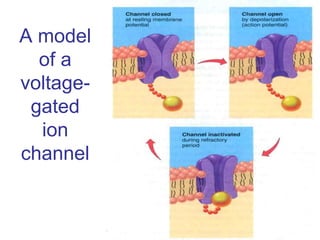
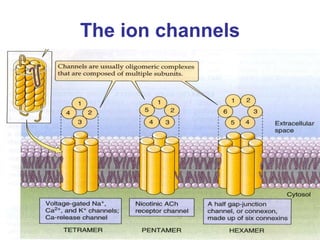
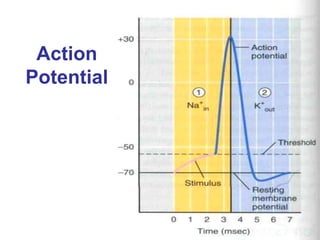
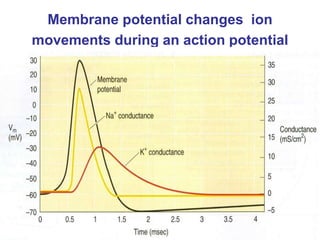
1. When an axon is depolarized past its threshold, voltage-gated sodium channels open, allowing sodium ions to enter and further depolarize the membrane in a positive feedback loop.
2. As the membrane depolarizes further, voltage-gated potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit and repolarize the membrane.
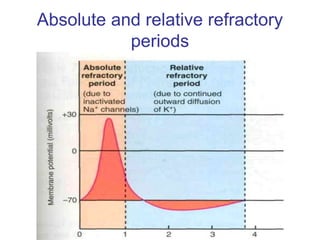
3. After an action potential occurs, sodium-potassium pumps actively transport ions to restore the resting membrane potential, before the axon can initiate another action potential.