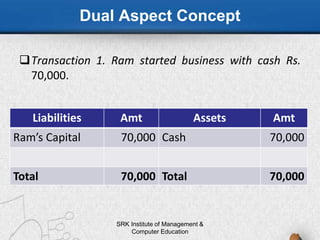
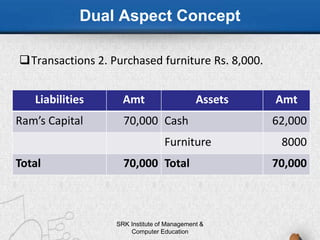
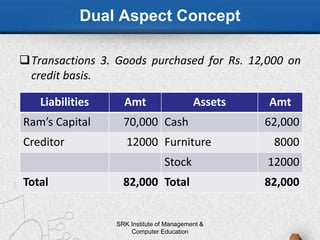
This document discusses accounting principles and conventions. It begins by defining accounting principles as the set of rules and guidelines that companies must follow when reporting their financial data, notably the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). It goes on to explain key GAAP concepts like relevance, reliability, understandability and comparability. The document then covers important accounting concepts such as the business entity concept, money measurement concept, and matching concept. Finally, it discusses key accounting conventions like consistency, conservatism, full disclosure and materiality.