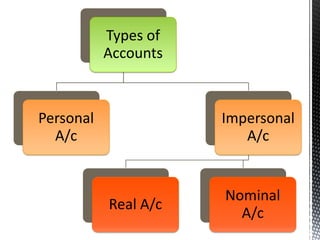
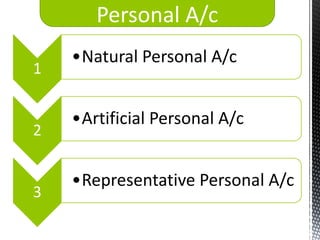
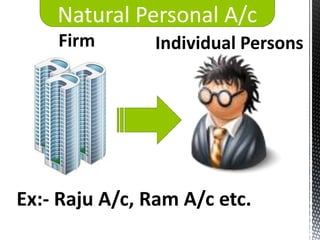
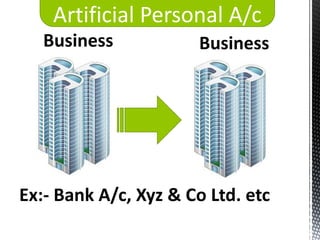
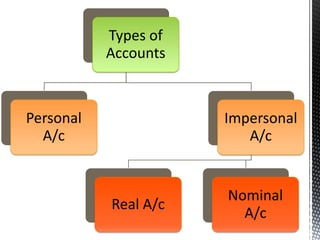
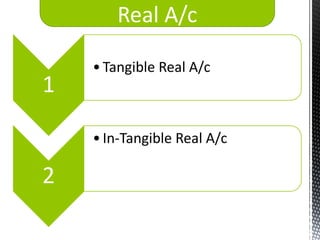
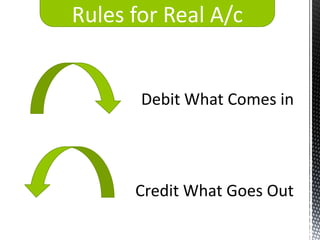
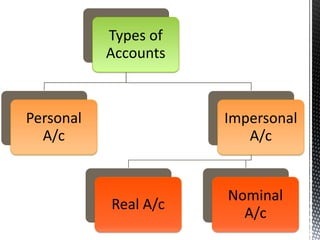
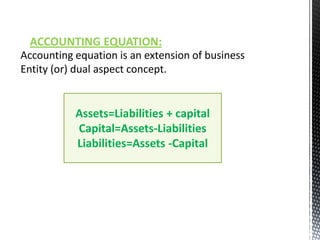
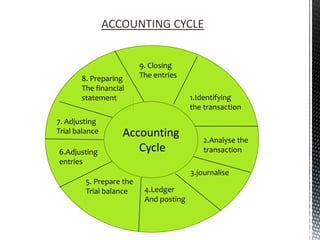
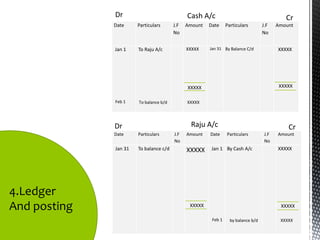
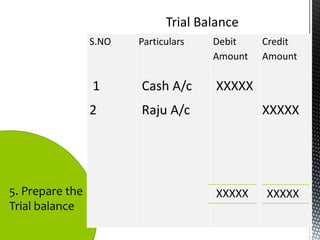
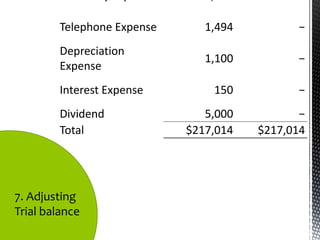
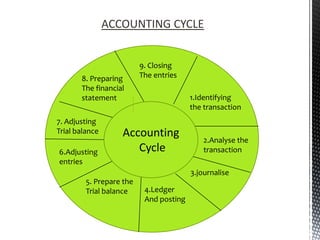
The accounting cycle involves 9 steps: 1) identifying transactions, 2) analyzing transactions, 3) journalizing, 4) posting to ledgers, 5) preparing an trial balance, 6) making adjusting entries, 7) preparing an adjusted trial balance, 8) preparing financial statements, and 9) making closing entries. The cycle ensures all financial activities are properly recorded and reported on an ongoing basis.