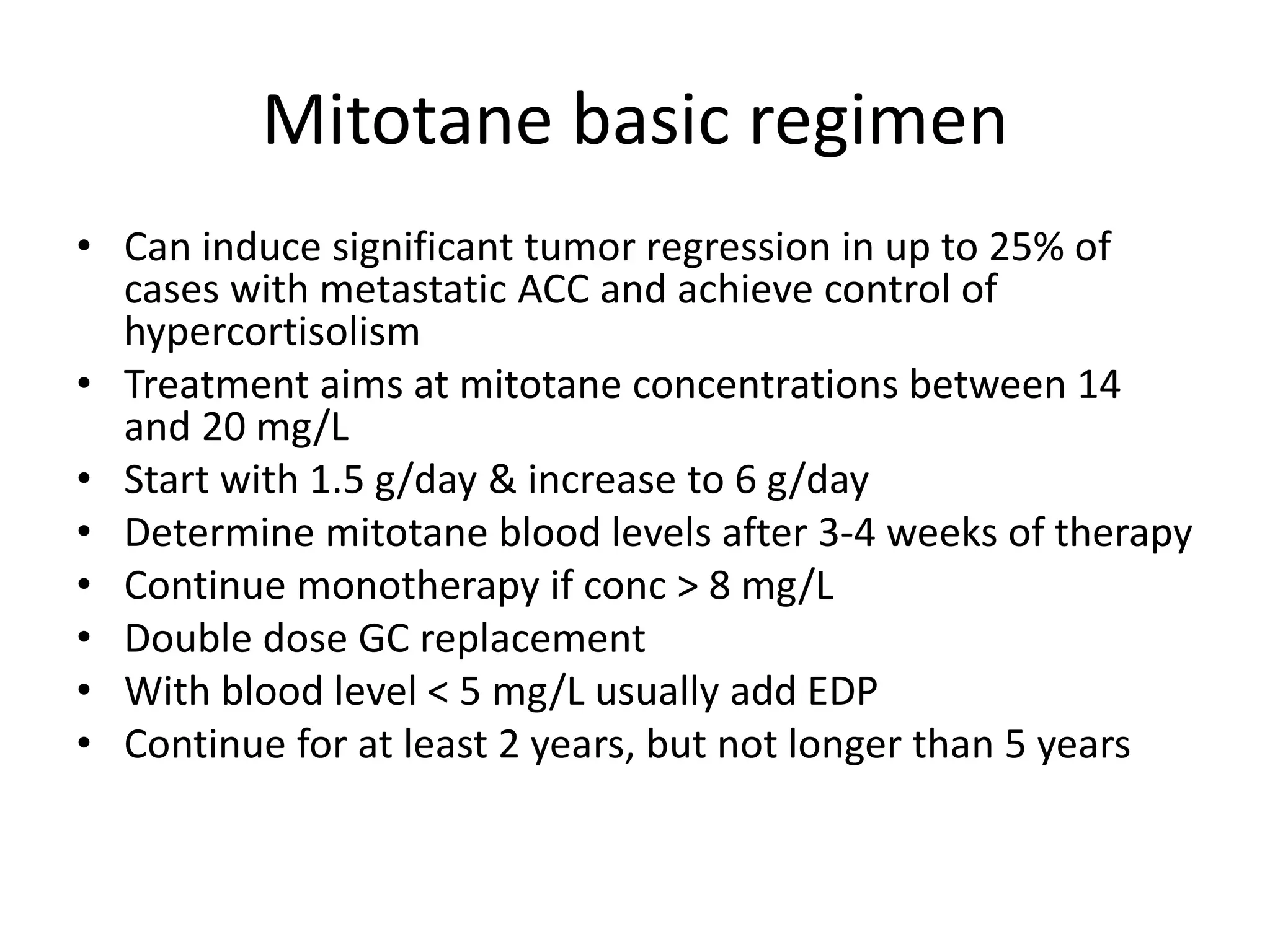
- Drug treatments include mitotane, which can induce tumor regression in 25% of metastatic cases. Targeted therapies have shown limited effectiveness so far.
- Follow up care involves repeated CT scans for at least 5 years,