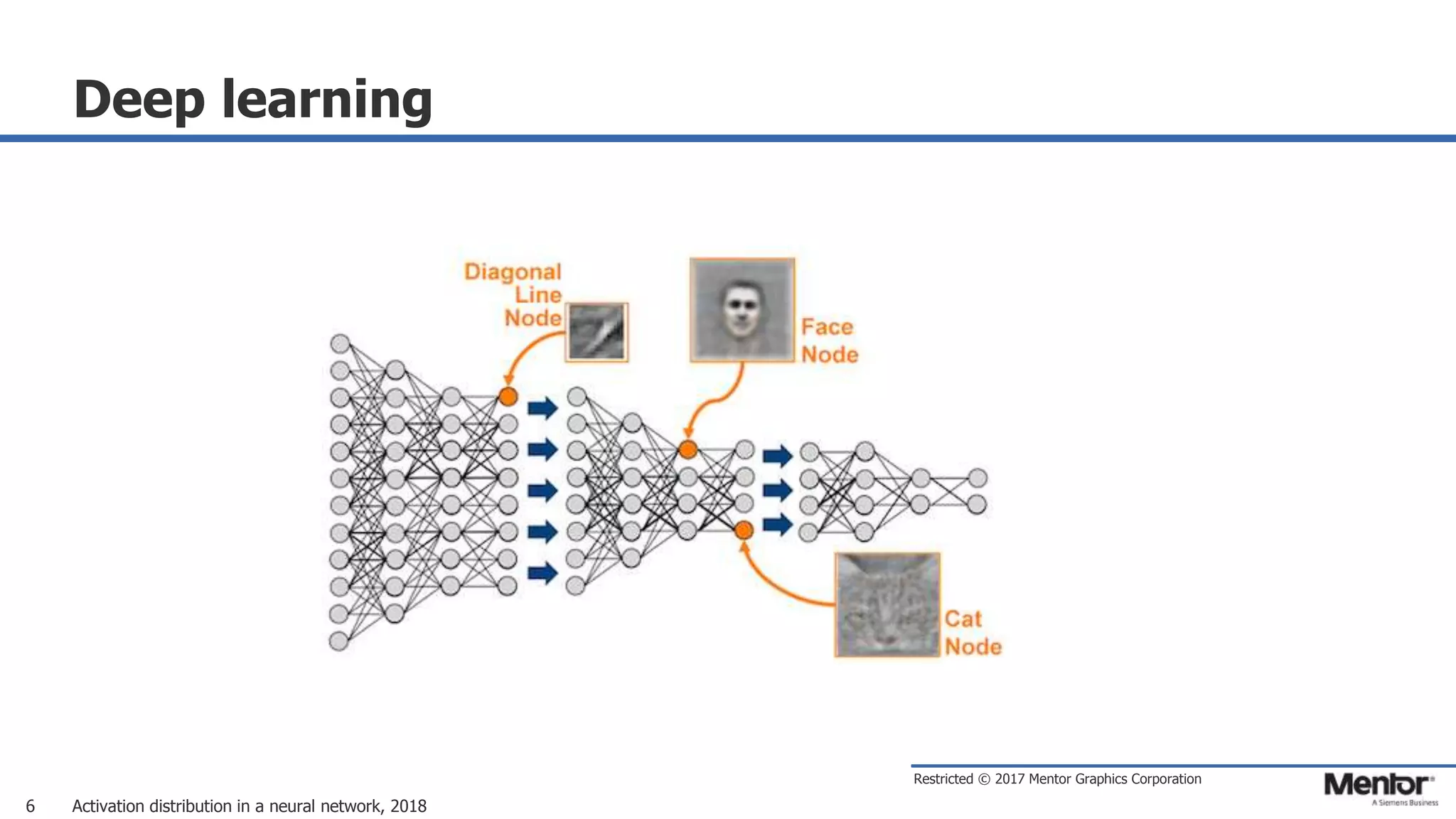
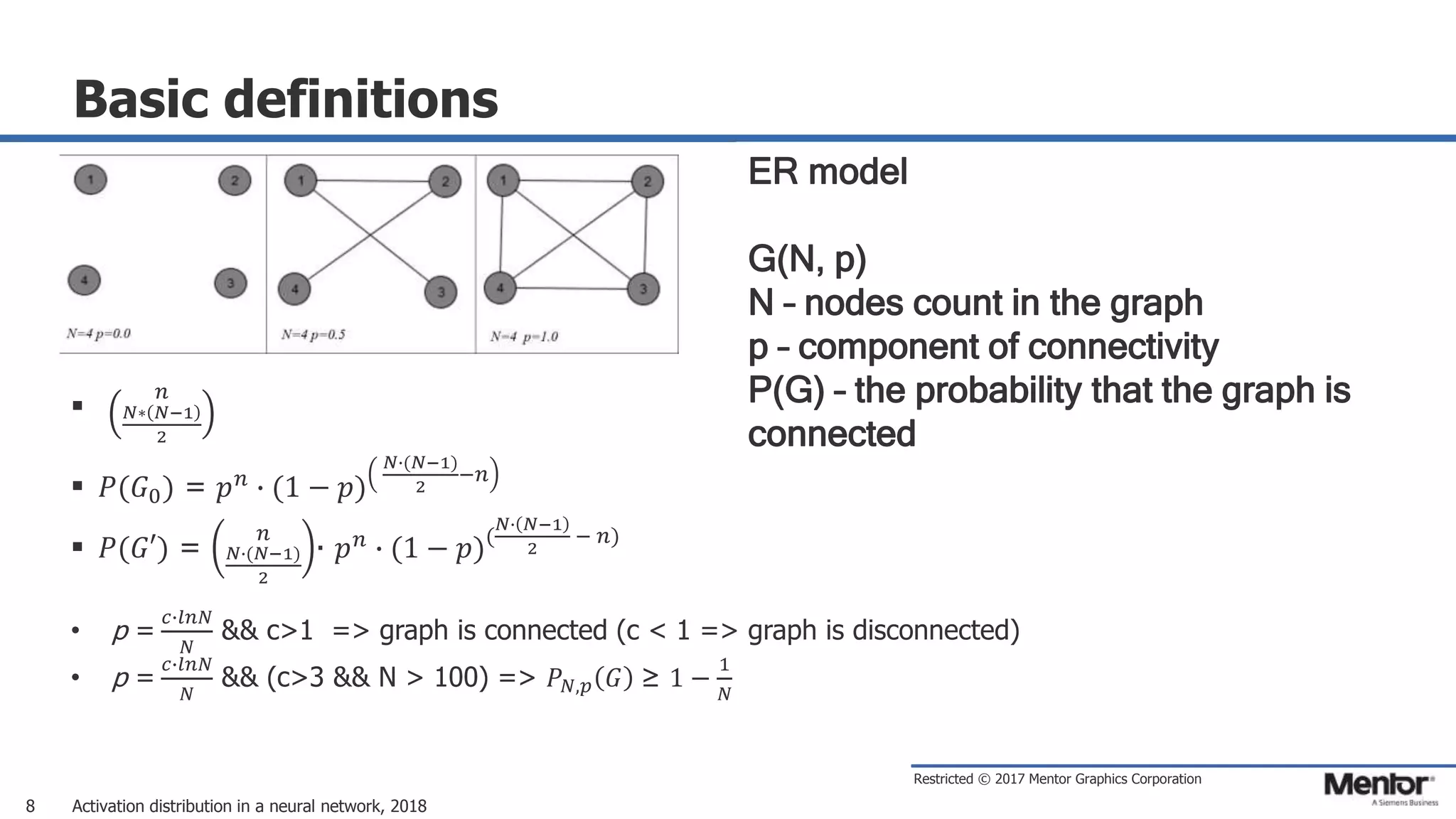
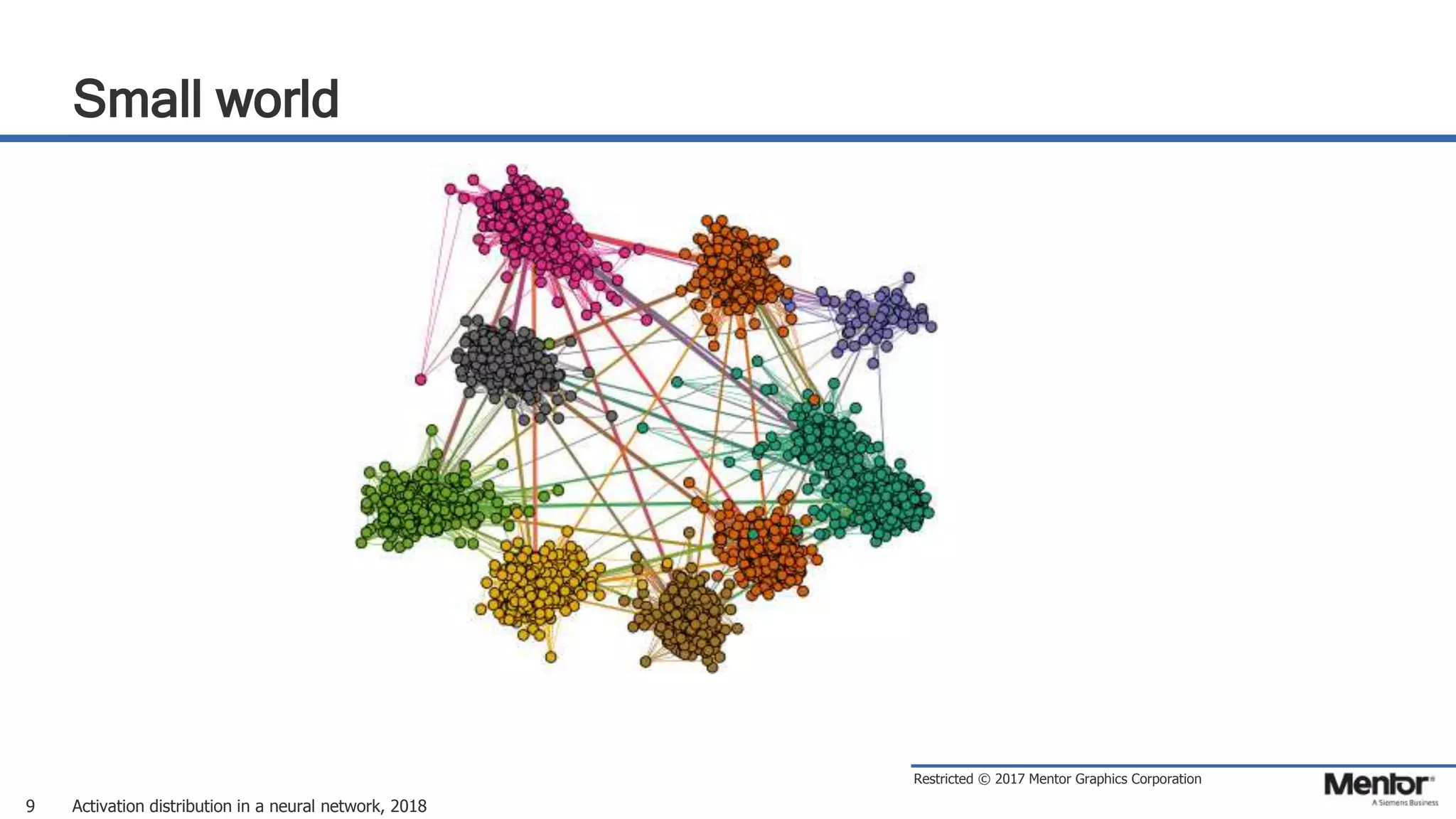
