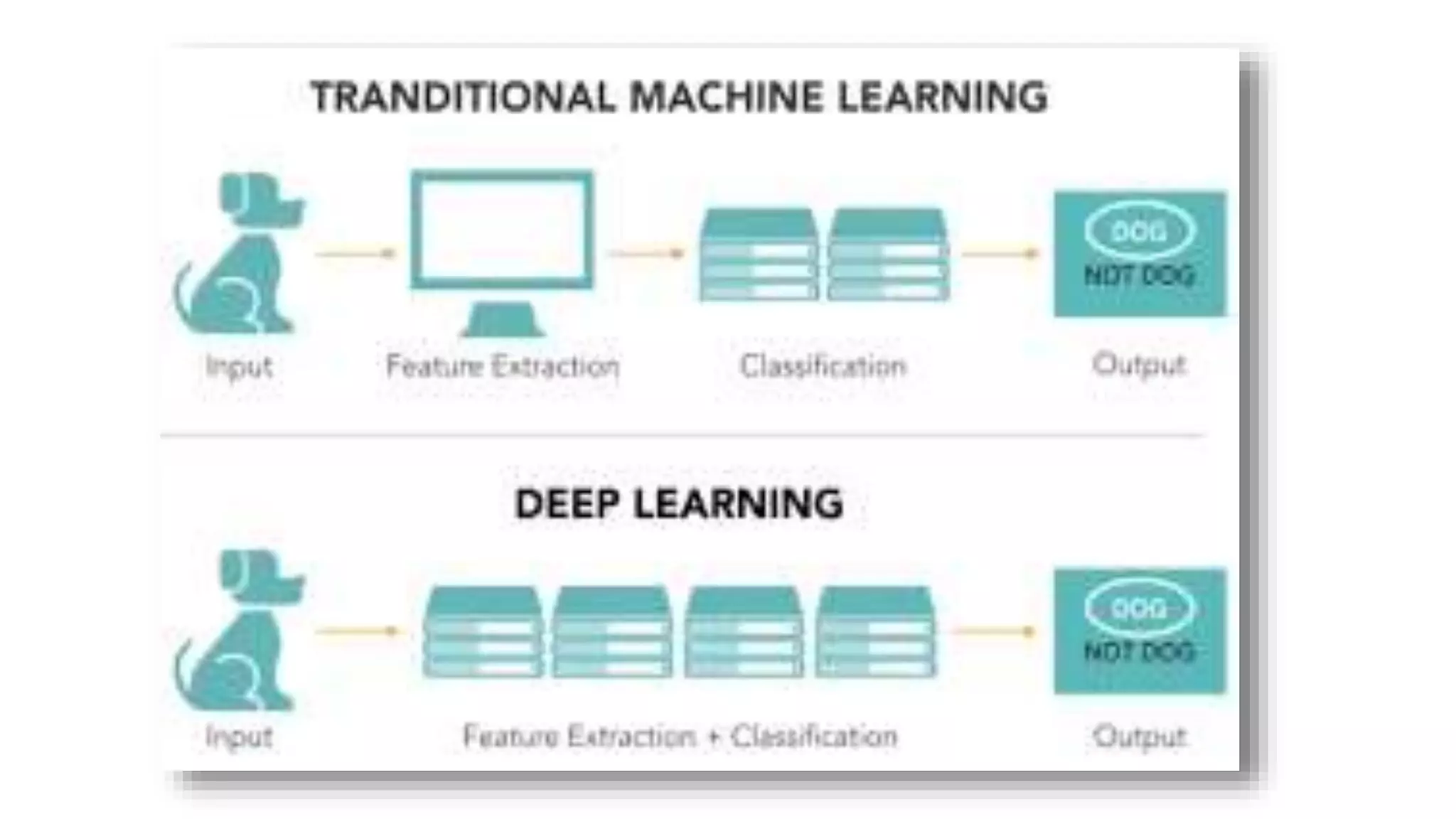
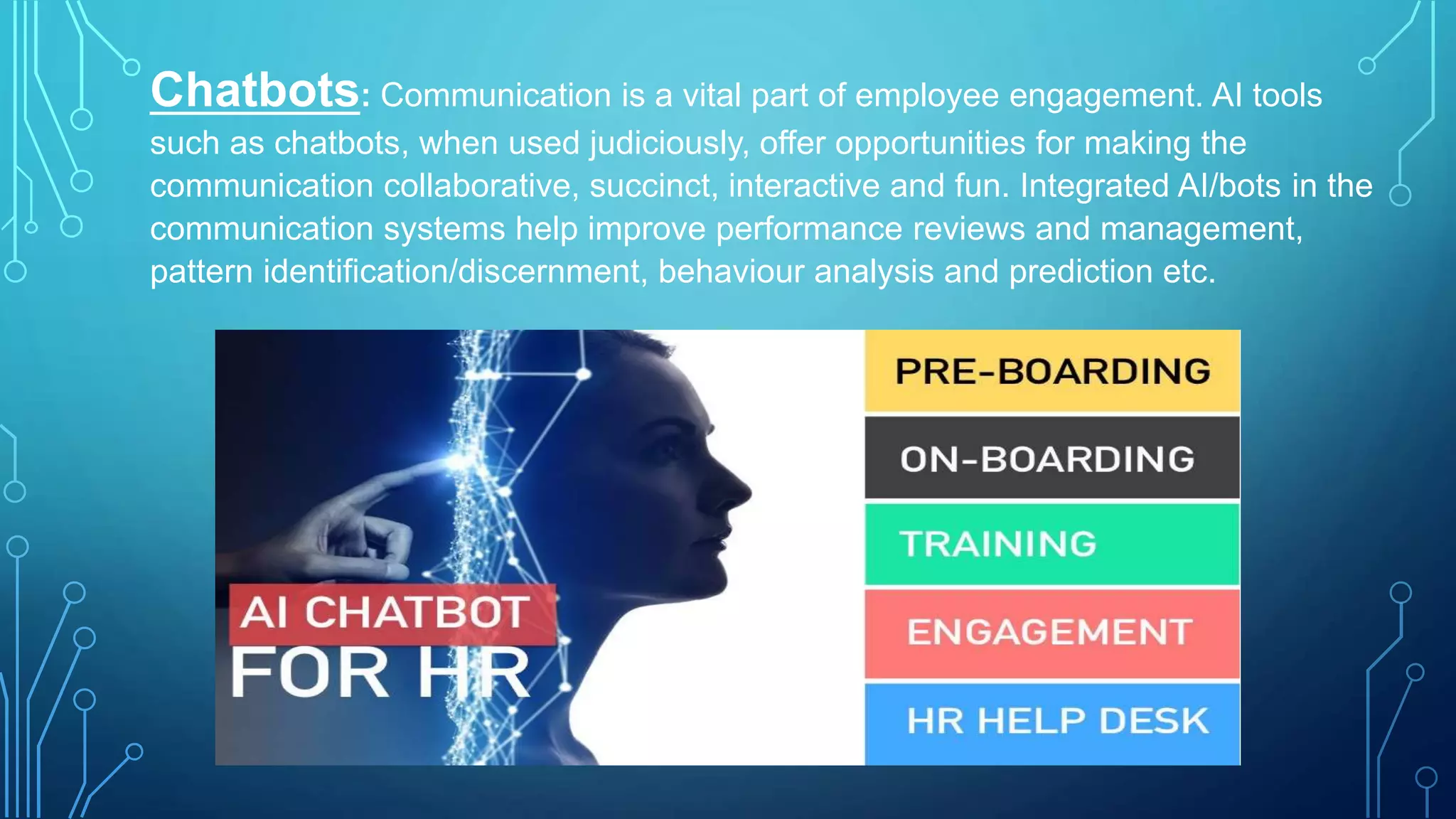
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly being adopted in human resource management. Deep learning uses neural networks to recognize patterns in large amounts of data without being explicitly programmed. Key uses of AI in HR include anomaly detection in data, background checks for candidates, predicting employee attrition, personalized recommendations for employees, and chatbots for communication. While adoption of AI in HR is growing, with over 80% of large companies using some form of it, concerns remain around data quality, skills shortage, and employee acceptance that could slow adoption in India. However, companies are demonstrating AI's potential through initiatives in training, benefits administration, recruitment, and other HR functions.