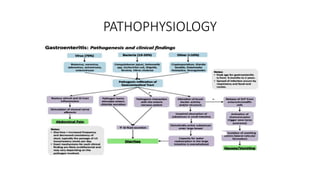
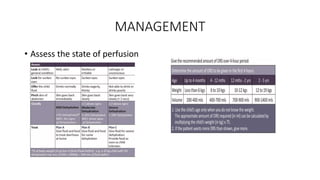
Acute gastroenteritis is characterized by increased stool frequency and loose consistency, with or without vomiting and abdominal pain. It is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in childhood. Dehydration and electrolyte loss due to diarrhea and vomiting are the main causes of death. Patients may present with diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal cramping. Diagnosis is usually clinical but workup including blood tests and stool culture may be needed if systemic infection is suspected. Management involves fluid resuscitation and oral rehydration therapy. Severe dehydration requires intravenous fluids while complications include dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities, and carbohydrate intolerance.