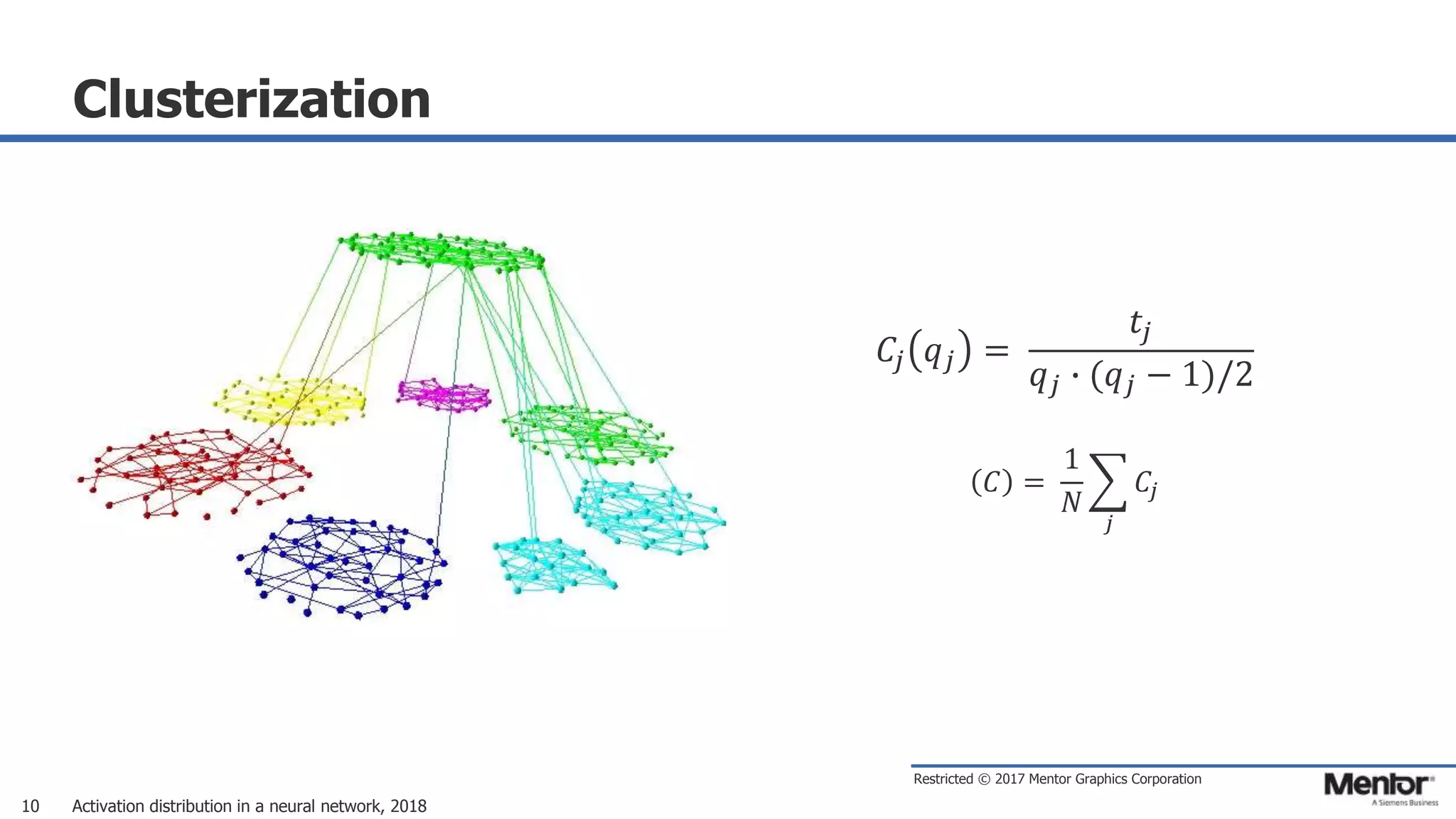
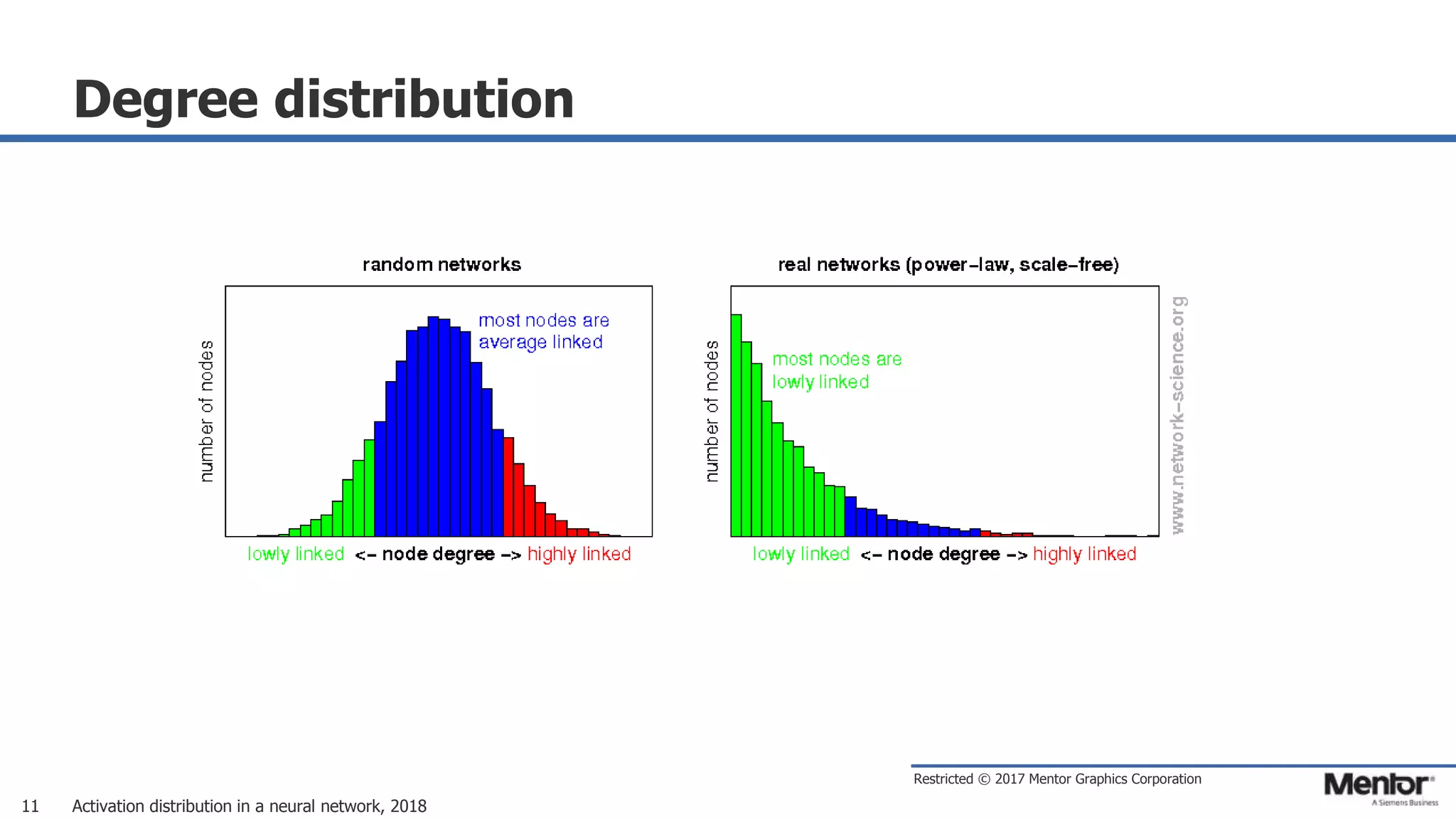
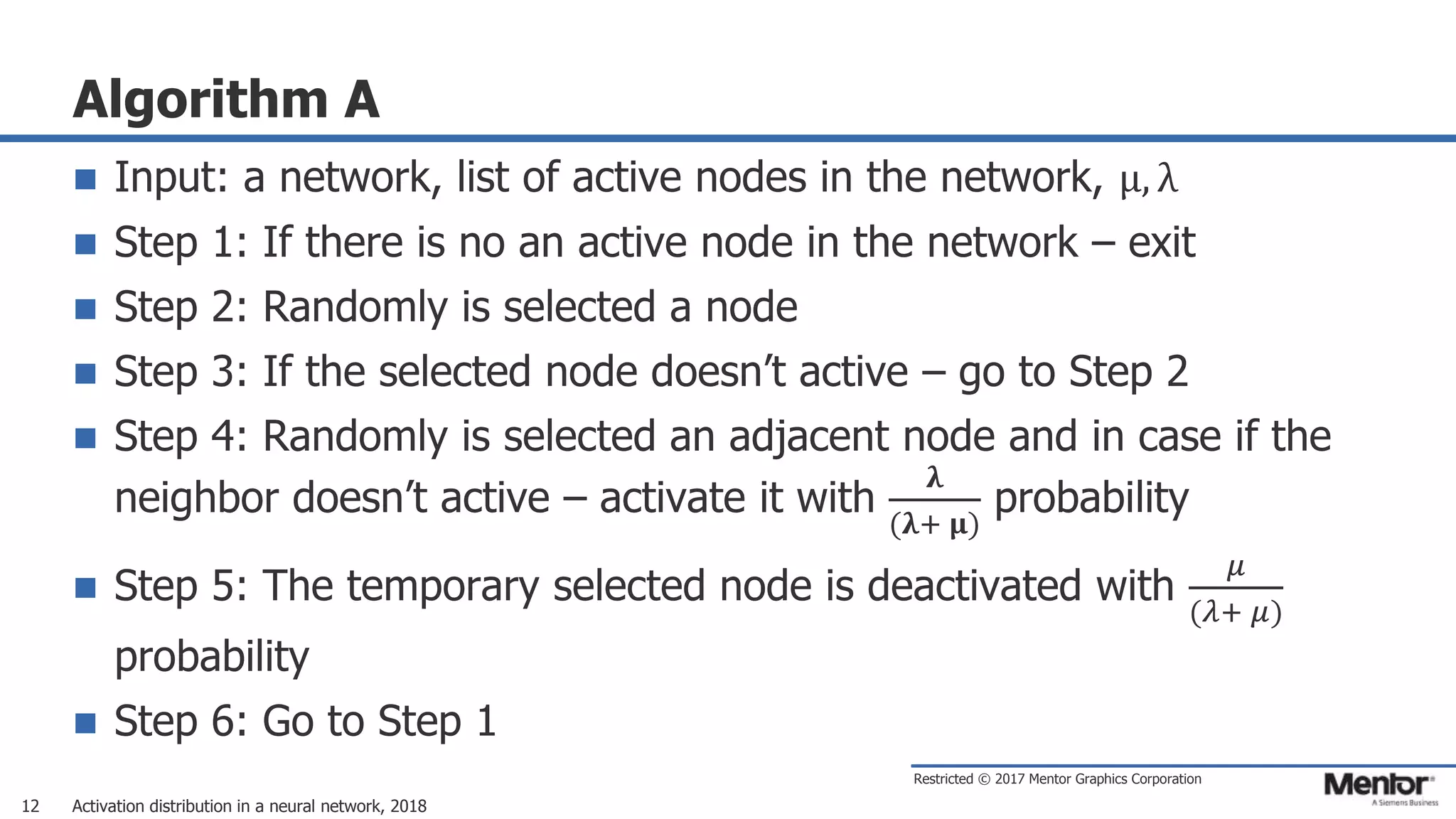
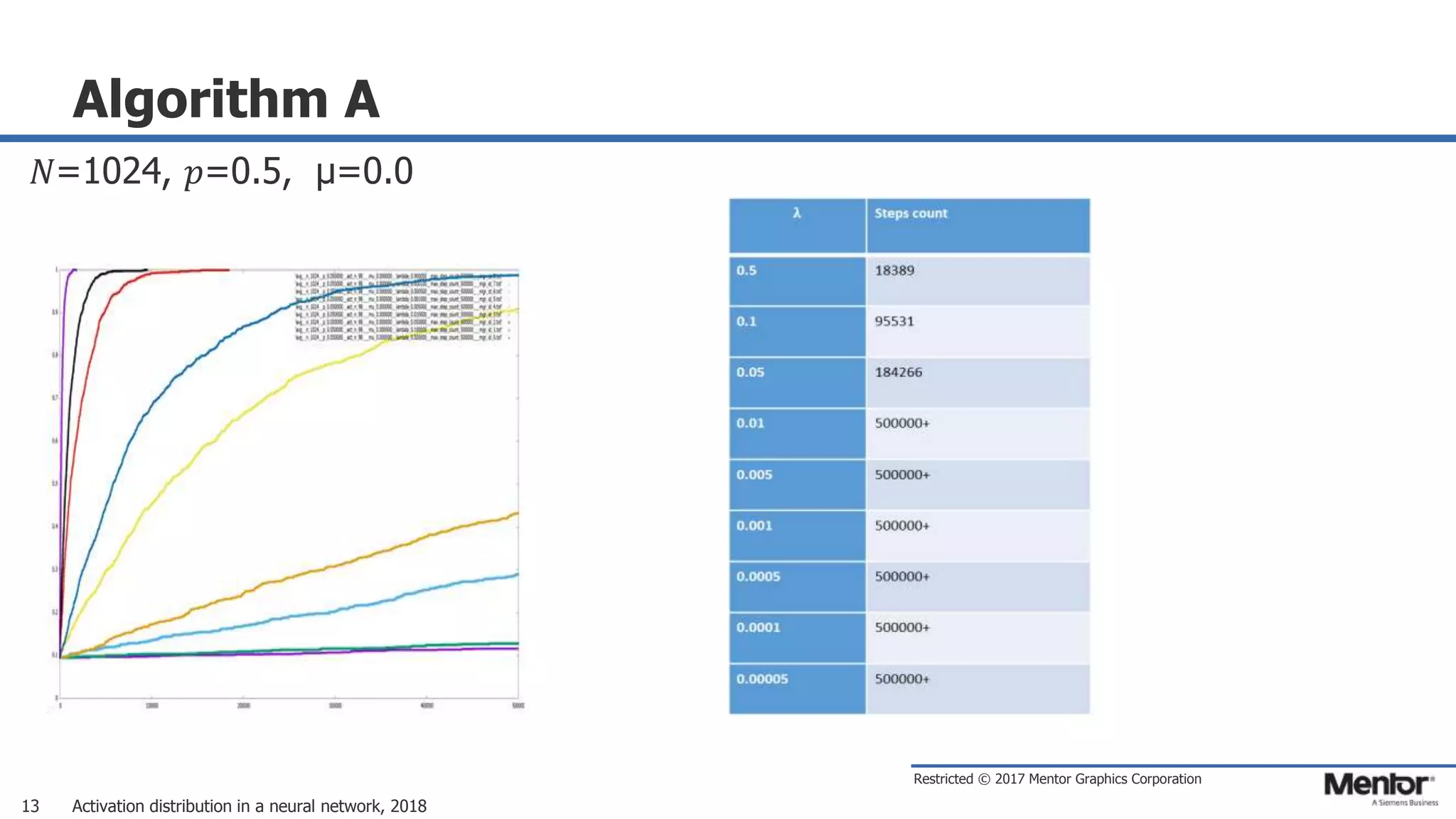
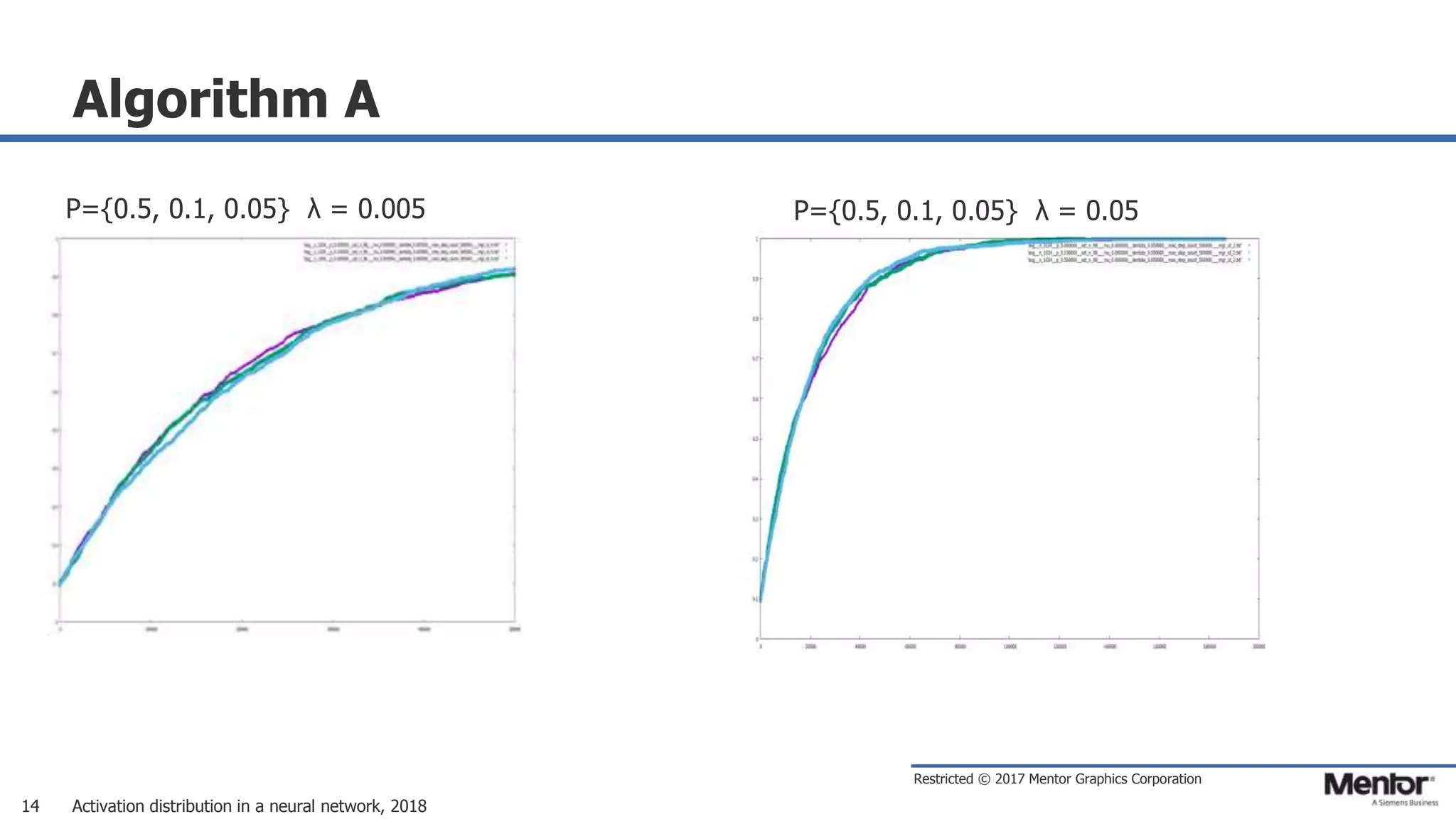
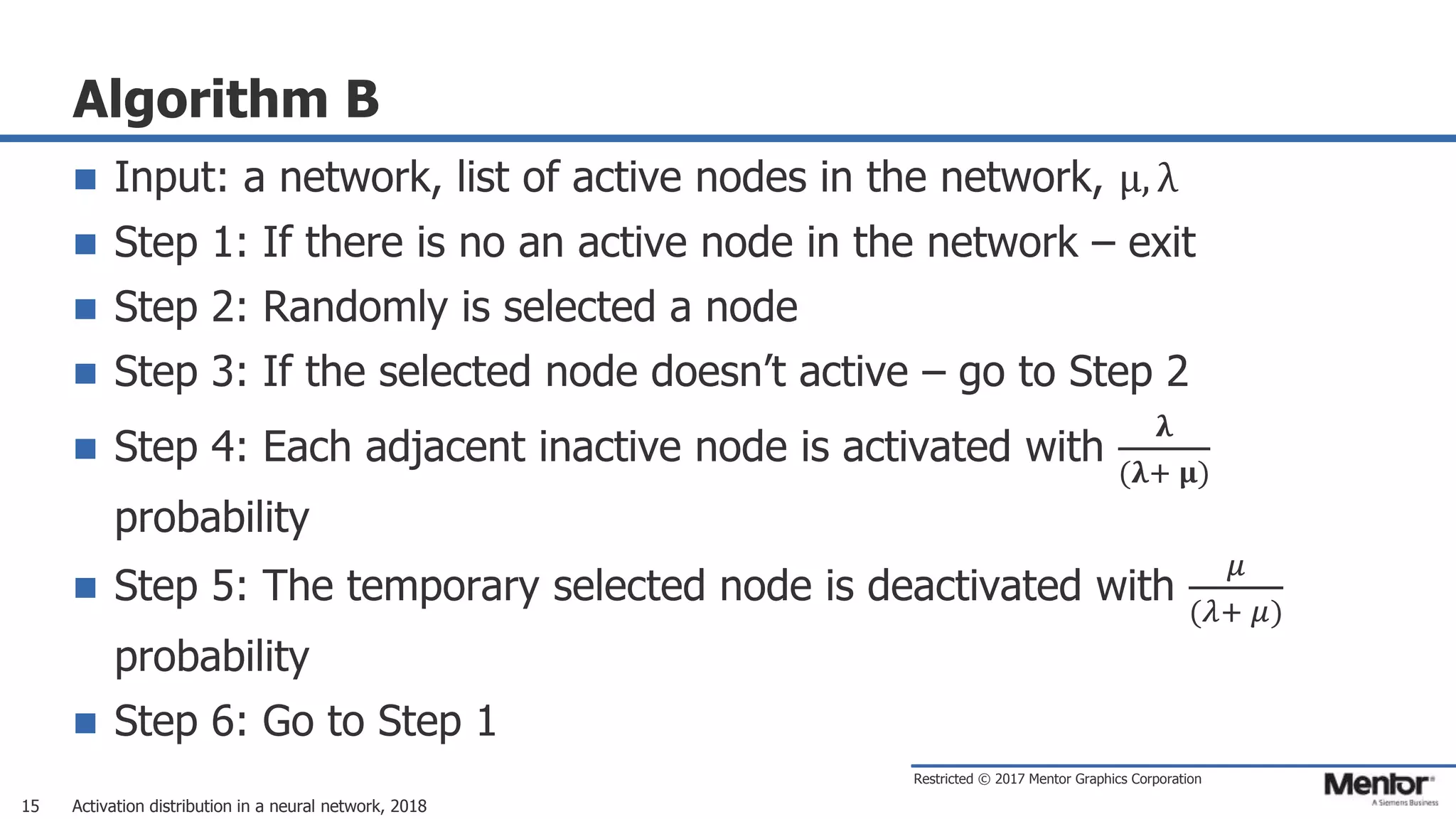
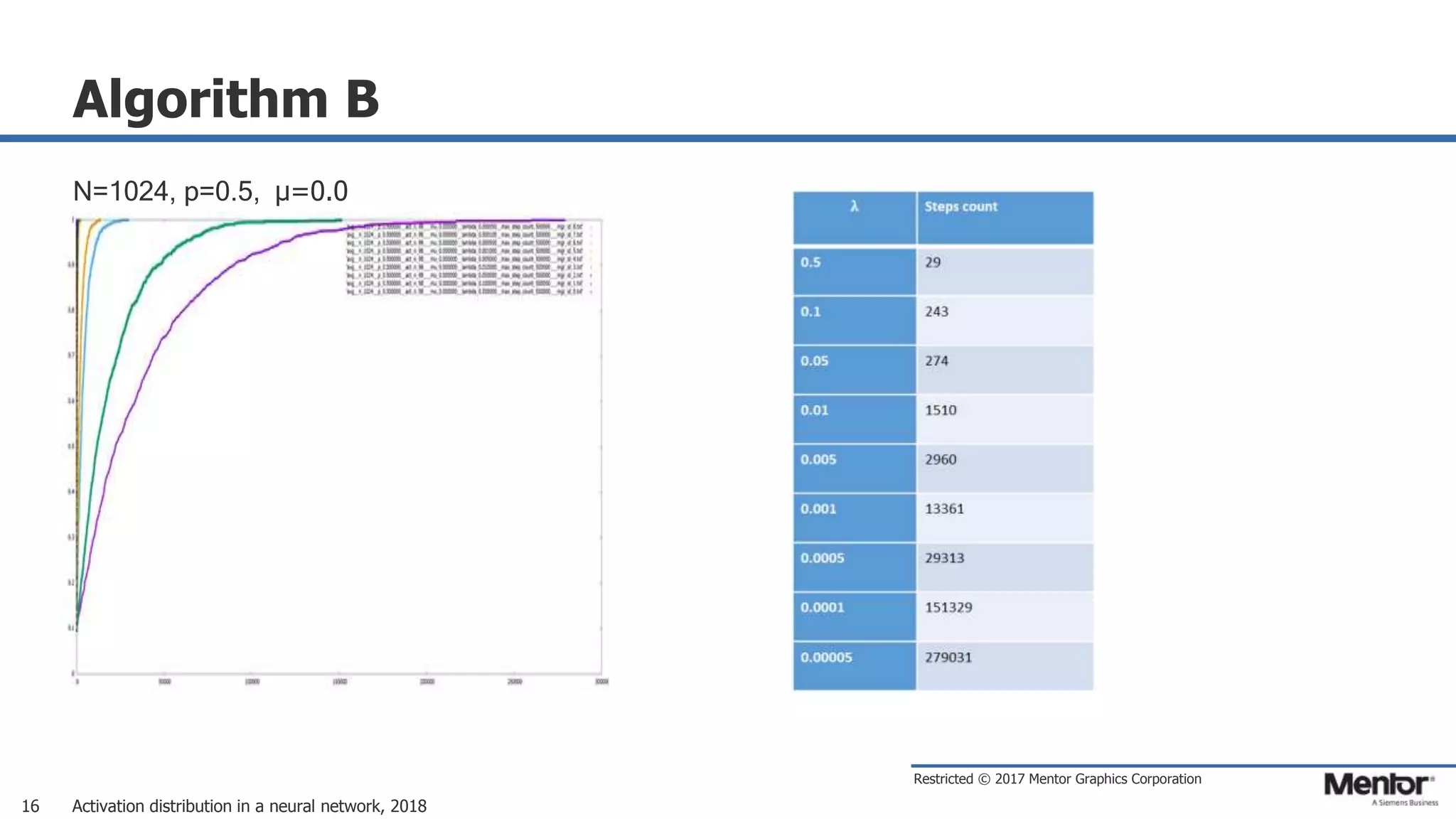
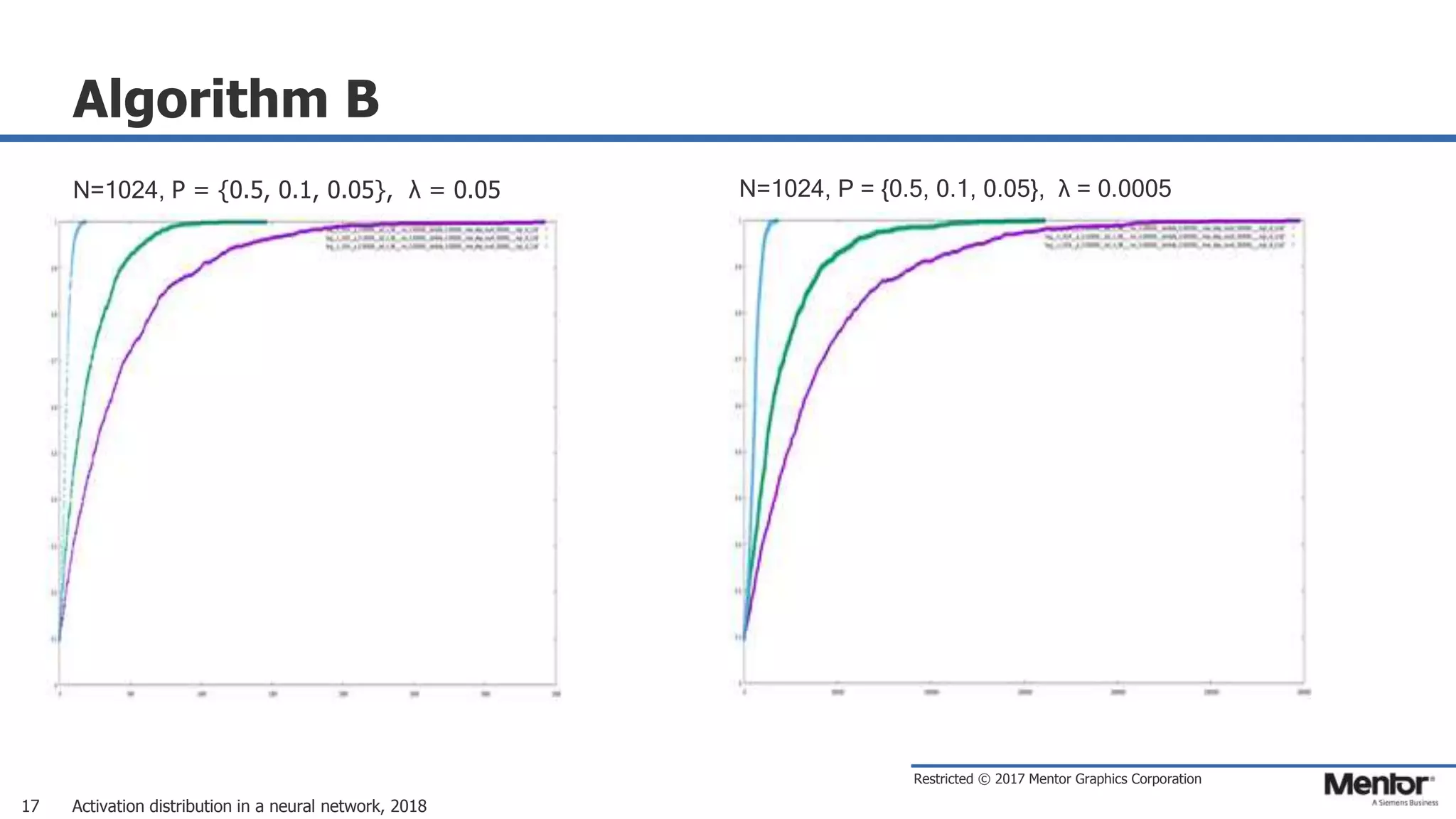
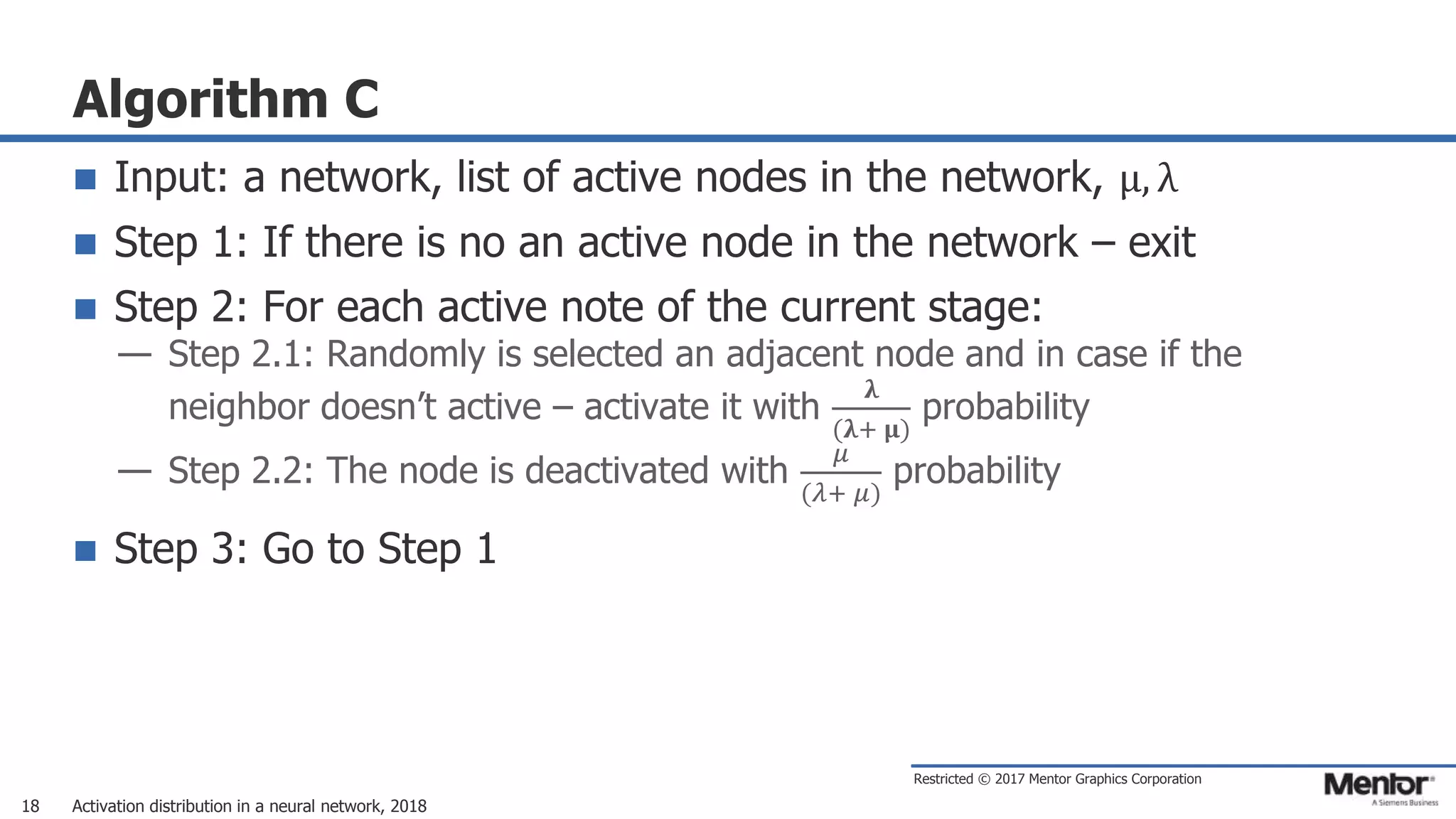
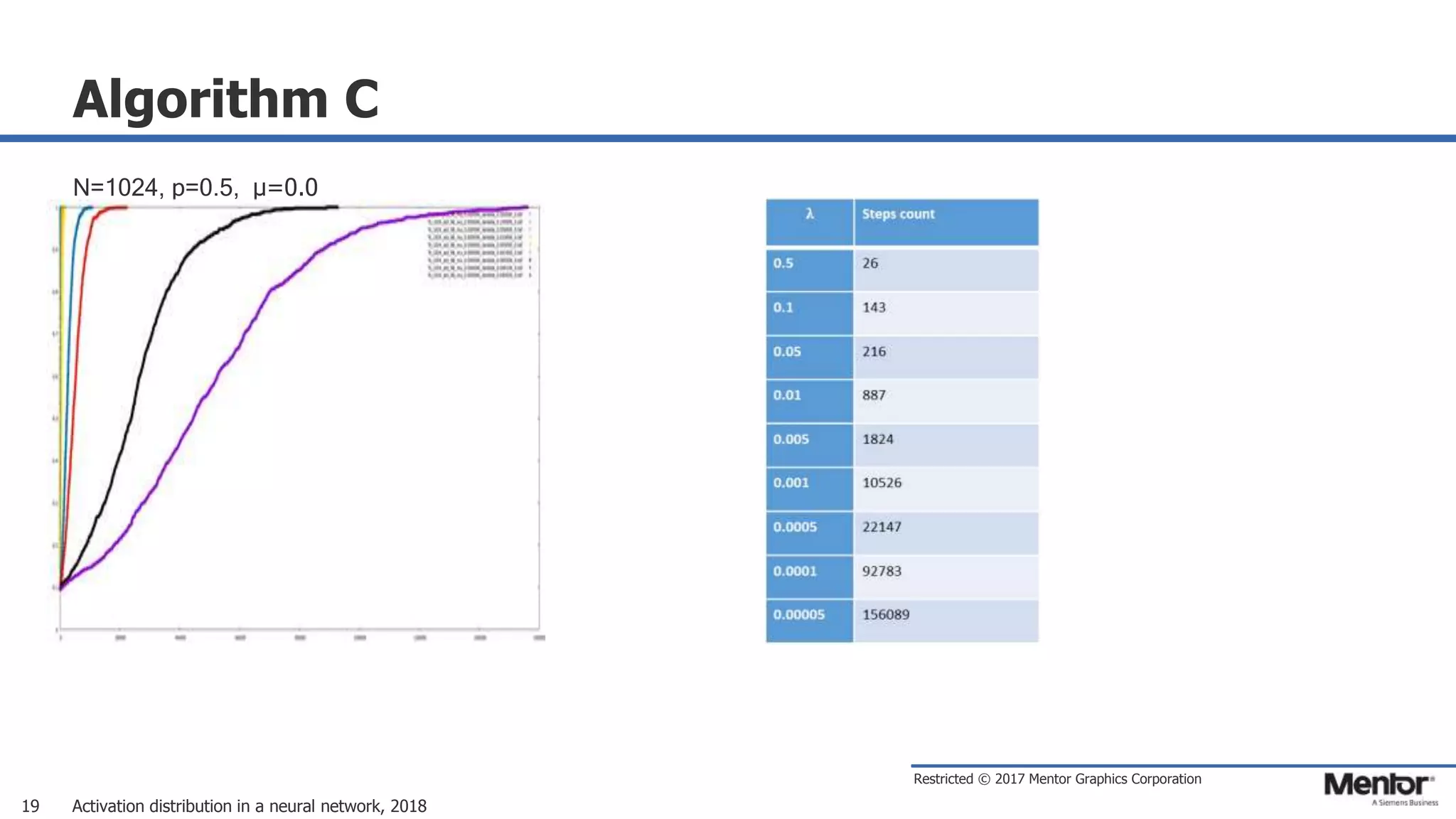
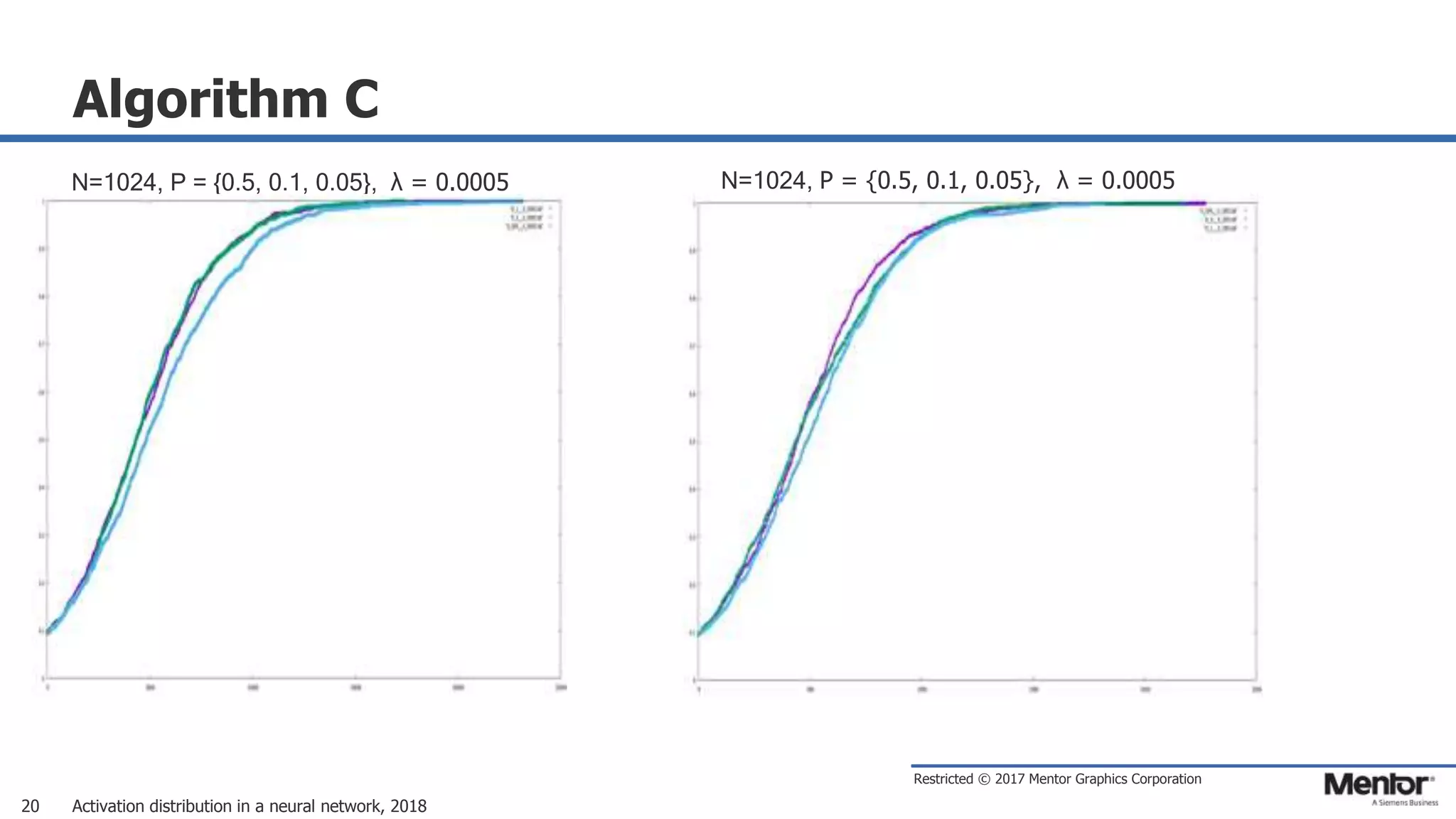
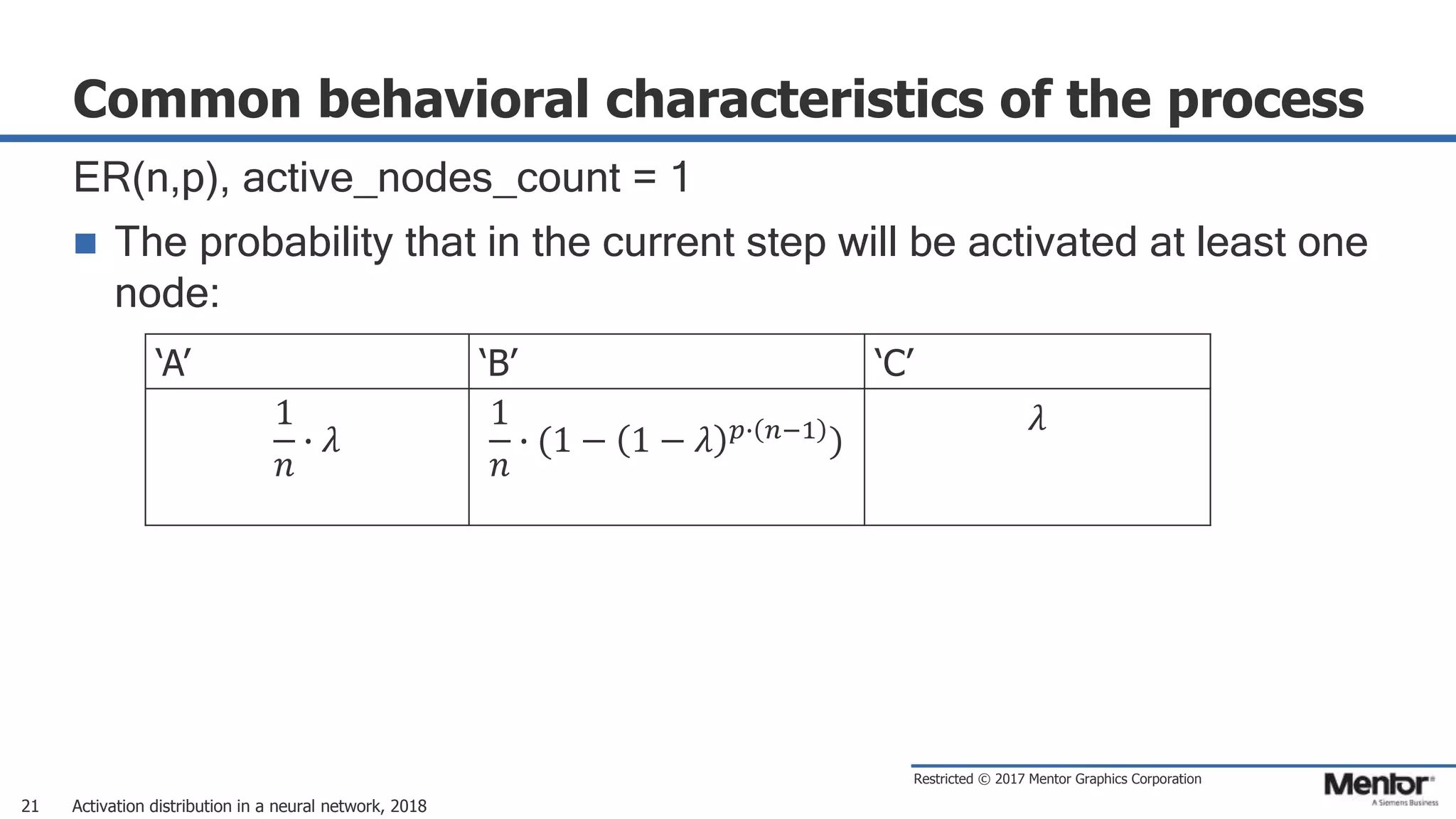
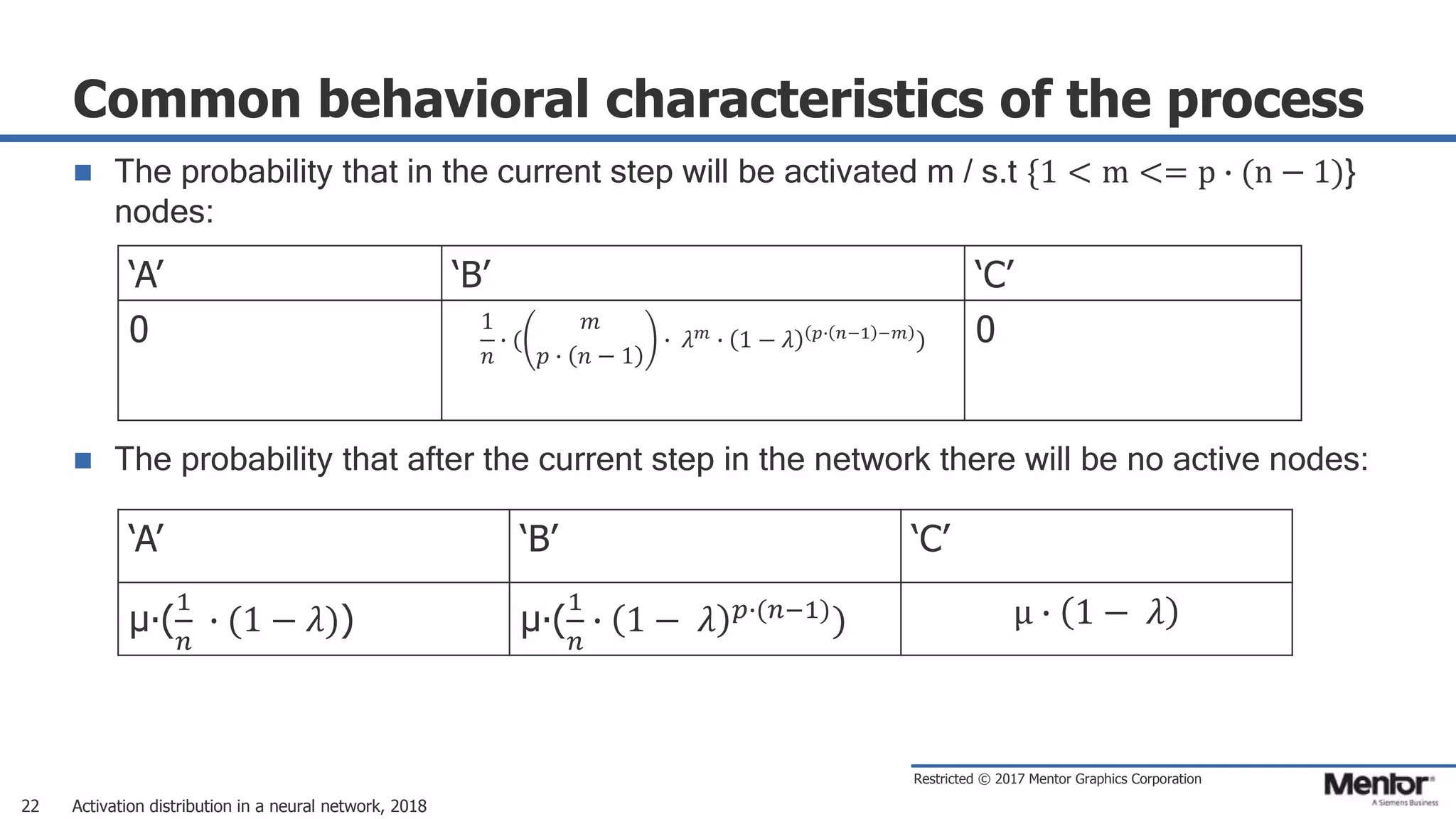
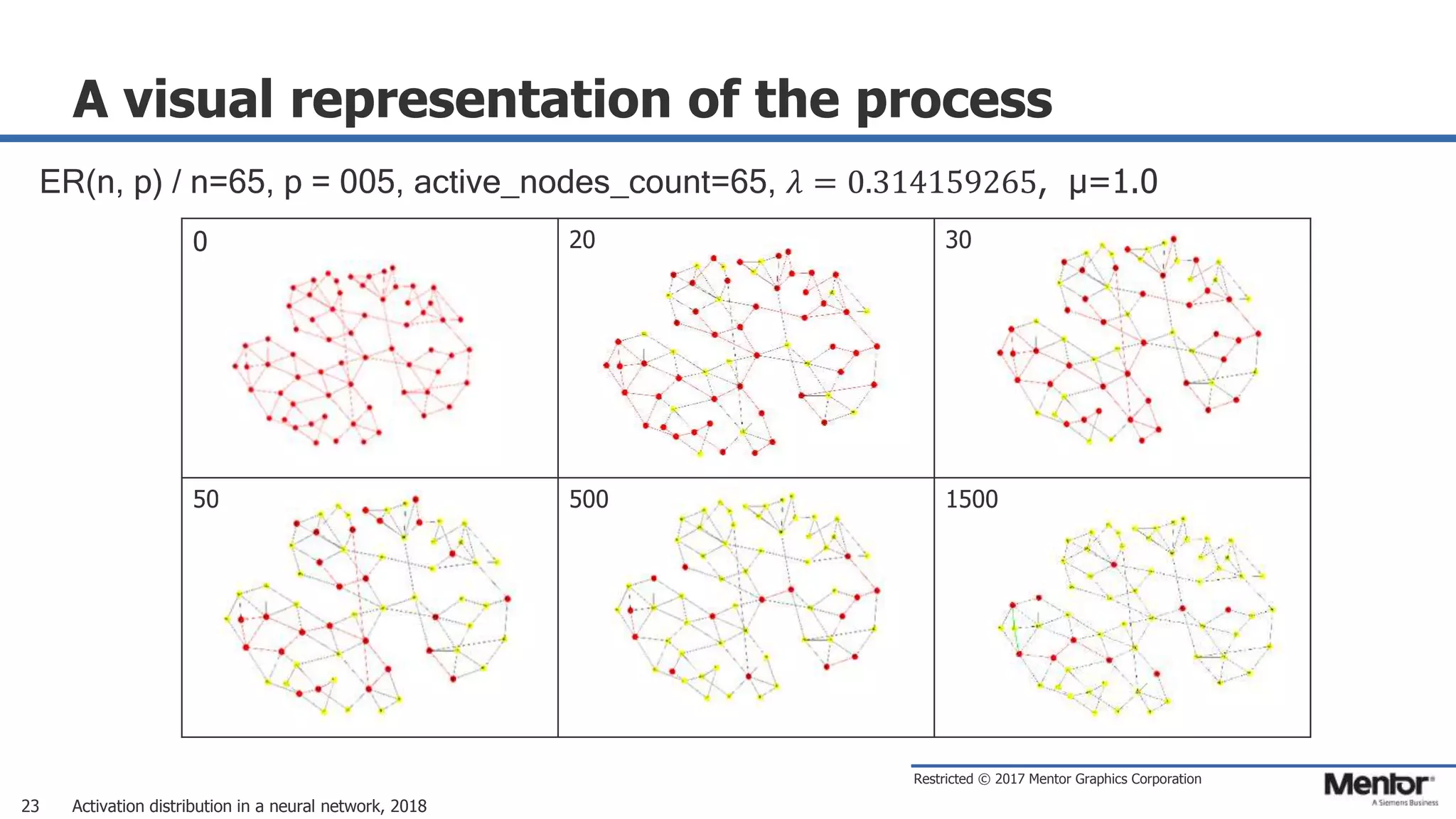
This document discusses neural network activation distribution and three algorithms (A, B, C) for modeling the process. It analyzes the common behavioral characteristics and provides visual representations. The core characteristics of related software discussed are accuracy, efficiency, and platform independency. Visual results are shown for the algorithms under different parameter settings on Erdos-Renyi graphs.